This is an automatically translated article.
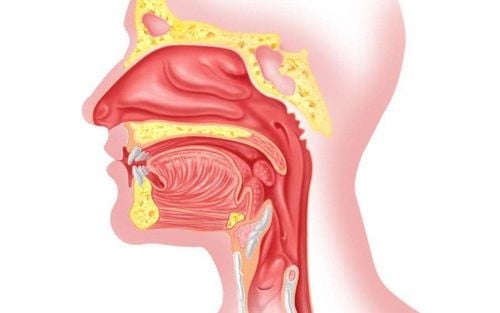
The article is professionally consulted by MSc, BS. Nguyen Vinh Toan, Department of Interspecialty - Vinmec Times City International General HospitalOtitis media is a common disease in infants and young children, when infected with this disease, children will have some symptoms such as: high fever, fussiness, refusal to eat, stop feeding, vomiting, etc. or shaking head, rubbing hands in ears, even convulsions ... If otitis media in children is not detected and treated promptly, after about 2-3 days, it can turn to the stage of otitis media. pus, burst pus, causing complications of perforation of the eardrum, pus draining out of the ear....
Purulent otitis media is a common type of otitis media in children, including 2 stages: pus stasis and purulent rupture, usually caused by rhinitis, tonsillitis or otitis media. Children with otitis media with purulent discharge will have symptoms. Symptoms include: Fever, cough, runny nose with digestive disorders, earache, crying, stop feeding, stop eating. At the stage of purulent rupture, the symptoms of otitis media with purulent discharge will decrease, the child will reduce fever, reduce ear pain, and begin to have a lemon-yellow and cloudy ear discharge.
After diagnosing a child with purulent otitis media, the doctor may suggest some pain relief measures for the child such as using pain relievers, warm compresses... It will depend on the cause and a number of factors such as the child's age, symptoms, and condition.
Usually, when a child has purulent otitis media, the otitis media injection will be considered to drain the pus out of the ear, helping to reduce the pressure in the middle ear cavity of the child. After injecting otitis media with pus, the whole body will be treated as in the congestive stage.
The technique of injecting pus for otitis media is considered when children with otitis media have acute pus stasis and need to be drained out urgently to limit dangerous complications. Injecting pus for otitis media not only helps to reduce pressure, but also limits the complications of eardrum self-perforation.
The technique of injecting pus in otitis media is easy, safe and does not cause complications, if children with otitis media are injected early and treated well, the disease tends to be cured in a short time of about 2 weeks. Children's hearing is guaranteed.