This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Digestive Endoscopy Doctor - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
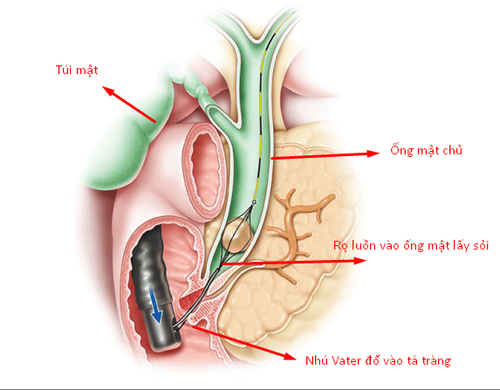
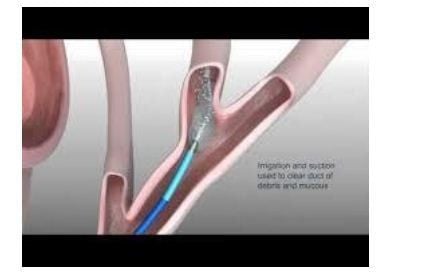
Like endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, SpyGlass is inserted through the patient's throat, through the stomach, into the bile duct and gives a visual image thanks to its deviated design in 4 different directions, the doctor can observe Monitor images at all 4 quadrants of the entire treatment area.
1. Overview of the SpyGlass . method
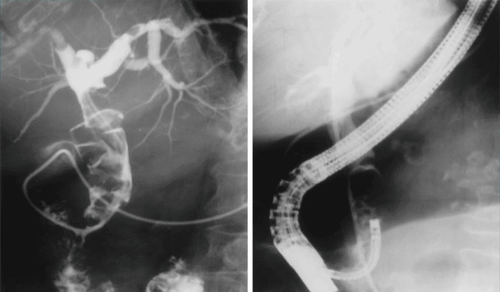
In the treatment of biliary tract disease, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatitis (ERCP) plays a huge role. ERCP is a procedure that uses an endoscope with imaging windows and a lateral procedure, combined with X-rays to view the pancreatic and bile ducts. In addition to treating biliary tract disease, ERCP is also used to remove gallstones, treat conditions such as: acute pancreatitis, chronic pancreatitis or take a small tissue sample for analysis (biopsy).
Pancreatic cholangiography is an X-ray of the bile ducts and pancreatic ducts, which are usually not visible on a regular X-ray. However, if an X-ray contrast agent (contrast) is injected into the lumen, the X-ray film will show a clear picture of these tubes.
Normally, bile or pancreatic juice flows in these ducts toward the papilla (a special structure that forms where the common bile duct empties into the duodenum). When contrast is injected into the papilla through a plastic tube placed in the endoscope, the drug will travel up the pancreatic and bile ducts, so it is called “retrograde”. X-rays are taken at that moment to show the bile duct.
However, for tumors inside the common bile duct, liver hilar tumors, to confirm the diagnosis is still a problem, because it is not possible to see directly, it is not possible to take tissue samples inside the biliary tract for testing. Histopathology to determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant, so most previous diagnoses of cholangiocarcinoma were made through the C-Arm screen of the radiograph. Another problem is that when performing ERCP, for large stones, it is often necessary to use a mechanical lithotripsy, or switch to a common bile duct stone removal surgery, and ERCP cannot completely remove the stones. stones in the right and left hepatic ducts.
With the advancement in technology, SpyGlass (intraoral cholangioscopy) was born to solve these problems.
With the sophisticated endoscope system Spyglass, most experts believe that oral cholangioscopy will soon become a universal technique applicable to the evaluation and treatment of biliary diseases. The system has proven to be an effective diagnostic and therapeutic tool. Studies have evaluated the clinical efficacy of transoral cholangioscopy to determine the benign or malignant nature of biliary strictures, diagnose intrabile duct tumors, and preferably identify biliary tract disease. unknown and treatment of gallstones . Spyglass was first launched in 2007 by Boston Scientific and in 2015 the company released the next generation SpyGlass DS system for advanced diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the pancreas and biliary tract.
Spyglass is considered a breakthrough technology in the diagnosis and treatment of gallstones.
