This is an automatically translated article.
Appendicitis is an urgent health condition, prompt surgical treatment is required before the appendix ruptures, avoiding dangerous complications for the patient. The performance of appendicitis tests plays an important role in the treatment and intervention process for patients.
1. What is appendicitis?
In the human body, the appendix is a small, narrow tube-shaped segment of intestine about a few centimeters long, located at the base of the cecum. The appendix is usually located in the lower right abdomen, near the junction between the small and large intestines.
When the lumen of the appendix becomes blocked, it can cause infection and lead to appendicitis. The bacteria in the appendix grow and multiply rapidly, causing inflammation, swelling, and pus filling in the appendix. If appendicitis is not treated in time, it can cause the intestine to burst, which is life-threatening.
In general, appendicitis is considered an emergency of the abdomen, tends to occur most commonly in children and young adults. According to research, one in 15 people will develop appendicitis during their lifetime.
2. What are the common symptoms of appendicitis?
Typical symptoms of appendicitis are pain in the epigastrium or around the navel, nausea, vomiting and loss of appetite. After a few hours, the pain will move to the right lower quadrant. The pain tends to increase when you cough or move.
One of the most recognizable signs of appendicitis is a reaction in the abdominal wall at McBurney's point - the junction of the medial and lateral 1/3 of the umbilicus with the anterior superior iliac spine.
Other symptoms of appendicitis are pain in the lower right corner of the abdomen when the lower left corner is pressed (Rovsing sign), pain that increases when you relax the iliac lumbago or passively rotate the thigh. In addition, you may also have a mild fever, the temperature when measured at the anus can range from 37.7 to 38.3 degrees Celsius. For a high fever, it can be a sign that the appendix is damaged. broken or at a late stage.
Most of these typical symptoms are present in only about 50% of patients with appendicitis. The disease can even cause a variety of symptoms, making it difficult to detect. The remaining half of appendicitis cases may experience less typical symptoms, especially in elderly patients, pregnant women or infants.
For women who are pregnant, the symptoms of appendicitis can be difficult to identify due to symptoms such as nausea or mild abdominal pain. Older patients may feel less abdominal pain, which can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment, causing a dangerous rupture of the appendix. Breastfed babies and young children tend to have fever, diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, making diagnosis difficult and confusing.
Người bệnh viên ruột thừa đau tại vị trí hố chậu phải
3. Importance of Appendicitis Test
Appendicitis usually occurs due to a blockage by stool, foreign matter or parasites in the appendix. When the appendix becomes blocked, bacteria accumulate inside it, leading to swelling, pain, and infection. If left untreated, the appendix can rupture and spread the infection throughout the body. This is considered a serious condition that can sometimes be life-threatening.
Appendicitis tests can help diagnose the condition, thereby providing timely treatment before the appendix ruptures or causes serious complications. To treat appendicitis , your doctor may recommend an appendectomy .
4. Tests performed in the diagnosis of appendicitis
Tests for appendicitis usually include a physical examination of the abdomen and some of the following:
Blood tests: The patient may have a blood test for appendicitis to check for signs of infection. coincide. A high white blood cell count is a typical sign of an infection. Urinalysis: Helps rule out urinary tract infection Imaging tests: Such as CT scan, abdominal ultrasound to help see inside the patient's abdomen. Imaging tests are often used to help confirm the diagnosis if a physical exam or blood test suggests you may have appendicitis. During the appendicitis blood test, the doctor will take a blood sample from a vein in the patient's arm through a fine needle and then collect the blood sample that needs to be tested. This procedure may cause a slight stinging sensation after the needle enters and exits the vein. Blood sampling usually takes 5 minutes or less.
For a urinalysis to diagnose appendicitis, you will give your doctor a sample of your urine. Before taking a urine sample, you should wash your hands and intimate area as directed by your doctor. Men should wipe the tip of the penis before urinating, women should open the labia and then clean from front to back. You need to collect at least 1-2 ounces of urine into a container marked with the amount available.
When performing an abdominal ultrasound, your doctor will use sound waves to examine the inside of your abdomen. During this procedure, you will be lying on an ultrasound table, after which the doctor will apply a special gel to the skin of your abdomen and use a hand-held transducer that is moved over your abdomen.
One of the other common appendicitis tests is a CT scan, which creates pictures of the inside of your body. Before the scan, you may be given a contrast dye to help the images show up better in the X-ray film. Contrast is sometimes given orally or intravenously. During the CT scan, you will lie on a table that slides into the CT scanner. The scanner's beam rotates around your body as it takes pictures from different angles, creating a clear 3-D image of your abdomen.
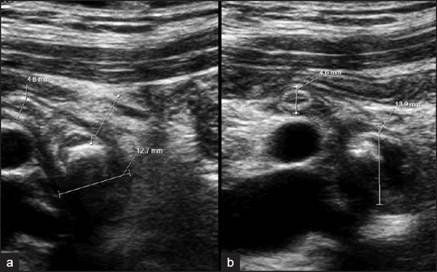
Hình ảnh viêm ruột thừa cấp trên siêu âm
5. What do you need to prepare for the appendicitis test?
In fact, you don't need any special preparation for a urine or blood test to diagnose appendicitis. For an abdominal ultrasound or CT scan, you should fast or drink for several hours before the procedure. If you have any questions about your test preparation, you should talk to your doctor specifically.
6. Are there any potential risks to the appendicitis test?
In general, appendicitis blood tests usually pose very few risks. You may feel slight pain or bruising where the needle was inserted, but these should go away quickly.
As for the urine test, it doesn't seem to pose any risks. Meanwhile, having an ultrasound can make you feel a little uncomfortable, but there are no risks.
If you have used contrast material for a CT scan, it may cause a chalky/metallic taste in your mouth or burning when given through a vein. In general, contrast medium is considered safe, but in rare cases it can cause an allergic reaction.
7. Meaning of Appendicitis Test Results
If the urine test result is positive, this means you are suffering from a urinary tract infection instead of appendicitis. In case you have symptoms of appendicitis and your blood test results show a high white blood cell count, your doctor will ask you to perform additional abdominal ultrasound or CT scan to confirm the diagnosis.
If the test shows appendicitis, you will have surgery to remove the appendix soon after being diagnosed. Most people have a quick recovery when the appendix is removed before it ruptures. However, if surgery is done after your appendix ruptures, your recovery may take longer and require a longer hospital stay. In addition, your doctor may also give you long-term antibiotics if your appendix ruptured before surgery.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: medlineplus.gov