This is an automatically translated article.
During pregnancy, if the mother does not eat enough, work - rest inappropriately or get sick, the baby is very susceptible to fetal malnutrition. Therefore, focusing on nutrition during pregnancy is important for the health of the baby.
1. What is Fetal Malnutrition?
Fetal malnutrition is the earliest form of malnutrition in children. Babies are considered malnourished if they are born at full term but weigh less than 2,500g at birth. In these children, organs such as skin, muscles, bones, liver, brain, kidneys,... are all affected.
Fetal malnutrition occurring in the last 3 months of pregnancy will slow the child's brain development, later the baby is often less intelligent. In addition, fetal malnutrition is often associated with other chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, metabolic disease, blood disease and birth defects.
In addition, babies with fetal malnutrition when born are also prone to hypoglycemia, hypothermia causing breathing disturbances, hypocalcemia causing convulsions. With proper nutrition, babies can grow normally, reaching the same weight as other children after 2-3 months. On the contrary, in case of poor nutrition, children will continue to suffer from malnutrition, illness, mental and physical retardation.
Especially, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 30% of babies with birth weight below 2,500g often die in the first year of life.
2. Nutritional care during pregnancy so that the child does not suffer from fetal malnutrition
The development of the fetus is greatly influenced by the mother's nutrition. Nutrition from the mother's body will follow the blood, cross the placenta to nourish the fetus, so it is necessary to ensure that the mother and baby provide enough necessary nutrients for the child to develop comprehensively, without fetal malnutrition. Some issues that need attention in nutritional care during pregnancy are:
2.1 Essential groups of nutrients for pregnant mothers Energy needs: Need 2,550 kcal/day; Protein and Fat: To build mother and baby's body organization. Protein needs to be increased by 15g/day compared to the average person's consumption and fat needs to account for about 20% of total energy (equivalent to 40g). Foods with a lot of protein and healthy fats for pregnant women are milk, eggs, shrimp, crab, fish, snails, soybeans, green beans, sesame, peanuts,...; Iron: Pregnant women should supplement with 60 mg of elemental iron/day during pregnancy to 1 month postpartum. Iron is abundant in meat, fish, clams, oysters, snails, mussels, cereals, animal blood,...; Zinc: Zinc deficiency can cause miscarriage, premature birth or premature birth, fetal death near the due date,... Therefore, it is necessary to ensure that the zinc requirement of pregnant women is 15 mg/day. The best sources of zinc are meat, fish and seafood; Calcium: Every day pregnant and lactating mothers should consume about 800 - 1,000 mg of calcium. Calcium is abundant in shrimp, crab, fish and dairy products such as fresh milk, yogurt, cheese,...;

Thai phụ nên bổ sung nhiều thực phẩm giàu sắt trong suốt thai kỳ
Folic acid: A lack of folic acid in the mother can cause low birth weight in the baby. At the same time, folic acid also prevents neural tube defects in the fetus. Therefore, it is necessary to supplement folic acid during pregnancy with an amount of about 300-400 mcg/day. Abundant sources of folic acid in foods are green vegetables, fruits, whole grains,...; Iodine: Pregnant women with iodine deficiency are at increased risk of spontaneous abortion, premature birth, and stillbirth. With severe iodine deficiency, babies can be born with permanent brain damage or birth defects such as slurred speech, deafness, paralysis of the limbs, muteness, crossed eyes,... Therefore, supplementation is needed. Adequate iodine intake for pregnant women is 175-200 mcg/day. Food sources rich in iodine are sea fish, seaweed, clams, iodized salt,...; Vitamins: Vitamin A (additional 600 mcg/day, abundant in milk, eggs, liver, dark green vegetables, yellow and red vegetables); vitamin D (additional 10 mcg/day, found in fish, eggs, milk,...); vitamin B1 (additional 1.1 mg/day, abundant in cereals and legumes); vitamin B2 (the daily requirement is 1.5mg, abundant in animal foods, vegetables, beans, milk,...) and vitamin C (the daily requirement is 80mg, abundant in ripe fruits). ). 2.2 Nutrition in the stages of pregnancy Nutrition in the first 3 months This is the stage of forming the organs and organizations of the fetus such as the spinal cord, heart, liver, lungs, brain,... so it is necessary to increase Increase the consumption of protein-rich foods such as eggs, meat, milk, legumes, etc. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure proper nutrition and overcome morning sickness to achieve an appropriate weight gain of about 1kg/month. .
In addition to adequate nutrition in the diet, pregnant women in the first 3 months of pregnancy need to take iron and folic acid supplements according to the dose prescribed by the doctor to prevent anemia and the risk of having a baby with anomalies. disability. When taking iron and folic acid tablets, pregnant women may experience some side effects such as nausea and constipation, but they are not harmful and usually go away after a few weeks.
