This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
H. capsulatum is a dimorphic fungus endemic to the Ohio Valley region, occurring as mycelium in the environment and inhaling the spores produced by this form can infect humans. Macrophages can spread the fungus to any organ in the body leading to histoplasmosis.
1.Overview of Histoplasmosis
Gastrointestinal histoplasmosis, also known as gastrointestinal histoplasmosis, is a rare entity. Gastrointestinal involvement in histoplasmosis is very nonspecific, can involve any region of the gastrointestinal tract, and is commonly seen in immunocompromised patients. However, the most common sites of involvement are the terminal ileum and colon because of the abundance of lymphatic tissue. Involvement becomes less common near the intestine. The literature reports a high prevalence of gastrointestinal histoplasmosis in autopsy samples, indicating a higher incidence of asymptomatic disease.
2.Common symptoms and differential diagnosis of Histoplasmosis
The most common presenting symptoms in patients with gastrointestinal histoplasmosis are abdominal pain and inflammatory diarrhea. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is characterized by chronic inflammation of the intestinal mucosa through a complex immune-mediated mechanism. The two main subtypes of inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC), are based on histological involvement of the intestine. Common symptoms of IBD include diarrhea or constipation, hemophilia, severe diffuse abdominal pain, unintentional weight loss, significantly reduced apatite, fatigue, and fever. Inflammatory diarrhea is a common feature seen in both gastrointestinal histoplasmosis and inflammatory bowel disease. Similarities in presentation, related patterns of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and associated inflammation are the reasons gastrointestinal histoplasmosis is considered an inflammatory bowel disease mimic.
3.Treatment of gastrointestinal Histoplasmosis
The treatment of histoplasmosis and the selection of the appropriate agent for treatment depends mainly on the severity of the disease. Treatment strategies are based on the severity of diffuse histoplasmosis.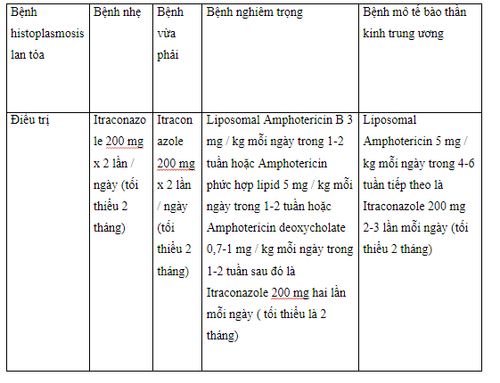
Severe illness: Liposomal Amphotericin B 3 mg/kg daily, or Amphotericin lipid complex 5 mg/kg daily, or Amphotericin deoxycholate 0.7 to 1 mg/kg daily for one to two weeks, followed by itraconazole 200mg two times per day, for a minimum of 2 months.
Mild to moderate disease : Itraconazole 200 mg x 2 times / day, minimum 2 months. CNS Tissue Disease: Liposomal Amphotericin 5 mg/kg daily for four to six weeks, followed by itraconazole 200mg two to three times daily for a minimum of 2 months. Most patients with disseminated histoplasmosis respond well to antifungal therapy.
Early diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal histoplasmosis is essential to prevent serious adverse outcomes. Intestinal perforation and bleeding are two of the most serious complications reported in patients with gastrointestinal histoplasmosis. The clinical manifestations of gastrointestinal histoplasmosis can mimic other gastrointestinal diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease, including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, tuberculosis, carcinoma, and lymphoma. However, it is not usually considered as one of the differential diagnoses in patients presenting with chronic abdominal pain and diarrhea with hemophilia. This often leads to inappropriate or delayed therapy, unnecessary surgical intervention, and adverse outcomes.
Gastrointestinal histoplasmosis often mimics inflammatory bowel disease due to similarity in presentation, pattern of involvement of the gastrointestinal tract, and associated inflammation. Therefore, for patients with inflammatory diarrhea, or those with diagnosed inflammatory bowel disease with clinical features of a possible exacerbation without an underlying cause, gastrointestinal histoplasmosis should be among the differential diagnoses. The diagnosis of gastrointestinal histoplasmosis was confirmed by colonoscopy and biopsies of the relevant area of the gastrointestinal tract. The treatment for histoplasmosis depends on the severity of the disease.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is a reliable address in diagnosing digestive diseases, chronic diarrhea, Crohn's disease... Along with that, the hospital also implements techniques Screening for gastric cancer, gastric polyps through gastric endoscopy with Olympus CV 190 endoscope, NBI function (Narrow Banding Imaging - endoscope with narrow light frequency band) for pathological analysis image results The mucosa is clearer than conventional endoscopy to detect ulcerative colitis lesions, early stage digestive cancer for the best treatment direction.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.