This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. CKII Nguyen Bang Phong - Internal Medicine - Cardiovascular Intervention and Head of Heart Failure Clinic, Cardiovascular Center, Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Echocardiography is a basic technique and provides a lot of valuable information in the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases. Clinical practice often uses the following types of ultrasound (ultrasound mode).
1. 2D echocardiography (Also known as 2 plane ultrasound)
2D echocardiographic images are obtained when the ultrasound beam passes through a cross section of the heart, thereby assessing the position and posture of the heart, the size of the heart chambers, the thickness and movement of the walls. Cardiac function, dilatation and contractility of the myocardium, major vessel roots, morphology and movement of heart valves, septal defects in the heart, intracardiac tumor or thrombus, pericardial fluid. The views commonly used in 2D echocardiography include: left sternal longitudinal axial view, left sternal transverse axial view, apex view, suprasternal view, and subcostal view.
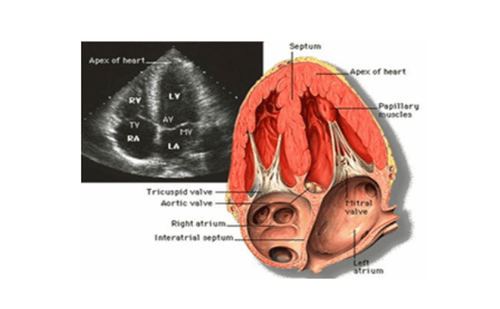
Siêu âm tim 2D
2. TM-type echocardiography (Also known as M mode)
Because the heart moves continuously according to the systolic and diastolic cycle, so do the heart valves, so when scanning the ultrasound beam through an anatomical component of the heart at a certain speed, we will obtain an image. The image of that component has a waveform. With the TM type, because it can locate the points in the cardiac cycle: systole, end systole, diastole, and end diastole, the measurement of the size and contractile function of the heart is very accurate. The main slices in M mode echocardiography are the left sternal longitudinal axis..., based on 2D images, the left sternal transverse axis, move the guide bar (cursor) to the position to be investigated to Cardiac imaging is obtained.
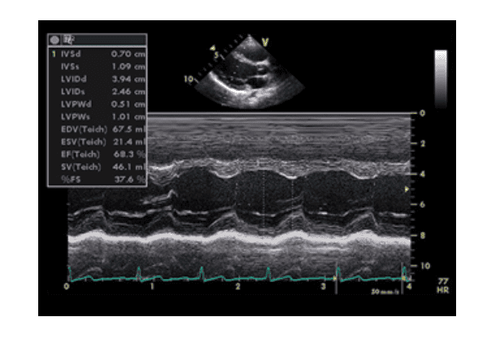
Siêu âm tim kiểu TM
Venous echocardiography, left sternal longitudinal axial slice, cursor close to the mitral valve terminal end, measured left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVIDd), left ventricular end-systolic diameter (LVIDs), through that calculates left ventricular systolic function (EF). In addition, right ventricular size and left ventricular wall thickness were measured at diastolic (IVSd and LVPWd) and systolic (IVSs and LVPWs).
3. Echocardiography 3D, 4D
Different from 2D ultrasound, when the image is obtained in 2 dimensional space, i.e. on 1 plane (slice), 3D ultrasound probe, 4D piezoelectric crystals in matrix, to obtain images Ultrasound in 3D space (cubic shape), called 3D ultrasound. If there is an extra dimension of motion (time dimension), then we have 4D ultrasound.
4D echocardiography provides vivid, comprehensive images, easier to visualize than 2D ultrasound, especially important in the following pathologies: aortic valve, mitral valve (especially in mitraclip technique: clamp: forceps) mitral valve prolapse without surgery), atrial septal defect, left ventricular assessment...
