This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Doctor Trinh Le Hong Minh - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Esophageal cancer is one of the most common cancers in the gastrointestinal tract - ranking 3rd in gastrointestinal cancers, after stomach cancer and colorectal cancer. Diagnosis of esophageal cancer needs to be accurate to distinguish it from other diseases of the esophagus.
1. What is esophageal cancer?
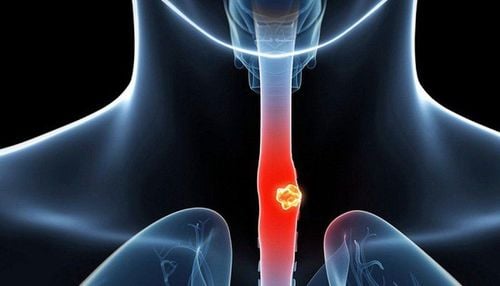
Esophageal cancer is cancer that occurs in the esophagus - the part of the digestive tube that runs from the throat to the stomach. Esophageal cancer originates in the cells of the inner lining of the esophagus. As it grows, it spreads through the muscular layers of the esophagus before metastasizing to the lymph nodes and other organs such as the lungs and liver.When having esophageal cancer, patients often have symptoms of difficulty swallowing, pain when swallowing, hoarse voice, dry cough, possibly vomiting or coughing up blood. Gradually, the patient becomes picky eaters, eats less and manifests with weight loss.
2. Diagnostic test for esophageal cancer
2.1 Tests to detect disease X-ray of the esophagus with oral contrast: Can identify any abnormal image of abnormal changes in the shape of the esophagus.Esophageal endoscopy, biopsy: Using a thin tube with a bright light called an endoscope, inserted into the esophagus - stomach. If an abnormal area of the esophagus is suspected, the doctor will take a sample of cells and histopathology through the endoscope to look at under the electron microscope, a procedure called pathology. From there can see the organization of cancer, abnormalities in the cell organization or other lesions.
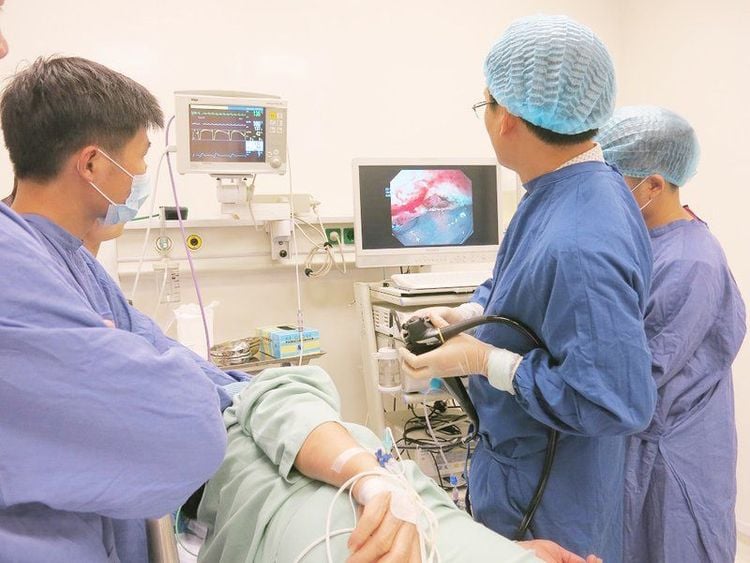
Stages of esophageal cancer include:
Stage 1: Cancer cells appear only in the top layer of the wall of the esophagus. Stage 2: Cancer cells have spread to the deeper layers of the esophageal wall or, more dangerously, have invaded nearby lymphatic tissue. At this stage, the cancer has not spread to other parts of the body. Stage 3: Cancer cells invade deeper layers of the esophageal wall/invade tissues or lymph nodes in the paraesophageal region. Stage 4: Cancer cells have invaded other parts of the body such as the liver, lungs, brain, and bones. Some of the tests that help determine the stage of cancer include:
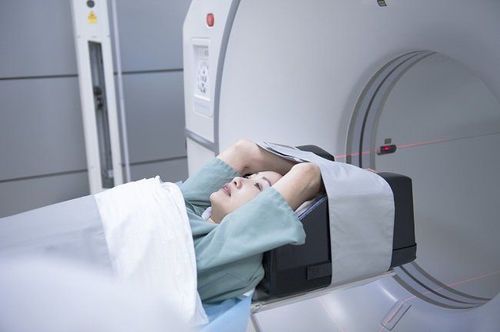
Computed tomography (CT Scanner): This is a very valuable diagnostic method in assessing the stage of the disease, response to treatment and development. now relapse. This is done using a computer connected to an X-ray machine. From there, the doctor can see details about the internal organs of the body. Specifically, computed tomography of the chest - abdomen helps to evaluate tumor invasion, lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis.
Endoscopic assessment of tracheobronchial invasion: Use a flexible and lighted bronchoscope through the patient's mouth/nose to descend through the airways to evaluate airway lesions.
Endoscopic ultrasound of the esophagus: This method is used to differentiate early lesions and to biopsies mediastinal and abdominal lymph nodes.
Esophageal cancer is one of the most common gastrointestinal cancers today. The disease in the early stages has no obvious symptoms, only when it begins to progress, there are manifestations such as choking or difficulty swallowing. Therefore, the diagnosis of esophageal cancer by laboratory measures and scans is very important for early detection of the disease.
Package for screening and early detection of gastrointestinal cancers (esophagus, stomach, colon) at Vinmec International General Hospital combining clinical and paraclinical examination, will give the most accurate results possible. , helping customers detect gastrointestinal cancers at the earliest.
Before taking a job at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital, the position of Doctor of Radiology since February 2018, Doctor Trinh Le Hong Minh used to work as a resident in the Department of Radiology at the hospital. hospitals: Cho Ray, University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Oncology, People's Gia Dinh, Trung Vuong... from 2012-2015. Working officially at Cho Ray Hospital from 2015-2016, City International Hospital from 2016-2018.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.