This is an automatically translated article.
Opportunistic infections are usually caused by opportunistic pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. Common types of opportunistic infections in HIV/AIDS patients include: Candida infections of the bronchi, trachea, esophagus, and lungs.Types of opportunistic infections that are common in sick people include:
1. Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PCP)
Definition
Pneumonia is one of the most serious opportunistic infections for people with HIV, caused by a number of fungi such as Coccidioidomycosis, Cryptococcus, Histoplasma, Pneumocystis jirovecii, certain bacteria such as Pneumococcus, and a few bacteria. some viruses such as Cytomegalovirus or Herpes simplex.
Among them, Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) is the leading cause of HIV death. The good news for patients is that the infection can be treated with antibiotics
Symptoms: Dry cough; Fever; Rapid breathing; Chest pain; Increased respiratory rate....
Diagnostic tests:
X-ray: Lower lobe interstitial infiltrates, but normal in 25% Sputoscopy for PCP
2. Cryptococcal meningitis
Definition
Cryptococcus neoformans is a fungus commonly found in soil. The disease is sometimes confined to the lungs, but it can spread to other parts of the body, such as the skin, bones, or even the urinary tract.
The fungus usually enters the patient's body through the lungs and can cause pneumonia. Sometimes it can also spread to the brain, causing cerebral edema. If the brain becomes infected with the fungus, the condition is called meningitis.
Clinical manifestations: Headache, Fever, Vomiting; Neck stiffness (only 25%); Confusion; Blurred vision, fear of light; CD4 < 10...
3. Toxoplasma encephalitis
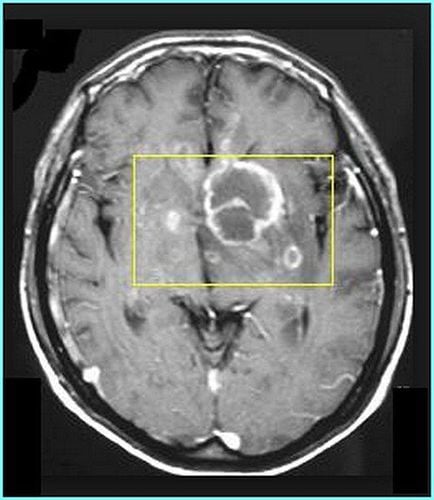
Viêm màng não
Definition:
Toxoplasmosis encephalitis is the most important opportunistic infection of the central nervous system. For people with AIDS, more than 95% of cases of Toxoplasma encephalitis are due to reinfection with the parasite.
Manifestations of Toxoplasma encephalitis include: Focal neurological signs (paralysis on one side); General neurological signs (confusion, seizures, coma, ...); Rarely meningeal signs
4. Candidiasis
Definition:
Candida infection also known as thrush, is caused by a harmless fungus called Candida. This is a fairly common opportunistic infection and usually occurs in HIV patients with a CD4 count of 200 to 500 cells/mm3.
Candida can appear on the skin, nails and mucous membranes throughout the body, especially in your mouth and vagina. However, Candida is considered an opportunistic infection only when it infects the esophagus or lower respiratory tract, such as the trachea and bronchi or deeper lung tissue.
Symptoms: The most obvious symptoms are white spots or white patches that appear on the tongue or throat. The disease can be treated with prescription antifungal medications. Good oral hygiene and using a chlorhexidine mouthwash can help you prevent this infection.
5. Tuberculosis (TB)
Definition: Tuberculosis is caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. TB bacteria can be spread through the air when someone with TB coughs, sneezes, or talks. Inhaling TB bacteria into the lungs can lead to infection in the lungs.
Symptoms: Symptoms of tuberculosis in the lungs include cough, fatigue, weight loss, fever, and night sweats. Although the disease usually affects the lungs, it can also damage other parts of the body, most commonly the larynx, lymph nodes, brain, kidneys, or bones.
In summary , many people with HIV are now infected with opportunistic infections, the main cause of which is their weakened immune system. The best way to prevent opportunistic infections is to see a doctor regularly and take HIV medications according to your doctor's instructions
The social disease screening package at Vinmec International General Hospital helps customers visit and perform screening tests, HIV Ab rapid test, Chlamydia rapid test, Treponema pallidium rapid test, qualitative and quantitative Treponema pallidum TPHA test, bacteriophage test and microscopic staining of the fungus to diagnose the risk of disease and provide a treatment plan.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.