This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Preeclampsia is the cause of many serious obstetric complications, endangering both mother and fetus. The risk of disease can be detected through examination right from the first trimester of pregnancy, thereby helping to prevent and manage preeclampsia effectively.
1. What is preeclampsia?
Preeclampsia is a complication of toxemia of pregnancy and usually develops after the 20th week of pregnancy, affecting 5-8% of pregnant women. Preeclampsia is a serious cause of obstetric complications, which can be fatal for both mother and fetus.
2. Who is at risk for preeclampsia?
Pregnancy history: Pre-eclampsia, eclampsia, placental abruption, intrauterine underdevelopment, stillbirth, multiple pregnancy.... Number of pregnancies: The uterus is higher than the contraction. A history of a parent with high blood pressure. Relative to maternal age: Age >35 or <20. Age over 35 doubles the risk. Medical history: Diabetes, high blood pressure, kidney disease, collagen disorder, hypothyroidism. Winter spring weather. Low economic life.
3. What are the main signs of preeclampsia?
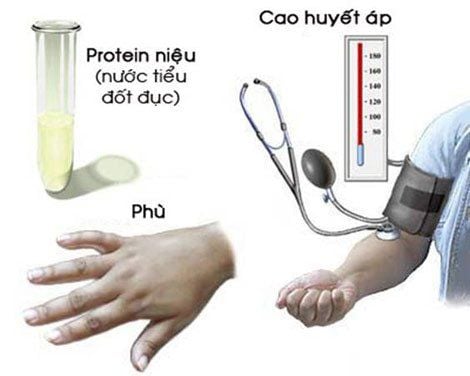
High blood pressure (BP ≥ 140/90mmHG). Proteinuria: 0.3g/l with 24-hour urine and 0.5g/l with random urine. Edema: white, soft, concave, does not decrease at rest. Other symptoms: headache, dizziness, blurred vision, epigastric pain, nausea.
4. How to prevent preeclampsia?
Supplement with adequate amounts of DHA, EPA. Food sources rich in Omega 3 for pregnant women such as salmon, cauliflower, cabbage, walnuts, sesame seeds... Meet the necessary amount of calcium. Foods high in calcium such as milk and preparations, broccoli, okra, asparagus, lettuce... Providing enough Vitamin D for the body helps reduce the risk of preeclampsia by 27%. Vitamin D is abundant in cod liver oil, shiitake mushrooms, and whole grains. Periodic antenatal check-ups and follow-up visits according to the doctor's appointment.
5. How to manage preeclampsia?

The patient needs to rest in bed, lying on the left side to increase the uterine circulation to benefit the fetus. The room is warm, soft light, less noisy, for the patient to be psychologically comfortable during pregnancy. Prioritize a light, high-protein diet. Drink 1.5 - 2 liters of water/day. Follow-up examination according to the doctor's appointment or when there are abnormalities: Headache, rapid pulse, palpitations... Do all ultrasounds and tests as prescribed by the doctor during pregnancy examination. Monitor fetal movements daily, if in 2 hours there are less than 10 fetal movements, you need to go to the hospital for re-examination immediately.
6. When should the patient be taken to the doctor?
Abdominal pain, bleeding, abnormal vaginal discharge. Headache, dizziness, blurred vision, epigastric pain, right lower quadrant pain... Urine decreased, edema increased. Reduced fetal movement.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.