This is an automatically translated article.
Treatment of thrush in children and adults can be with topical antifungal agents for mild cases, or systemic antifungals for severe cases, depending on age, health and disease status.
1. Overview of Tongue Fungus Tongue or oral thrush is a condition in which the tongue is thrush caused by an overgrowth of Candida fungus in the mouth, tongue or inner cheeks, even the fungus can spread to the roof of the mouth, gums or down. throat.
More seriously, the fungus can travel down the digestive system, from the esophagus to the intestines, or other organs such as the lungs, liver and cause multi-organ fungal infections. People with HIV infection and other medical conditions, such as diabetes, kidney failure or cancer, requiring long-term intensive care treatment are at high risk of severe thrush.
Anyone can get thrush, thrush, but the most common groups of tongue fungus are young children and the elderly. Because of resistance, the immune system of children is immature and the elderly are immunocompromised. Therefore, detection and treatment of thrush in children and the elderly is especially important.

Bệnh nấm lưỡi hoặc nấm miệng là tình trạng lưỡi bị tưa do nấm Candida phát triển quá mức trong miệng
2. Signs of tongue fungal infection in children and adults 2.1 Manifestations of thrush in adults In adults, thrush causes lesions in the mouth and tongue as follows:
Pseudo-layers appear thin ivory-white or cream-white fascia in the roof of the mouth or tongue. Or it can be thick red inflamed patches, accompanied by tiny red bumps. In the mouth, the tongue may feel lumpy or entangled. The middle of the tongue or gums (gingiva) is red, swollen, painful and itchy. When the tongue fungus attacks deeper, it will cause discomfort in eating, swallowing, swallowing pain in the chest, accompanied by fever. There may be loss of taste or changes in taste. There may be slight bleeding when rubbed. The corners of the mouth are red and inflamed. 2.2 Manifestations of tongue fungus in children Similar to adults, tongue fungus in children also causes lesions as follows:
Appearance of white patches on the surface of the tongue or in the oral cavity. Children are uncomfortable, in pain, so they often cry, stop feeding or stop eating. With breastfed babies, the baby's oral thrush can spread to the mother's breast, causing the breast to become red, cracked, and very painful.
3. Treatment of thrush in adults and children Depending on your health and age, the treatment for thrush in children and adults will be different. However, treatment is all about stopping the fungus from spreading.
3.1 Treatment of thrush in infants Treatment of thrush in nursing infants should be carried out in both the child and the mother to avoid recurrence of the infection. Mild antifungal medication will be prescribed for the baby and anti-fungal cream on the breast for the mother. For bottle-fed babies, tools including bottles, nipples, and pump parts should be disassembled and washed with water and vinegar. In addition, care and brushing should be done for children with thrush as follows:
Place the child on his or her back. Parents wash their hands thoroughly and then use a clean, soft cloth to wrap the tip of the index finger. Then, use your index finger to take the antifungal medicine prescribed by the doctor and then put it in the child's mouth, gently wipe 1 time from the inside to the outside of the surface of the tongue. You can do it one more time if the blade surface is not clean. It is necessary to make gentle and decisive movements to avoid choking or suffocating the child. 3.2 Treatment of thrush in adults and children In mild cases, antifungal sprays and mouthwashes can be used to reduce fungal infections. Besides, combine using yogurt or acidophilus capsules to restore the body's healthy bacterial flora.
With the severity and the ineffective use of topical antifungal sprays, the doctor will prescribe systemic antifungal drugs, the dose is from 1 to 2 weeks.
If the disease is more severe and in the group of subjects with weakened immune systems, the treatment time for thrush can be longer, up to several months. Some antifungal drugs doctors may prescribe such as amphotericin B, Clotrimazol, Fluconazole, Miconazole, Nystatin ...
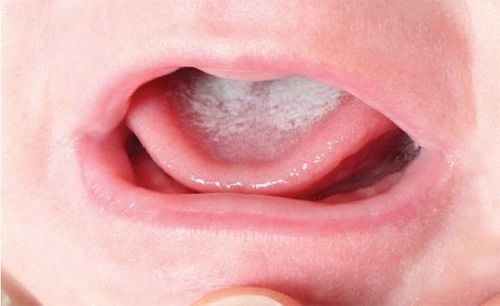
Việc điều trị bệnh nấm lưỡi ở trẻ còn bú mẹ cần được tiến hành ở cả trẻ và mẹ
4. Care and prevention of tongue fungus Children, especially infants, have fungal tongue disease and are not treated and cared for very carefully, affecting their health. Therefore, parents should note:
Do not kiss children with their mouths to avoid spreading bacteria and fungi to children. You need to wipe your breasts with a clean, warm towel before and after feeding your baby. Clean your child's toys with antibacterial soap and hot water, let them dry or let them dry before giving them to your child. To prevent fungal infections of the tongue in children and adults, it is necessary to pay attention to:
Maintain oral hygiene by using physiological saline or mouthwash to disinfect fungi and bacteria, and at the same time balance the level of infection. moisture in the mouth and tongue. However, avoid abuse in the long run. Give up harmful habits that affect oral health in particular and in general, such as drinking alcohol, smoking, or using stimulants. The diet needs to be full of nutrients, combined with regular exercise to strengthen the body's immune system. Do not share personal utensils or have direct contact with people who have fungal infections of the tongue as well as other pathogenic fungi to avoid fungal infection. If you plan to become pregnant, it is important to treat vaginal thrush first because during pregnancy and childbirth can transmit the fungus to the baby causing thrush. As soon as a fungal infection of the tongue is detected, children and adults need to be examined and treated specifically to prevent the fungus from spreading down the throat, esophagus, digestive system and other internal organs, seriously affecting health.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.