This is an automatically translated article.
Gestational hypertension, also known as pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) is a condition that most commonly occurs during pregnancy. High blood pressure during pregnancy affects about 5-10% of pregnant women. If not diagnosed and treated promptly, it can cause dangerous complications for both the fetus and the mother.1. What is gestational hypertension?
Gestational hypertension is hypertension that develops after the 20th week of pregnancy and returns to normal 6 weeks postpartum (measured twice 4 hours apart) and the absence of protein in the urine.When the diastolic blood pressure is over 90 mmHg and/or the systolic blood pressure is over 140 mmHg (for people who don't know their normal blood pressure readings: When the diastolic blood pressure increases by 15 mmHg or the systolic blood pressure increases by more than 30 mmHg compared to with normal blood pressure before pregnancy (measured after at least 10 minutes of rest)
Gestational hypertension is divided into mild when blood pressure is 140-159/90-109mmHg, severe when blood pressure blood pressure ≥160/100 mmHg
Types of hypertension during pregnancy:
Hypertension without proteinuria or edema (Gego hypertension) Mild preeclampsia Severe preeclampsia Seizures in people with chronic hypertension Eclampsia Chronic hypertension Risk subjects for gestational hypertension include:
Pre-eclampsia in pre-pregnancy Age >40 or <18 Chronic hypertension Chronic kidney disease Autoimmune disease (Systemic lupus erythematosus) Diabetes mellitus Obesity Pregnancy by artificial insemination Multiple pregnancy
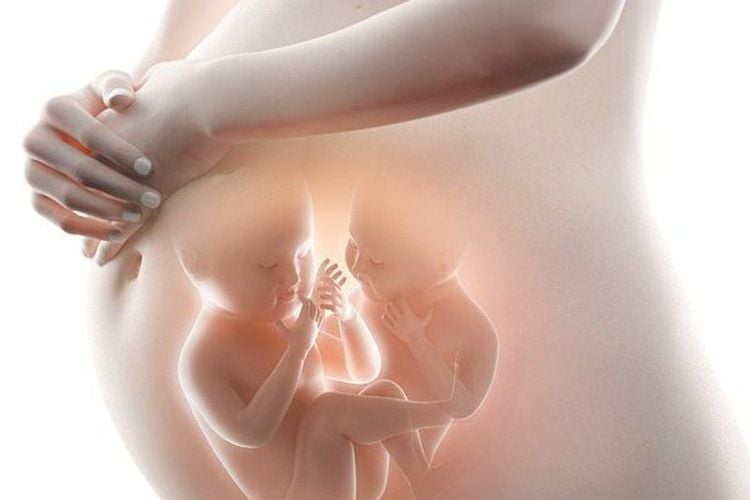
Mẹ bầu mang đa thai có nguy cơ tăng huyết áp thai kỳ cao hơn bình thường
2. Symptoms of gestational hypertension
To know the exact measurement of blood pressure, it is necessary to use a blood pressure monitor, but if pregnant women pay attention to their own health, they can recognize through some signs such as feeling stressed, uncomfortable, hot. flushing, nausea, sometimes vomiting, leading to electrolyte disturbances, headache, tinnitus, dizziness, dizziness, chest tightness, shortness of breath, blurred vision are also symptoms indicating the condition. severe complications of hypertension.When the above symptoms appear, you must immediately think of high blood pressure due to pregnancy toxicity. This disease usually occurs after the 20th week of pregnancy.
3. Diagnosis of gestational hypertension
3.1 Measures to diagnose gestational hypertension include Proper blood pressure measurement to diagnose gestational hypertension Tests should be made: total urinalysis, 24-hour urine for proteinuria, prenatal diagnosis Seizure Periodic fetal ultrasound to assess fetal development Liver function tests, kidney function tests, blood sugar... assess organ damage if pre-eclampsia is present 3.2 Diagnostic signs of hypertension Hypertension chronic pressure before pregnancy.Diastolic blood pressure 90mmHg or higher, before 20 weeks of gestation. Or blood pressure ≥140/90 mmHg before pregnancy or diagnosed before 20 weeks of pregnancy. Or hypertension diagnosed after 20 weeks and persists more than 12 weeks postpartum. Diastolic blood pressure 90-110 mmHg, measured twice 4 hours apart, after 20 weeks of gestation. No proteinuria. Gestational hypertension (Pregnancy causes hypertension)
Diastolic blood pressure 90-110 mmHg, measured twice 4 hours apart, after 20 weeks of gestation. Proteinuria can be up to 2+. No other symptoms. Mild preeclampsia.
Diastolic blood pressure 110mmHg or higher or systolic blood pressure 160mmHg or higher after 20 weeks of gestation and proteinuria 3+ or more. In addition, the following signs may be present: Hyperreflexia. Increased headache, dizziness. Blurry vision, dizziness. Oliguria (less than 400ml/24 hours). Epigastric pain. Pulmonary edema. Severe preeclampsia (diagnosed with hypertension and at least one of the features listed above). Hellp syndrome is suspected when there is microscopic hemolysis (manifested by increased bilirubin), elevated liver enzymes (elevated SGOT and SGPT levels of 70 dv/l or more) and a platelet count less than 100,000/mm3 of blood.
4. Treatment of gestational hypertension?

Bệnh nhân tăng huyết áp thai kỳ hoặc tiền sản giật mức độ nhẹ được khuyến cáo chấm dứt thai kỳ ở tuần 37
The pregnancy process is monitored by a team of qualified doctors Regular check-up, early detection of abnormalities Maternity package helps to facilitate the process. birthing process Newborns get comprehensive care
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Department of Maternal and Child Health - Ministry of Health