This is an automatically translated article.
Diagnosis of diabetes should be based on laboratory tests, including the following basic tests: fasting blood glucose test, random blood glucose test, oral glucose tolerance test, and HbA1C.
1. Overview of diabetes
Diabetes or diabetes is a metabolic disorder related to the consumption and use of sugar in the body. In a normal person, the pancreas, an organ in the abdomen, secretes the hormone insulin that helps the body use and store sugar from food. Diabetes occurs when one of the following abnormalities is present:
The pancreas does not produce the hormone insulin or produces very small amounts that are not enough to metabolize the sugars in food; The body no longer responds to the effects of insulin. This condition is called insulin resistance. In both of the above cases, insulin does not guarantee the metabolism and use of sugar, causing high blood sugar levels in the blood. High levels of sugar for a long time cause various complications for many organs in the body.
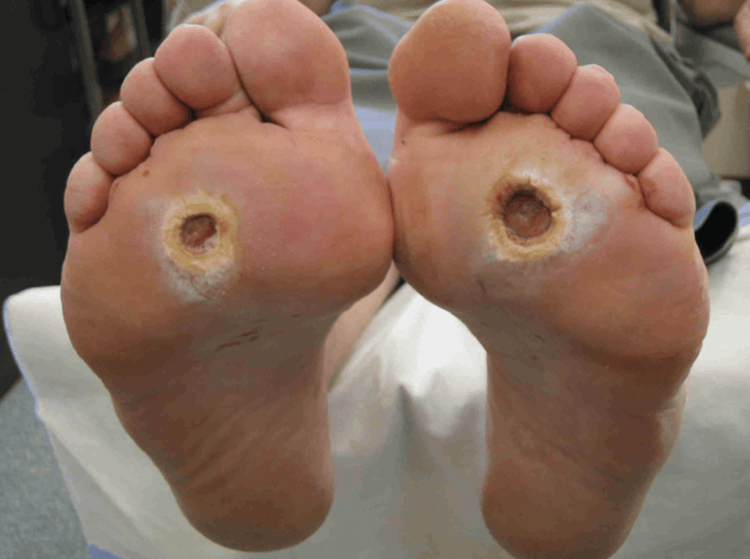
Biến chứng tiểu đường gây loét bàn chân
Trắc nghiệm dành riêng cho người mắc đái tháo đường: Chế độ ăn của bạn đã hợp lý chưa?
Người bị bệnh đái tháo đường cần phải quan tâm nhiều hơn đến cách tính toán khẩu phần ăn sao cho phù hợp với nhu cầu và tình trạng sức khỏe. Nếu chưa rõ, bạn có thể tìm hiểu kỹ hơn thông qua bài trắc nghiệm ngắn sau đây.2. Diagnosing Diabetes
People with diabetes often have suggestive clinical manifestations such as eating a lot, drinking a lot, urinating more and losing weight without an identifiable cause. These symptoms are unique to all patients with diabetes and are often nonspecific for diagnosis. Patients with type 1 diabetes often have sudden onset of clinical symptoms, and they often feel fatigued. However, the majority of patients with type 2 diabetes have no clinical manifestations or other suggestive nonspecific symptoms such as delayed wound healing, weight gain, and paresthesias in the hands and feet. The establishment of a diagnosis of diabetes should mainly rely on laboratory tests, including: fasting blood glucose, oral glucose tolerance test, random blood glucose testing, and HbA1C. More specifically, according to the American Diabetes Association, diabetes is defined when the patient has one of the following four criteria:
Fasting blood glucose concentration >= 126 mg/dL ; Perform oral glucose tolerance test, measure blood glucose concentration at 2 hours >= 200 mg/dL; Quantitative HbA1C >= 6.5%; Blood glucose concentration at any time >= 200 mg/dL and typical clinical manifestations of diabetes such as eating a lot, drinking a lot, urinating a lot, losing a lot of weight for no apparent reason.
Chẩn đoán tiểu đường thông qua xét nghiệm máu
In addition, a patient diagnosed with diabetes also needs to investigate complications on other organs in the body such as kidneys, blood vessels, cardiovascular, nerves, eyes,... Complications of diabetes include: ophthalmoscopy, urea test, blood creatinine, liver function, 10 urine parameters, blood lipid components such as triglycerides, LDL - cholesterol, HDL - cholesterol.
3. Tests to be performed in the diagnosis of diabetes
According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA) stated, to diagnose a case of diabetes requires the following basic tests:
Fasting glucose plasma test: Fasting blood glucose is the amount of glucose measured after fasting for at least 8 hours. In fact, patients are often advised to take the test early in the morning, when they have not eaten anything. The time after fasting for at least 8 hours is chosen as the ideal time to diagnose diabetes because at this time, in normal patients, blood glucose levels will decrease when the body is no longer supplied with energy from the outside. outside; The patient's high glucose concentration at this time is evidence of a disturbance in glucose metabolism in the body. The normal value of this test is < 100 mg/dL. People with diabetes have a fasting blood glucose level >= 126 mg/dL. Those whose results fall between 100 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL and are found to have pre-diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance may be scheduled for a second test; Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: The patient is asked to fast for at least 8 hours, then slowly drink about 200mL of water mixed with 75g of glucose. Patients were tested at two times, before the test and 2 hours after drinking 75g of sugar. The normal value of a 2-hour blood glucose test is < 140 mg/dL. When this value is above 200 mg/dL, the patient will be diagnosed with diabetes;

Xét nghiệm dung nạp glucose đường uống
Quantitative test of HbA1C: HbA1C is a parameter reflecting the average blood sugar concentration in the last 3 months. HbA1C is used to measure the amount of glucose attached to red blood cells in the patient's blood. This test is commonly ordered to diagnose and monitor response to treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes. The HbA1C test must be performed in laboratories that meet international standards. The HbA1C value in a normal person is < 5.7%. When HbA1C > 6.4%, the patient is diagnosed with diabetes.
These are the three most basic tests that are most often performed in the clinic when trying to diagnose diabetes. In patients who have been diagnosed with diabetes, if they have a blood glucose monitor at home, they can perform a blood sugar test by themselves to monitor and adjust their lifestyle, nutrition, and treatment plan. a reasonable way. Blood sugar testing should be done at the following times: before breakfast, before lunch, before dinner, before going to bed. Patients with type 1 diabetes should test their blood sugar about 2 to 4 times a day. Patients with type 2 diabetes do not need to be monitored as often as type 1 diabetes, blood glucose testing should be done every 2 to 3 times a week.

Các xét nghiệm cần thực hiện tại cơ sở y tế được trang bị máy móc hiện đại
At Vinmec National General Hospital, we are currently implementing a screening package for diabetes and dyslipidemia to help detect pre-diabetes early, accurately classify diabetes type, develop a nutritional regimen, monitoring to minimize the risk and complications caused by diabetes.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health System nationwide to visit or contact the hotline HERE for support.
MORE:
What is a normal person's glycemic index? What is an oral glucose tolerance test? 3 steps to measuring blood glucose when performing an oral glucose tolerance test