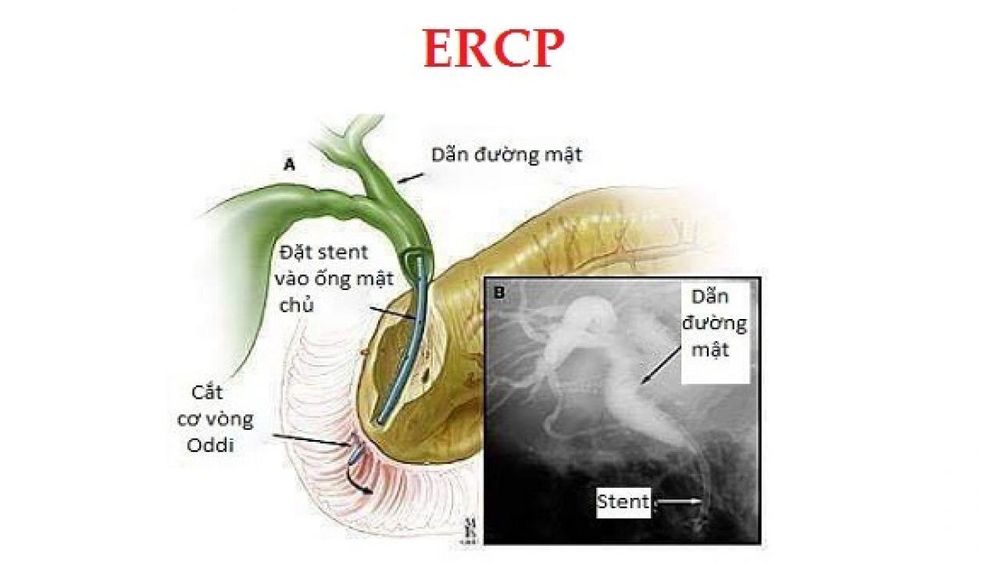
2. What tools does SpyGlass include?
SpyGlass is a small flexible endoscope system with a light and a micro camera mounted at the end that provides a visual view of the bile ducts (liver ducts) that cannot be obtained with older devices. can be done.
Dr George Webster - University College Hospital, London said: Using SpyGlass technology gives a success rate of up to 90% of the 100 patients he has treated to date. He added that the device could also be used to help detect bile duct cancer early. "The direct imaging provided by the device makes it possible to identify tumors at an earlier stage than before."
3. Advantages of SpyGlass over ERCP
Like endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, SpyGlass is inserted through the patient's throat, through the stomach, and into the bile duct. But unlike ERCP, which relies on X-rays to determine the location of gallstones, Spyglass gives a more intuitive image thanks to its design that is deflected in 4 different directions, allowing the doctor to see the image at all 4 angles. coordinates of the entire treatment area. This helps doctors make a more accurate diagnosis.
When stones are detected, a small probe in the tube can emit an electric current to break the stone (electrohydraulic) or use a laser to break up the stone. In particular, electrohydraulic lithotripsy is more effective with bile pigment stones (bilirubin stones). Fragments of gravel are removed using small baskets or balls to catch and remove from the body.
In 2015, the new generation SpyGlass system was born and approved by the FDA (US Food and Drug Administration), providing clinicians with a superior technology in disease diagnosis and treatment. pancreas and biliary tract. Developed on the basis of traditional equipment, the new SpyGlass DS system with advanced features to enhance images and simplify operation. The system includes a SpyScope DS Access cord and a single-use Catheter to eliminate reprocessing and image degradation over multiple uses. The integrated digital sensor provides superior images with higher resolution, 60% more extended field of view than the first generation.
SpyGlass system is fast to set up and operate, good image quality and high stability. This technology can be implemented as an extension of the ERCP procedure. This will increase our ability to diagnose and treat pancreatic disease and reduce the number of repeats of the ERCP procedure.”
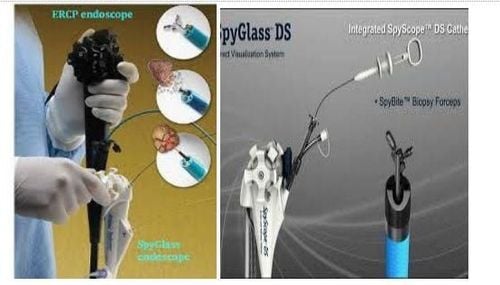
Performing the SpyGlass procedure usually takes between 45 minutes and 1 hour. Recovery time is fast, no pain, patients can be discharged after 4-6 hours. Very few cases have to stay overnight for monitoring. Thus, the treatment cost is significantly reduced by 30-40%.
SpyGlass brings many benefits to patients, helping doctors diagnose more accurately, faster and reduce unnecessary testing requirements. Different from the old technology of just 2D images, black and white, SpyGlass provides us with a vivid color image, which is the difference between day and night.
However, this is an expensive tool that is still not commonly used in Vietnam.
