This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Ho Thi Xuan Nga - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Total atrioventricular canal, also known as atrioventricular septal defect, accounts for 2% of congenital heart diseases, associated with about 30% with Down's disease. In children with Down syndrome, 40% are associated with congenital hearts and 30% of congenital hearts with Down syndrome are atrioventricular canal lesions.
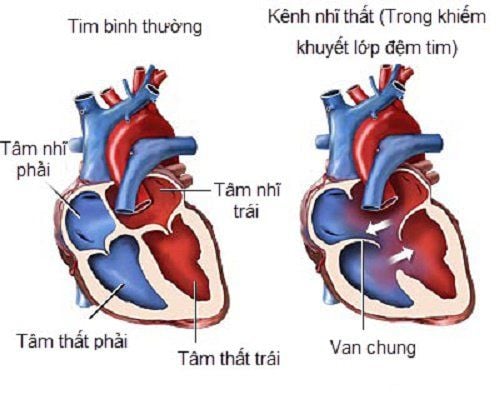
1. Total atrioventricular canal anatomy
The total atrioventricular channel includes the first foramen septal defect, the receiving part ventricular septal defect, the anterior mitral septal cleft, the tricuspid septum that forms the anterior and posterior leaflets of the common atrioventricular valve. When there is no ventricular septal defect, it is called a partial atrioventricular septal defect or a first foramen septal defect.
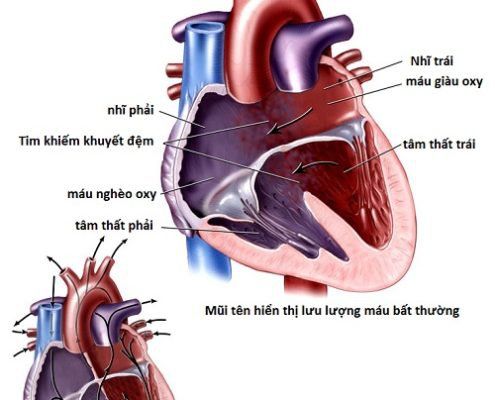
Hình ảnh giải phẫu kênh nhĩ thất
2. Symptoms of total atrioventricular canal
Children with total atrioventricular canal disease will have clinical symptoms:
Anorexia, slow weight gain Heart failure: Heart failure begins at 1 month and lasts until 6 months of age From over 6 months of age, it will progress to fixed pulmonary hypertension. Without surgery, most children will die at 2-3 years old, the rest will have obstructive pulmonary vascular disease and die in adulthood.
Subclinical symptoms:
X-ray: Very large heart shadow in all 4 chambers, severe pulmonary hypercirculation Electrocardiogram: ventricular hypertrophy or bundle branch block (P), ventricular hypertrophy (T), first degree atrioventricular block Ultrasound Cardiac : Image of endothelial knee defect, atrial septal defect and/or ventricular septal defect, mitral regurgitation, tricuspid regurgitation due to mitral valve prolapse or lack of valvular tissue, with or without pulmonary hypertension, dilation chambers of the heart and decrease myocardial contractility.
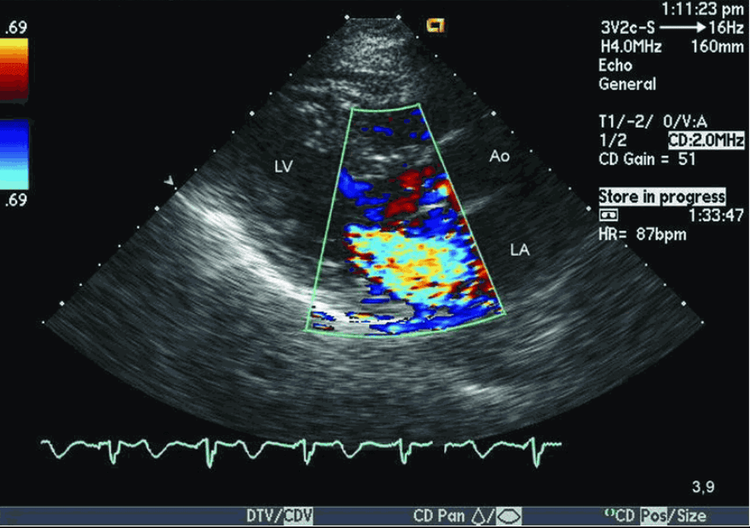
Siêu âm tim Doppler màu hở van hai lá
3. Treatment of total atrioventricular canal
Treatment of total atrioventricular canal:
First-degree treatment: Like a ventricular septal defect Level 2: Intensive resuscitation treatment for heart failure, both respiratory failure treatment with respiratory failure support means, moderate Keep SPO2 <90% to avoid pulmonary edema. Radical surgery at 3-6 months of age. Pulmonary artery ligation if multiple ventricular septal defects cannot be closed surgically. Radical surgery has a 5% mortality rate, sequelae of atrioventricular block, and persistence of mitral regurgitation. To protect heart health in general and detect early signs of myocardial infarction and stroke, customers can sign up for the Cardiovascular Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination of Vinmec International General Hospital. The examination package helps to detect cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests and modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders and is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
SEE MORE
When should surgery for congenital heart disease atrioventricular canal What is the total atrioventricular canal? What are the causes and warning signs of the atrioventricular canal? How many types are there?