This is an automatically translated article.
Dysphagia is one of the problems of swallowing disorders that cause many difficulties for patients. This problem can happen to anyone, but it is most common in the elderly or premature babies who have brain/nervous system abnormalities...1. What is a swallowing disorder?
When you have a swallowing disorder, you will have many difficulties in eating and living everyday, including:Cough while eating or right after eating. It takes time and effort to chew or swallow. Food/liquids may leak out of the mouth uncontrollably. Food stuck in the mouth. Feeling short of breath after a meal... From there, a series of other consequences will occur:
Body dehydration, lack of nutrition. Food/liquids go directly into the airways. Capable of causing pneumonia, other lung infections... Based on the main characteristics, swallowing disorders can be divided into 2 main categories:
Difficulty swallowing: Difficulty swallowing. Swallowing pain: When swallowing, there is a sharp pain in the throat or esophagus.

Người bị rối loạn nuốt cảm thấy khó thở sau khi ăn
2. What is dysphagia?
Dysphagia is a term used to refer to difficulty in moving food from the mouth to the stomach. Dysphagia can occur in all subjects, most of which are the elderly and children.
2.1 Classification of dysphagia
Based on the 3 stages of swallowing, dysphagia is divided into 3 main types:
Oral dysphagia: Problems occurring in the mouth, often caused by a weak tongue after a stroke. People with this type of dysphagia often have difficulty chewing food and transporting food from the mouth to the throat area. Difficulty swallowing in the throat: Problems occurring in the throat, often caused by abnormalities in the nervous system and nerves, have been linked to stroke, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson's disease .. Esophageal dysphagia: Problems occur in the esophagus, usually due to a blockage or irritation at this site. Usually, for treatment, one is required to use surgery.
2.2 Some causes of difficulty swallowing
Dysphagia can have many causes such as:
Lateral scleroderma: An incurable form of progressive neurodegeneration. Over time, the nerves in the spine and brain lose function. Stroke: There are brain cells that die from lack of oxygen because blood flow to the brain is reduced. If this dead brain cell controls swallowing, dysphagia or other swallowing disorder occurs. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Occurs when eosinophils are elevated in the esophagus. The overgrowth of these white blood cells attacks the gastrointestinal system, leading to vomiting and difficulty swallowing food. Multiple Sclerosis: The central nervous system is attacked by the immune system, destroying the myelin. Parkinson's disease: A degenerative neurological disorder that over time can impair many normal activities of the patient, including swallowing. Goldflame disease: Under control muscles become fatigued and weakened due to problems in the nerves that stimulate muscle contractions. This is an autoimmune disorder. Esophageal spasm: The esophagus is narrow, often associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Esophageal cancer: Cancer that occurs in the esophagus, often related to alcohol, tobacco... or gastroesophageal reflux...
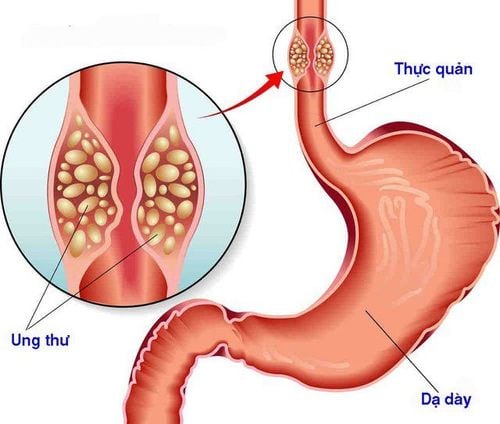
Ung thư thực quản gây khó nuốt
2.3 Complications of dysphagia
Dysphagia if not treated will cause many dangerous complications such as:
Pneumonia, upper respiratory tract infection: occurs when food due to errors in the swallowing process can enter the lungs. Malnutrition . Water loss...
3. Diagnosing dysphagia/dysphagia
The diagnosis of swallowing problems mentioned above will be determined by several methods:Swallowing test. Barium swallow test: The patient will swallow a liquid containing barium and this barium will show up in the X-ray, helping the doctor to clearly identify what is happening in the esophagus, especially the functioning of the cells of the esophagus. muscle. Endoscopy: The doctor will use a camera to hold down the esophagus and if cancer is suspected, they will do a biopsy...
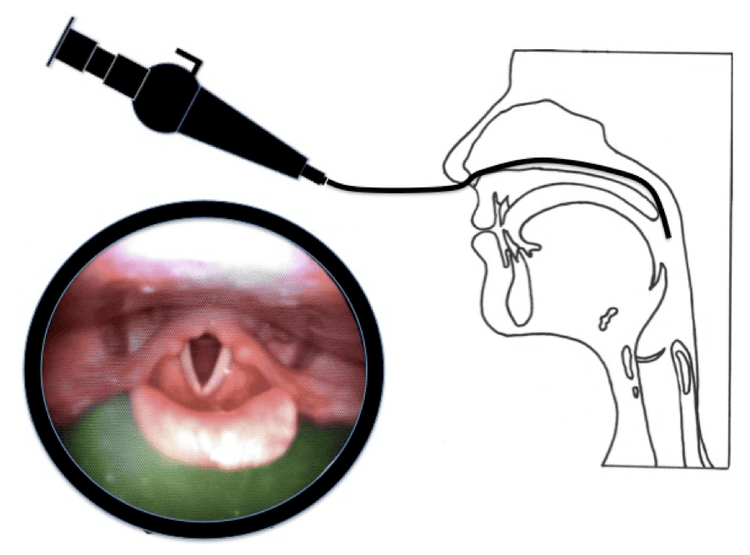
Nội soi giúp chẩn đoán bệnh
4. How is swallowing disorder/dysphagia treated?
Depending on the type of dysphagia that's happening, doctors will have different treatments.4.1 Treatment of dysphagia in the oropharynx
The problem is often neurological, so effective treatment is a challenge. Besides treating the underlying disease, some methods will be used such as swallowing therapy, diet... and if necessary, the patient will be fed through a tube.4.2 Treatment of dysphagia in the esophagus
Mainly surgical intervention.It can be seen that dysphagia in particular and swallowing disorders in general have created many inconveniences for patients, and at the same time caused many dangerous complications and are also signs of many worrisome diseases. Therefore, if you have unusual symptoms, you need to see a doctor for timely examination and treatment.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as if you have a need for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website to be served.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.