This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Tran Hong Nhat - Interventional Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. The doctor has more than 10 years of experience in examining and treating interventional cardiovascular diseases.Congenital heart disease is a defect of the heart or vascular system that develops during the fetal stage. In order for a child to live and develop after birth, it is necessary to make physiological adjustments. Therefore, the intervention to treat congenital heart disease needs to adhere to certain principles, suitable for physiological and hemodynamic functions.
1. Medical treatment of congenital heart disease
Medical treatment of congenital heart disease is mainly prevention or treatment of complications caused by congenital heart disease. Although medical treatment does not cure congenital heart disease, it will help improve quality of life, reduce symptoms, and prepare for further treatment (surgery or intervention)1.1. Treatment of heart failure Heart failure is a very common complication of congenital heart disease. Early detection and timely treatment help prevent, improve symptoms, and improve children's quality of life. Treatment of heart failure is mainly based on the main classes of drugs such as inotropes, diuretics and peripheral vasodilators. Besides, the doctor may need to combine some other measures depending on the condition of the disease.
1.2. Treatment of pulmonary hypertension A group of congenital heart diseases with increased blood flow to the lungs, if left untreated, can lead to pulmonary hypertension. In the early stages, the disease often has no obvious symptoms, later will manifest as fatigue, shortness of breath, cyanosis .... Treatment of pulmonary hypertension helps to improve symptoms, prevent irreversible lung damage, to intervention or surgery.
1.3. Prophylaxis Prophylaxis of infective endocarditis should be performed in patients with cyanotic congenital heart disease, with a history of endocarditis, after 6 months of intervention with metal instruments or treatment. prolonged in cases of residual circulation after intervention.

2. Treatment with percutaneous interventional cardiac catheterization
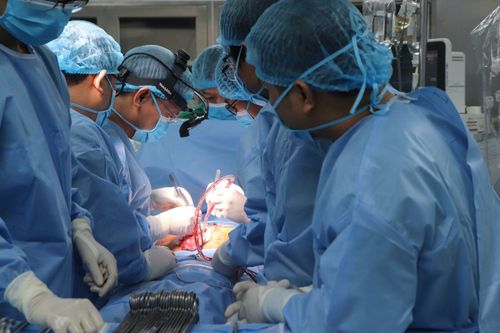
In recent years, the field of Interventional Cardiology has developed strongly, helping to solve many congenital heart diseases that previously had to be operated or given up.Cardiovascular interventional technique is performed by inserting an instrument into a patient's blood vessel, thereby bringing the instrument to the heart to either block openings in the heart or widen narrow spaces in the heart valves or blood vessels. This method helps patients avoid open surgery, shorten the hospital stay.
Commonly used interventional cardiac catheterizations are:
Atrial septal tear; Narrow heart valve dilation; Angioplasty narrowed blood vessels; Closure of atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, ductus arteriosus Obstruction of vascular malformations
3. Surgical treatment of congenital heart disease

With too severe injuries, the hemodynamic prognosis of the child is difficult to meet to maintain life, surgical repair should be carried out quickly. With minimal damage, assess that the child can tolerate medical drugs, the time of surgery can be delayed, to choose the most appropriate time of intervention or surgery
There are two types of surgery : closed heart surgery (surgery that does not use extracorporeal circulation) and open heart surgery (surgery using extracorporeal circulation).
There are 2 types of surgery: radical repair surgery and temporary repair surgery
- Radical repair surgery is a method that helps repair all defects in the heart, returning the heart to normal for the patient . perform a total repair, so that the child can grow temporarily and prepare for the next surgery
Types of temporary surgery:
Aortopulmonary - Pulmonary bypass Banding of the pulmonary artery Atrial septal fat Glenm surgery, Fontan
4. Principles of tracking
Follow-up is an important principle to help choose the right treatment. For children applying medical treatment, it is necessary to follow-up care and visit periodically to assess drug response and identify warning signs such as children. stop feeding, fussiness, rapid breathing, labored breathing, sweating, tachycardia or not gaining weight, for intervention or surgeryEven after the intervention, the child is closely monitored for regeneration ability hemodynamic management and tolerability with the new "path". For children who have not been thoroughly intervened, periodic monitoring is also necessary to plan a second intervention.
In short, congenital heart disease is a relatively complex group of diseases in cardiology, both in terms of pathophysiology and principles of treatment. Therefore, the significance of cardiac examination in the fetus as well as in the newborn is extremely important, helping to detect early and intervene properly, so that the child can have the best first days of life.
Vinmec International General Hospital currently has all the professional conditions and technical means to effectively implement methods of treating congenital heart disease. Vinmec gathers a team of highly qualified and experienced cardiologists; modern medical equipment, up to international standards; professional service quality, helping to improve the efficiency of disease diagnosis and treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: nih.gov; webmd.com; mayoclinic.org