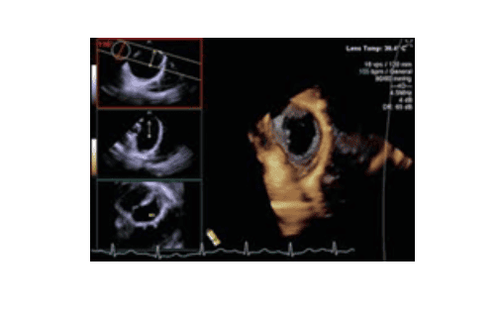
Thông liên nhĩ kích thước lớn trên siêu âm 4D (3 hình đen trắng nhỏ bên trái là siêu âm 2D qua thực quản, từ đó dựng thành hình 4D)
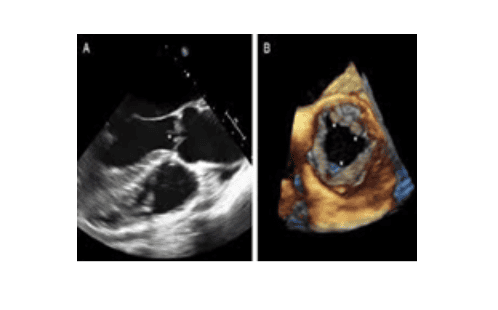
Siêu âm 4D van động mạch chủ (hình đen trắng bên trái là siêu âm 2D với đầu dò qua thực quản)
4. Doppler echocardiography
When the ultrasonic beam passes through a moving object, the Doppler effect will be generated. The Doppler effect is a quantity that reflects the velocity of a moving object that is acquired, processed, and expressed through sound, waveform, or color coding. In Doppler echocardiography, the Doppler effect reflects the velocity of blood flow and of the heart muscle. The blood flow through the narrow area has a high velocity, then the audio signal will have a high volume and high timbre, and the waveform signal will have a large amplitude. With color Doppler, blood flow is coded as red when moving towards the transducer and blue when moving away from the transducer, thereby detecting abnormal blood flow in the heart. In a nutshell, Doppler echocardiography is a very effective means of hemodynamic assessment through heart valves, detecting abnormal blood flows in the heart, and myocardial motility.
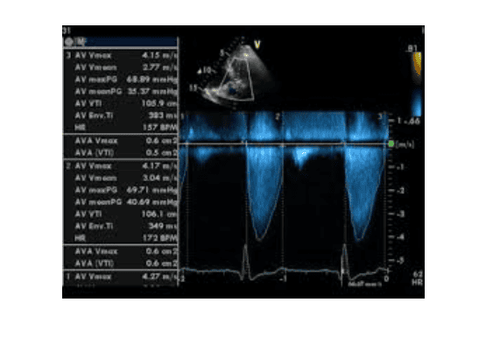
Phổ Doppler liên tục của hẹp nặng van động mạch chủ
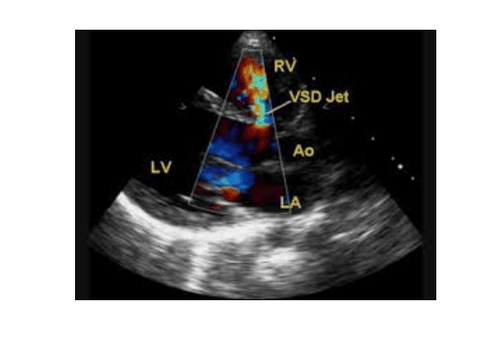
Thông liên thất được phát hiện bằng Doppler mầu (VSD jet): dòng chảy từ thất trái (LV) qua vách liên thất sang thất phải (RV), đi về phía đầu dò được để ở phía thất phải nên có mầu khảm đỏ
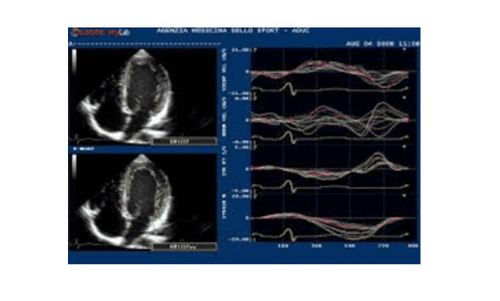
Doppler đánh dấu mô (speckle tracking) đánh giá sức căng theo trục dọc của thất trái và tình trạng tưới máu cơ tim thất trái