This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor I Vo Thi Thuy Trang - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Gut microbiota is believed to be responsible for obesity, a global disease. So what is the link between the gut microbiome and obesity?
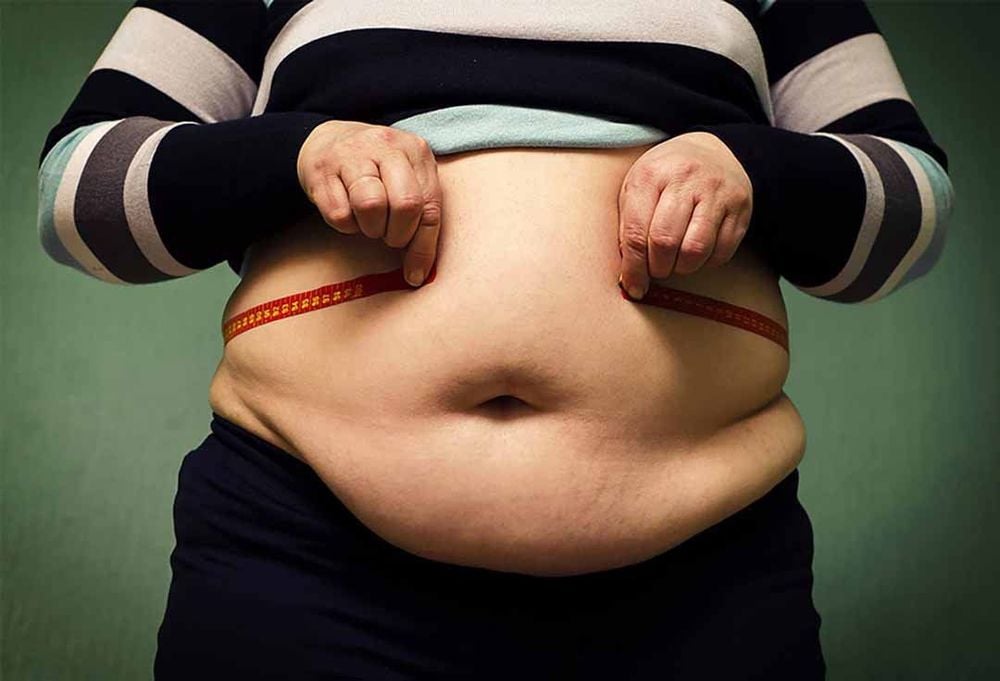
Obesity is the greatest and most serious public health threat to date. The increasing prevalence of obesity has been, and continues to be, a global burden and increases the risk factors for cardiovascular diseases, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia. and some cancers.
Therefore, researchers have been constantly working to understand the causes of obesity to find solutions to this global disease.
1. Multifactorial causes of obesity
Although the core cause of overweight and obesity stems from an imbalance between energy intake and energy expenditure, it is difficult to assess the external factors that regulate this imbalance process.In fact, besides tracking calories intake (diet) and calories consumed (physical activity), monitoring energy metabolism in the body is a challenge. Because man is an amazing machine, conceived and through millions of years of evolution to preserve body weight the hard way.
Under the influence of many variables including genetic, social and environmental factors, complex and coordinated human mechanisms are fine-tuned to preserve body weight.
Therefore, it is difficult to find the main reasons or several causes to explain the global disease - obesity. While in reality, obesity is a multifactorial phenomenon and so when studying it, researchers need to put in the big picture instead of focusing on a specific mechanism or observation. there.

2. Relationship between obesity and gut microbiota
The gut microbiome is a very specific environmental factor that has a potential impact on obesity. The gut microbiome is a diverse community of microorganisms including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and protozoa that exist in the gut.In addition to the various species living in the gut (components of the microbiome), there are also microbial metabolites, which are also considered key players.
There is a lot of research literature that has been stated about the gut microbiome, however, in reality there is very little confirmed, especially the link between the gut microbiome and fat obesity and this is still a controversial issue.
Early pioneering studies suggested that the gut microbiome was the primary cause of energy storage and increased body fat mass. Subsequent studies found that the gut microbiome causing obesity has the following characteristics:
Decreased microbial community diversity Change in the representation of bacterial genes Altered metabolic pathways Evolution of a new species of bacteria that are metabolically differentiated to enhance food absorption Causes of changes in gut microbiota as evidenced by studies on weight-loss interventions such as gastric bypass surgery and calorie-restricted diets.
Further studies further clarify the mechanism of intestinal microbiota that works and affects metabolism and energy balance in the body, specifically the microbiota that regulates absorbed energy absorbed from the daily diet, participates in metabolism, changes the permeability of the intestine and the release of intestinal hormones.
In addition, the gut microbiome also alters obesity patterns because bacteria increase fermentation, releasing energy from the undigested components of food.

3. Factors affecting the relationship between gut microbiota and obesity
It is difficult to assess the composition of the gut microbiota because bacteria produce many metabolites that affect other microorganisms or act as a signal to the host, including short-chain fatty acids. such as acetate, butyrate, propionate).In addition, the composition of the gut microbiota is also not fixed and can be influenced by a number of factors such as the composition of the daily diet. Even in normal and healthy people, the diet significantly changed the gut microbiota on a daily or weekly basis, whereas the studies only observed one point in time and very little follow-up over a period of time.
Follow-up at a certain time may lead to erroneous results due to the influence of drugs, physical activities or other comorbidities. Thus, all these factors make it difficult to identify imbalances in the composition of the gut microbiota.
In addition, new studies on dysbiosis also find that the composition of the gut microbiota is different when the body is healthy or diseased, increasing complexity and difficulty in identifying determine the changes in the gut microbiota.
In fact, understanding of the link between gut microbiota and obesity is still limited, descriptive, and needs further research. Therefore, obesity treatment interventions are also individualized.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: nestlenutrition-institute.org