This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Vo Cong Hien - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Currently, liver biopsy is still considered the gold standard for the assessment of cirrhosis. However, this is an invasive method, so there may be complications and some limitations. Therefore, the methods of non-invasive assessment of cirrhosis are increasingly developed and are being widely applied to limit the need for liver biopsy. Among them, MRE elastic magnetic resonance measurement can be mentioned.
1. What is cirrhosis?
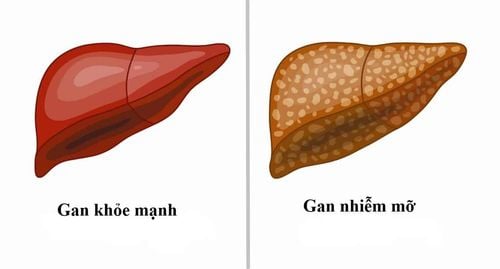
Liver fibrosis is a consequence of chronic damage to the liver, manifested by the accumulation of intercellular substrates due to an imbalance between production, deposition and destruction. Liver fibrosis will progress slowly to cirrhosis.Cirrhosis is a diffuse fibrous tissue process that changes the normal structure of the liver into an abnormal nodular structure.
Causes of cirrhosis include:
Chronic viral hepatitis: hepatitis B, hepatitis C Alcohol, beer Chronic cholestasis (gallstones, cystic fibrosis, congenital biliary atresia, ...) Cardiovascular (failure) Cardiomyocarditis, pericarditis, Budd-Chiari syndrome) Metabolic/genetic abnormalities (iron retention, copper, dyslipidemia,...) Drugs, toxins Autoimmune hepatitis Unknown Degree of fibrosis Liver is a very important and significant predictor of liver disease-related morbidity and mortality. Assessing the degree of liver fibrosis is very important in the indications for treatment, monitoring and prognosis of chronic hepatitis, making an important contribution to reducing the rate of progression to cirrhosis and liver cancer.
2. The role of liver fibrosis assessment
Cộng hưởng từ đàn hồi là phương pháp chẩn đoán hình ảnh hiệu quả trong đánh giá xơ gan.
Determine the extent of liver damage to decide when to start treatment, avoid progression to cirrhosis, especially when there is significant fibrosis. Establish a special monitoring regime, determine the optimal time to start screening for complications (liver cancer, esophageal varices) for severe fibrosis and cirrhosis. Monitoring and predicting the patient's response to treatment The techniques in the assessment of cirrhosis are divided into 2 groups: invasive and noninvasive
Invasive assessment methods: Liver biopsy
Noninvasive assessment methods Invasion includes:
Biological markers Indirect fibrosis markers Direct fibrosis markers: Unspecified, specific. Imaging Cross-sectional images
Liver elastography:
Static: Real-Time Elastography (RTE)
Dynamic: Transient Elastography (TE)
Measurement Magnetic Resonance Elasticity (MRE)
ARFI Technique
Shear Wave Elastography (SWE)
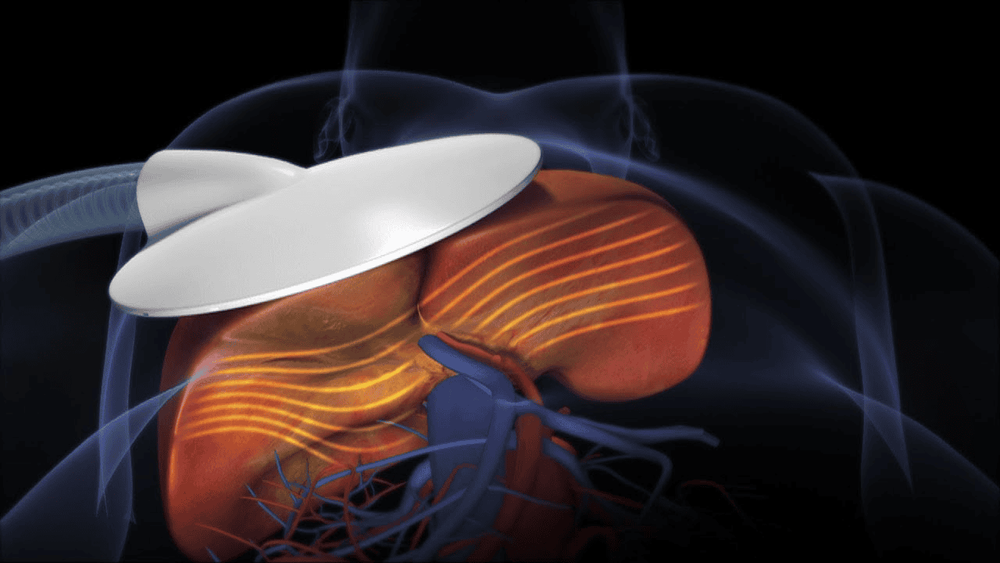
3. The role of magnetic elastic resonance (MRE) in the assessment of cirrhosis

Nếu bạn bị xơ gan, MRE có thể giúp đánh giá mức độ nghiêm trọng của bệnh gan
Indications for elastography of liver tissue are quite widely used to diagnose, evaluate the effectiveness of treatment as well as prognosis in most chronic liver diseases:
Chronic hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis C Alcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis Cirrhosis Alcoholic liver disease Of course, liver biopsy remains the gold standard in the assessment of cirrhosis today. However, the application of elastic magnetic resonance measurement also brings many benefits in the diagnosis of cirrhosis:
This is a non-invasive technique and is generally safer and more comfortable than biopsy. This method helps evaluate the entire liver, not just the portion of liver tissue that is biopsied or imaged with other noninvasive tests. Can detect fibrosis at an earlier stage than other imaging methods. Effective in obese people. Helps predict risk of several liver complications, including cirrhosis ascites. Magnetic resonance elastography is an effective imaging method in the assessment of cirrhosis. However, in order to get accurate results, patients need to choose a reputable medical examination address to perform this technique.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, customers can perform at the same time as MRI screening for liver tumors and can do it in most patients including those with ascites or obesity. Can replace unnecessary liver biopsy method, causing many complications.
The MRI procedure to assess cirrhosis at Vinmec is carried out methodically and in accordance with the process standards by a team of highly qualified medical professionals and modern machinery, thus giving accurate results, contributing to not insignificant in determining disease and disease stage.
BSCK I Vo Cong Hien has many years of experience in the field of imaging, especially in diagnostic ultrasound for general abdominal diseases, advanced cardiac - vascular, obstetrics and gynecology. Doctor Vo Cong Hien used to work at the Imaging Department of the University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital - Hoang Anh Gia Lai before working at the Imaging Department of Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.
If you have a need for medical examination by modern and highly effective methods at Vinmec, please register here.
References: mayoclinic.org
SEE ALSO:
Methods to assess the stage of cirrhosis How dangerous is decompensated cirrhosis? Treatment of decompensated cirrhosis: What you need to know