This is an automatically translated article.
Amodianate is a combination of 2 tablets Artesunate and Amodiaquine. Amodianate is indicated in the treatment of malaria caused by all types of Plasmodium, including severe malaria caused by multi-resistant strains of Plasmodium falciparum.
1. What disease does Amodianate treat?
Amodianate is a combination drug with 2 types of tablets: Artesunat 50mg and Amodiaquine 200mg.
Amodianate is indicated for the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum or Plasmodium vivax malaria. Amodianate is also effective against malaria caused by Plasmodium ovale, Plasmodium malariae and Plasmodium knowlesi, treating severe malaria (including drug-resistant malaria) if the patient is able to take it.
Amodianate is not used for treatment in the following cases:
Prophylactic treatment of malaria due to hepatotoxicity and the risk of agranulocytosis. People who are sensitive to the ingredients of Amodinate. Patients with severe liver and kidney failure.
2. Dosage and how to use Amodinate
2.1. How to use Amodianate Amodianate is prepared in the form of tablets, taken orally. When taking, the patient should swallow the tablet whole, do not crush the medicine. The drug should be taken after meals. Patients should talk to their doctor or pharmacist if they have any questions about the drug for more information, do not self-medicate because it may cause unwanted consequences.
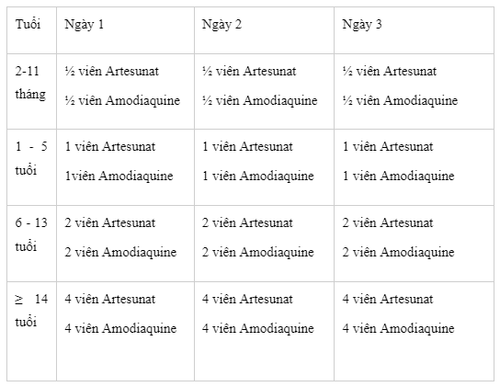
2.2. Dosage of the drug Amodianate Amodianate is a combination drug with 2 tablets in a blister, Artesunate 50mg each and Amodiaquine 200mg each.
According to the recommendations of the World Health Organization (WHO), the total amount of drug used for the treatment of Artesunat is: 4mg/kg/day and that of Amodiaquine is 10mg/kg/day. Take a single dose a day, take it continuously for 3 days in a row.
Recommended age-adjusted dose of Amodinate:
Patients are not allowed to change the dosage on their own, but need to use the drug under the guidance of a doctor or pharmacist to avoid taking the wrong drug, causing unwanted consequences.
3. Amodinate drug overdose
Cases of overdose are usually caused by the Amodiaquine component in the drug Amodinate:
Nervous system: Headache, drowsiness, visual impairment, blindness, convulsions, coma. Cardiovascular system: Hypotension, arrhythmia, followed by cardiac arrest, sudden respiratory arrest are characteristic manifestations of Amodiaquine poisoning. When the patient has any symptoms of overdose, it is necessary to immediately contact a doctor or go to a medical facility for timely treatment. Patients who have passed the acute attack and no longer have symptoms still need to be closely monitored for at least 6 hours.
4. Side effects of the drug Amodinate
When using Amodinate, the patient may appear the following side effects:
Body and skin: Fever, possible keratinization of the skin / nails, hair loss when using the drug for a long time, allergic reactions . Digestive system: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, the anterior part of the nasopharynx is blue-gray. Nervous system: Fatigue, headache, generalized pain Eyes: Sensitivity to light. After stopping treatment, the side effects may disappear, but the patient needs to have a general health check, check the eyes if using the drug for a long time. A number of toxicological studies have recommended that Amodianate should not be used for more than 3 days.
5. Be careful when using Amodinate
Caution should be used when using Amodinate in the following cases:
Use caution when taking the drug with people with liver disease, hearing loss, alcoholism, psoriasis, porphyria, history of epilepsy, use of drugs that are toxic to the liver. Patients need to clearly report their medical history and medications to the treating doctor for advice on proper use. If the patient takes the drug for a long time or takes a high dose, a follow-up blood test, eye and hearing test should be done. Discontinue the drug immediately if during treatment it is found that the patient has a clotting disorder or a serious abnormality in the blood count test. Amodianate should not be used in the prophylaxis of malaria because the drug can easily cause hepatitis and increase the risk of agranulocytosis. Pregnancy: Amodinate should not be used during pregnancy, except in cases of necessity and prescribed by a doctor if the potential benefits outweigh the possible risks. Do not use Amodianate for pregnant women in the first 3 months. Lactation: There are no data on the safety of Amodinate in lactating women. Therefore, mothers should stop taking Amodinate while breastfeeding. For people who are driving and operating machinery: The drug can cause side effects such as fatigue and headache when used. People who are driving and operating machinery should use caution. Amodianate is indicated for the treatment of malaria caused by all Plasmodium species, including severe malaria caused by multi-resistant strains of Plasmodium falciparum. However, Amodianate is only available on prescription. Patients with symptoms of suspected malaria can go to Vinmec General Hospital to be examined and treated by a team of highly qualified and experienced medical doctors. Patients should not arbitrarily use the drug because it can cause unwanted consequences.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.