This is an automatically translated article.
Urology is the most commonly used test in urology. The technique of urodynamic measurement is currently being widely applied in the examination and treatment of urinary dysfunction.
1. What is a urinary tract disorder?
Manifestations of urinary dysfunction include:
Difficulty urinating : Pain, burning or difficulty urinating; Urinary incontinence: Inability to control urination; Urgency: Leaking urine right when urinating; Urinary frequency: More than 1 time per hour; Urinary frequency: Less than 3 times per day. There are 3 main causes of urinary dysfunction:
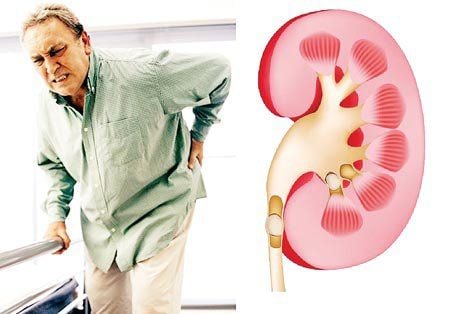
There are structural abnormalities of the urinary tract; There are abnormalities in the nerves that control urination; Urinary incontinence with no known cause. Urinary disorders can only affect the patient's daily life, but can also lead to more serious consequences such as: recurrent urinary tract infections, acute pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis, vesicoureteral reflux,... If not detected and treated promptly, urinary tract disorders can lead to kidney failure.
Rối loạn tiểu tiện lâu ngày làm ảnh hưởng nghiêm trọng tới thận
2. The application of urodynamic measurement in the diagnosis of urinary tract disorders
2.1 What is urodynamic measurement? Urodynamics is a laboratory test used in urology. This test evaluates the bladder and urethral bladder function to store and expel urine, and the bladder neck sphincter.
Urology includes many different measurements that help evaluate different functions in urination. After combining the results of these measurements, the doctor will determine the cause of the urinary disorder.
2.2 Urodynamic measurements 2.2.1 Bladder pressure Self-study of the change in pressure inside the bladder according to bladder capacity. Bladder pressure was monitored at the time of passive bladder filling and active bladder contraction. When measuring, the doctor records the feeling of needing to urinate, the slope of the line shown at the time of filling and contraction of the bladder cone muscle;
2.2.2 Electromyography When using this measurement, people stick electrode plates on the perineal area or insert electrodes into the muscle group of the perineum to record the activity of the urethral sphincter. Electromyography provides information about smooth sphincter activity, which is valuable if combined with cystogram manometry;

Đo điện cơ đồ bằng cách dán bản điện cực vào nhóm cơ ở vùng đáy chậu
2.2.3 Urethral pressure During the procedure, the doctor inserts a small catheter with a side hole into the bladder, passing the prescribed amount of water into it. Then pull out the tube slowly. The urethral pressure varies depending on the urethral location and is recorded as the values changed on the graph when the urinary catheter is removed;
2.2.4 Urodynamics The only non-invasive urodynamic measurement. How to measure: The patient urinates into the collection funnel of the meter, the device will convert the urine weight into volume, record it into a graph at the rate of ml/sec. Urinalysis results are used to quickly assess lower urinary tract function.
2.3 Urodynamic measurement procedure The urodynamic measurement steps include:
Have the patient urinate into the collection funnel of the meter to measure urine volume and urine flow rate. Immediately after the patient finished urinating, the doctor placed a urinary catheter to assess the amount of urine remaining in the bladder; Place the patient on the bed, insert a small catheter into the urinary tract, inject a specified amount of water into the bladder. This is done to assess bladder pressure and bladder compliance. The patient may be asked about the feeling of needing to urinate or asked to cough or strain to assess the level of pressure causing urine leakage; Measure intra-abdominal pressure by inserting a catheter into the anus. This method also helps to indirectly assess bladder muscle pressure; Remove urinary catheter and anal catheter slowly to measure urethral pressure. If the patient has not urinated into the collection funnel before, the patient will be asked to urinate to measure urine flow.
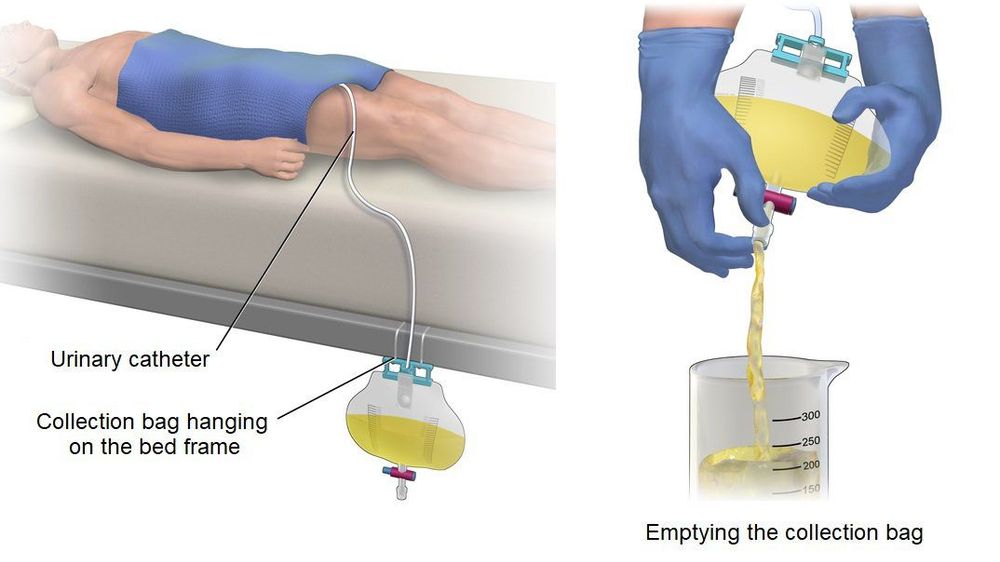
Đặt ống thông đường tiểu cho bệnh nhân
Note: A few cases after urodynamic measurement may have hematuria (pink urine). However, this symptom can go away within a few days, relatives need to pay attention to the patient to drink a lot of water. In case the symptoms of blood in the urine get worse, the patient has symptoms of fever, abdominal pain or chills, they should go to the hospital for examination and treatment.
Urinary tract disorders are common problems that affect patients' quality of life or even lead to serious consequences. Patients are often assigned to measure urodynamics to examine and accurately diagnose problems on the urinary system for timely and appropriate treatment.
Vinmec International General Hospital provides customers with a Urinary Pathology Screening Package with the goal of early detection of possible urinary diseases. Especially prostate diseases (benign prostatic hypertrophy, prostate cancer), urolithiasis, etc. From there, the doctor will give advice and treatment regimens. Scientific treatment helps to reduce the disease.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.