4. Indication of SpyGlass
Usually, SpyGlass is indicated for diagnosis in cases of:
Biopsy of undetermined stricture in patients without sclerosing cholangitis Exclude malignant stricture in sclerosing cholangitis by providing imaging imaging, biopsy guide Diagnosing cholangiocarcinoma carcinoma (bile duct cancer) Redefining bile duct defects seen on ultrasound or ERCP. Nondiagnostic ERCP findings for biopsy Precise location of biliary and pancreatic tumors Preoperative visual assessment and biopsy to assess for problems following biliary tract transplantation, mucinous tumors, and eosinophilic cholangitis Evaluation of cytomegalovirus, fungal and parasitic infections Blood in the bile Indications for treatment of SpyGlass:
Bile duct stenting Cholangiocarcinoma photodynamic therapy (potential indications) ) Argon photocoagulation of mucinous tumors (potential indication) Alternative to surgery in patients with Mirizzi syndrome type II (potential indication) Surgery and lithotripsy using mechanical, electrical, or laser diffusion Chronic pancreatitis Pancreatitis Pancreatic stones Pancreatic duct tumor Role in autoimmune pancreatitis However, this technique also has a number of complications ranging from relatively mild to life-threatening, including:
Cholangitis (most common) complications) Infection Abdominal pain Pancreatitis Low blood pressure Nausea Liver abscess Perforation of the bile duct (from the conductor) Increased amylase and lipase without inflammation Clinical pancreas Inflammation syndrome
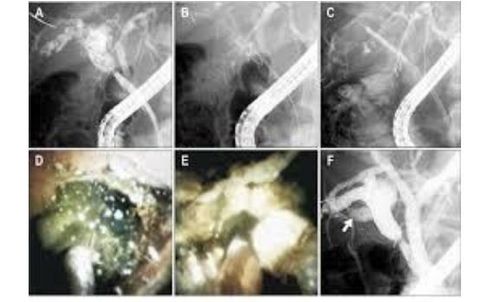
A study by Awadallah et al. showed that biopsy-guided cholangoscopy was able to rule out malignancy in 31 primary sclerosing cholangitis patients who had a prior finding of biliary stricture. . A study by Itoi et al reported that cholangioscopy with biopsy was able to diagnose benign and malignant lesions with 99% sensitivity and 95.8% specificity. Peroral cholangioscopy has also been evaluated as an effective tool for the evaluation of pancreatic ducts. A study by Yamaguchi et al. reported an improved ability to diagnose pancreatic papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas using a mother-infant cholangioscope. Importantly, this study also concluded that there is no cytological value with pancreatic juice in the diagnosis of pancreatic carcinoma. Studies evaluating the effectiveness of the Spyglass cholangioscopy system have reported that direct observation improves the accuracy of cholangioscopy results and has a positive good predictive value in the evaluation of patients with symptoms of biliary obstruction of unspecified origin. In one series, cholangioscopy-guided biopsies of the bile ducts could be successfully performed in 89% of cases. An unexpected benefit of the high sensitivity of cholangioscopy is that it revealed a previously unrecognized weakness in ERCP in the evaluation and diagnosis of choledocholithiasis. Parsi et al were able to diagnose at least 29% of ERCP missed gallstones by performing endoscopic cholangiography, leading them to conclude that the rate of stone loss on ERCP may be higher than previously thought. this. Studies have reported a 92% success rate in the treatment of gallstones using electrohydraulic lithotripsy and laser lithotripsy. Moon et al. reported excellent success with electrohydraulic or laser lithotripsy using an ultrathin biliaryoscope. In patients with difficult to treat stones, Arya et al. described transoral cholangioscopy with electrohydraulic lithotripsy in 94 patients reporting a 96% fragmentation rate and a 90% stone clearance rate. Furthermore, Hui et al demonstrated significantly less cholangitis and a proportional reduction in mortality with lithotripsy-guided endoscopic cholangiography compared with biliary stenting alone in elderly patients. Many other studies report similar success rates in the treatment of gallstones using transoral cholangioscopy and electrohydraulic or laser therapy. Therefore, when performed by experienced and trained personnel, transoral cholangioscopy can be a safe and highly effective technique for intractable gallstones.
With the introduction of the SpyGlass system, a new treatment cycle has opened up for patients with pancreatic disease, reducing invasive interventions, and providing a better quality of life for patients.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit examination and treatment of biliary tract disease at the hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
MORE
Possible side effects or complications of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography Advantages of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography at Vinmec Learn how to remove gallstones by ERCP at Vinmec