Nutrition in the second 3 months This is a period of rapid fetal development, so it is necessary to meet the energy needs of pregnant mothers. Accordingly, the diet of pregnant women in the second trimester should increase by 250 kcal/day (equivalent to 1 bowl of rice and a reasonable amount of food).
In addition, the second 3 months of pregnancy is also a period of bone development and height of the baby, so mothers need to pay attention to eating foods rich in calcium and zinc such as eggs, milk, shrimp, crabs, seafood, etc. ..
Nutrition in the last 3 months This is the period when the fetus develops the fastest weight, so pregnant women need to ensure adequate nutrition to meet the needs of the fetus, avoiding fetal malnutrition. Regarding the diet, the mother should increase 450 kcal/day, equivalent to 2 bowls of rice and have a reasonable amount of food.
In addition to eating enough rice, pregnant mothers need to add more protein and nutrients to their diet to contribute to the construction and development of the child's body.
2.3 Notes on nutrition and activities during pregnancy Absolutely do not smoke, drink alcohol or use stimulants; Reduce the intake of hot and spicy spices such as pepper, chili, garlic,...; Limit processed foods and limit drinking coffee and tea; Mothers with edema, hypertension or pregnancy toxicity should reduce salt intake to avoid complications during childbirth;
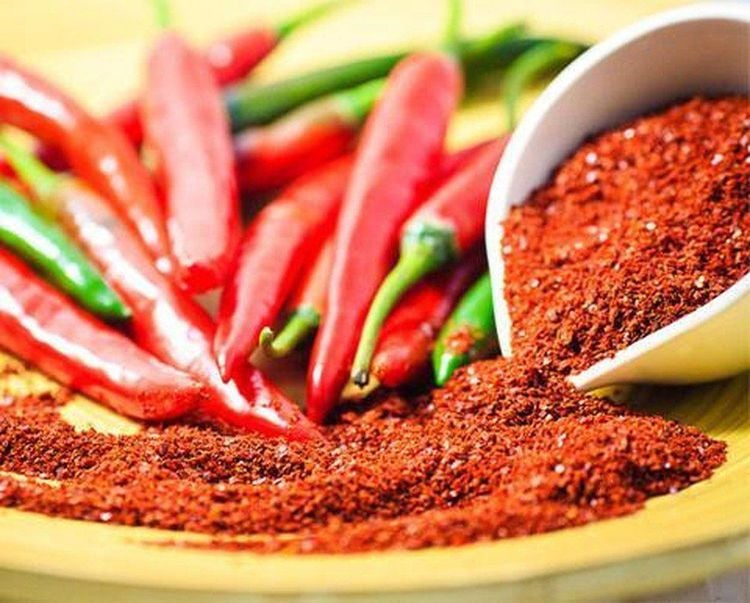

Thai phụ không nên ăn đồ cay nóng
Should eat a lot of vegetables because this food group provides enough fiber, vitamins and minerals needed; Choose foods that are fresh, clean and of high nutritional value, ensuring hygiene; Meals need to be diverse with many different foods, should not be too abstinent; Pregnant women with morning sickness should divide their meals and eat several times a day; The use of drugs during pregnancy should be especially careful, strictly follow the instructions of the doctor; Pregnant women should work according to their ability, not overwork; Avoid working at height or submerging in water. In the last month, it is advisable to gently exercise by doing housework and not to passively rest; Make sure to sleep at least 8 hours a day, nap for 30 minutes - 1 hour; Keep mentally comfortable, avoid stress, anxiety and limit travel; Keep the living environment clean, avoid dust and cigarette smoke; Periodic antenatal check-ups according to schedule and antenatal check-up immediately if there are abnormal signs such as intermittent abdominal pain, severe abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, low or absent pregnancy,...; Examine the breast, note abnormalities of the nipple such as a short nipple or an inverted nipple to guide mothers on how to breastfeed; Get all the vaccinations as recommended by your doctor. Nutritional care during pregnancy plays a key role in the prevention of fetal malnutrition in infants. This is also an important premise for the comprehensive development of children's mind and body.
Pregnant women can see a nutritionist for advice on nutrition throughout pregnancy, to ensure that the baby is not likely to suffer from fetal malnutrition.
Vinmec International General Hospital now has a package maternity service as a solution to help pregnant women feel secure because of the companionship of the medical team throughout the pregnancy. When choosing Maternity Package, pregnant women can:
The pregnancy process is monitored by a team of highly qualified doctors; Regular examination, early detection of abnormal problems; Maternity package to facilitate the birthing process; Newborns receive comprehensive care.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.