This is an automatically translated article.
If a large mediastinal tumor is detected, the patient should be treated early to prevent the bad effects of the disease on the lungs and surrounding organs. In which, thoracic surgery to remove large mediastinal tumors (5cm) is one of the most optimal treatment methods today.
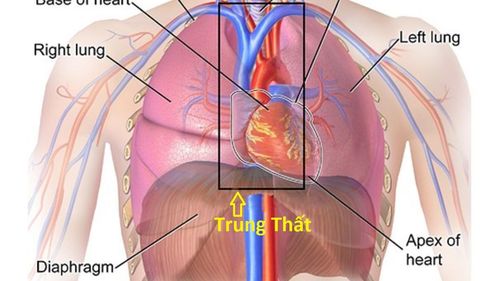
1. Why does a large mediastinal tumor (5cm) need to be treated early?
Most large mediastinal tumors are formed from abnormal proliferative or germ cells in nerve, thymus, or lymphatic tissue. Mediastinal tumors (also called mediastinal cancers) can be malignant or benign.
In the early stages, the patient has almost no symptoms. This is also the reason why the tumor quickly invades organs, compressing the lungs, heart and large blood vessels, hindering the circulation and breathing process.
At a later stage of the disease, common symptoms will quickly appear such as: Shortness of breath, chest pain, exhaustion, weight loss, more serious, coughing up blood, adversely affecting the health of the body. circulatory and respiratory function of the patient.
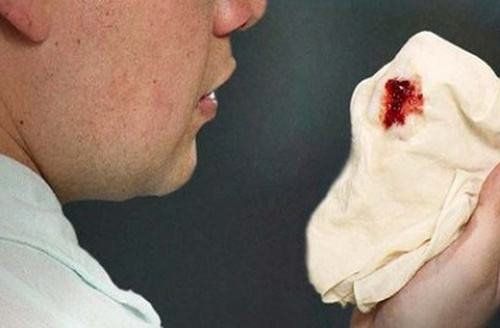
Khi bệnh nhân ho ra máu thì bệnh đã tiến triển đến giai đoạn muộn
Large mediastinal tumor (5cm) is a dangerous cancer. If not detected and treated promptly, the tumor will metastasize to the pericardium and lungs, which can be fatal. Therefore, in order to diagnose and prevent large mediastinal tumors, you need to have regular checkups to help diagnose suspicious signs of the disease in a timely manner. Laparoscopic surgery to remove large mediastinal tumors (5cm) is a measure used first in the treatment of large mediastinal cancer.
2. What should be noted in thoracic surgery to remove large mediastinal tumors (5cm)?
2.1 Indications For patients diagnosed with mediastinal tumor with size determined on computed tomography from 5cm or more. The tumor is in the early stages of development, has not or only slightly invaded nearby organs in the patient's chest, benign tumor.
2.2 Cases of contraindications Based on the conditions of the surgical facilities, caution should be exercised when appointing surgery for the following cases:
Patients with severe systemic diseases: Patients with prior chest trauma that patient has not recovered, or is in a state of hemodynamic instability after an injury, has serious chronic diseases, blood diseases,... The opposite lung of the patient is damaged, so one lung cannot be ventilated or the pleural cavity of the patient is attached causing difficulty during surgery.
Người bị chấn thương ngực chưa hồi phục không thực hiện nội soi
3. What to prepare before laparoscopic surgery?
3.1 The person performing the surgery The person performing the surgery consists of 3 teams:
In which, the surgical team will include: Specialized surgeon with 2 supporting assistants, 1 instrument, 1 runner outside the specialty. Specialist anesthesia team includes: anesthesiologist with 12 assistants. Technical operation crew (applicable if problems occur due to endoscope system). 3.2 Surgical instruments for large mediastinal tumors (5cm) A set of tools to help open and close the chest (only tighten the ribs, rib...), to prevent complications. Prepare specialized tools for major surgery for common thoracic surgeries. Specialized instruments used to conduct laparoscopic surgery in general and thoracic surgery in particular. 3.3 The patient prepares for laparoscopic surgery according to the thoracotomy procedure (including hygiene, prophylactic antibiotics), then undergoes anesthesia and resuscitation, the main surgeon will explain and provide necessary information for patients and their families according to regulations, completing legal documents.

Bác sĩ trao đổi thông tin với bệnh nhân và người nhà trước phẫu thuật
3.4 Follow-up of patients after surgery After successful thoracotomy to remove large mediastinal tumor (5cm), the patient will have a blood count test while resting in the recovery room after The surgery takes 15-30 minutes, and at the same time, take a chest X-ray right at the bed (if possible) to check the health status.
The doctor will prescribe antibiotics to help the patient relieve pain and treat intravenous infections, blood transfusions (if necessary), use of blood replacement solutions, etc., based on hemodynamic status and other medical conditions. specific test parameters.
Respiratory therapies are also often applied from the first days after surgery.
3.5 Management of Complications A stroke is a term used to describe bad changes after surgery. So what should we do when there are complications after thoracic surgery to remove large mediastinal tumors (5cm). Here are some common conditions and how to deal with them:
3.5.1 Patient with postoperative bleeding Blood may flow from the sites of adhesion removal, or missed lung parenchyma. The specialist will give an indication to carry out emergency hemostasis surgery for the patient if the bleeding is > 100ml/hour, along with signs of hemodynamic disturbance.
3.5.2 Atelectasis after surgery Occurs when the patient is not breathing well, sputum is blocked after surgery. Common clinical symptoms such as shortness of breath, fever, chest X-ray showed that the patient had atelectasis. The quick treatment method is to relieve the patient's pain, use systemic antibiotics, the patient should be woken up early to cough up sputum. If necessary, bronchoscopy can be performed.
3.5.3 Respiratory failure The patient had respiratory failure due to diaphragmatic paralysis during surgery, the technician cut the testicle nerve. Carry out active rehabilitation after surgery, limit the use of ventilators gradually, or conduct surgery to suture the patient's diaphragmatic folds.
Breast endoscopic techniques need to be performed at a reputable medical facility to minimize the potential for bad complications.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.