Worldwide, there are an estimated 250 million new cases of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) each year. Most of these diseases can be transmitted directly or indirectly. However, for some common genital infections in women such as gonorrhea, syphilis, hepatitis B, etc., the main mode of transmission is not sexual intercourse.
Due to differences in body characteristics and hormonal factors, sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) in women often present with few or no symptoms. This can lead to delays in diagnosis and an increased risk of infection and complications, such as:
- Ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, stillbirth
- Congenital disorder
- Premature rupture of membranes, preterm birth
- Congenital infections
The information below aims to help women gain a better understanding of some common and dangerous sexually transmitted diseases.
1. Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is transmitted through contact with blood and other body fluids, which can cause serious liver damage. Although there is no cure, hepatitis B can be controlled by specific medications or vaccination. In the early stages, people with hepatitis B may experience typical symptoms such as nausea, abdominal pain, dark urine, jaundice and frequent fatigue. In more severe stages, patients have chronic infections that can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer.
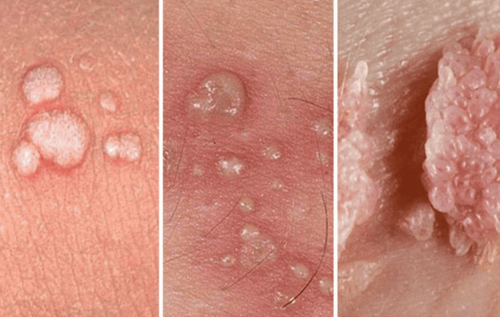
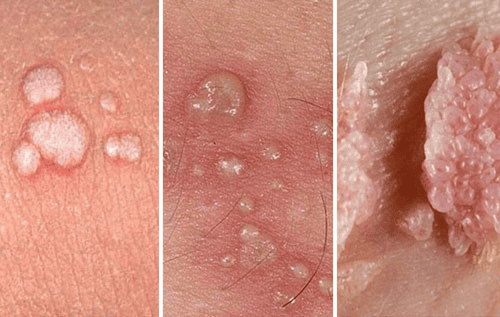
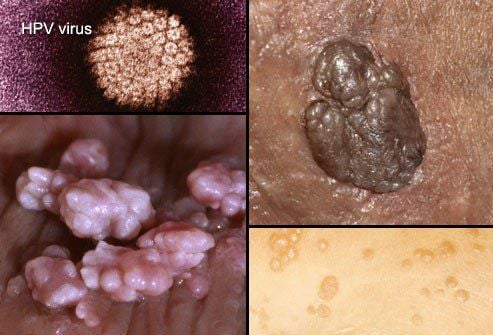
2. Genital warts (Human Papilloma Virus -HPV)
Many people mistakenly believe that genital warts are only transmitted through sex. However, this assumption is completely wrong. Because skin-to-skin contact is enough to spread HPV.
Some types of warts are harmless, but many types lead to cervical cancer or anal cancer. Currently, there is no cure for HPV, the only way to protect yourself is to get vaccinated.
>>See more: Ureplasma: 1 of the agents causing sexually transmitted diseases - Article written by BSCKII Nguyen Thu Hoai - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
3. Scabies
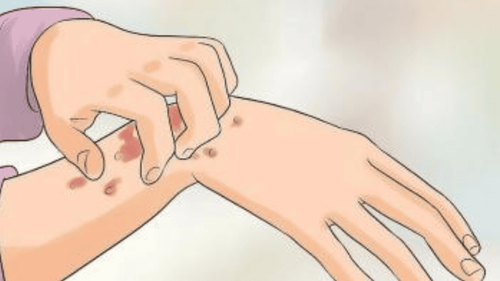
For young people, scabies are often contracted through unsafe sex with symptoms of red, itchy spots on the skin.
Scabies can be treated with specific topical creams.
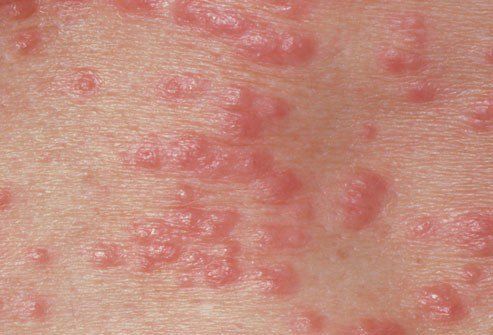
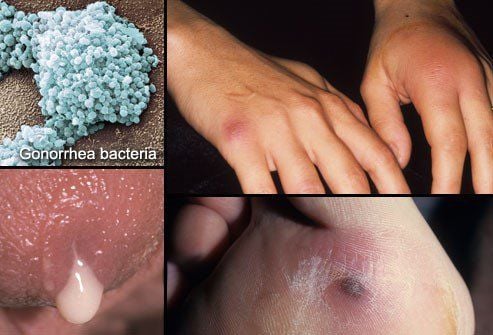
4. Gonorrhea
Painful urination, pus discharge or increased vaginal discharge are common symptoms when contracting gonorrhea for the first time or when newly infected. These symptoms are often confused with urinary tract infections or vaginal infections. In later stages, gonorrhea can cause infections, skin rashes, or spread to the joints and blood.
Gonorrhea is a disease that can lead to infertility in both men and women. However, if detected early, antibiotic treatment can cure the disease.
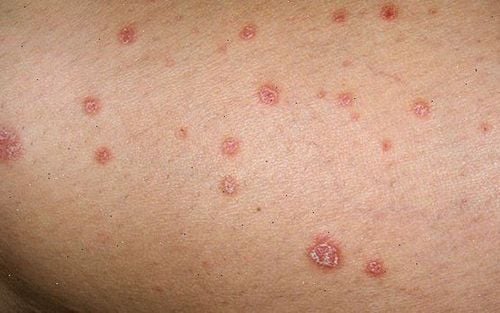
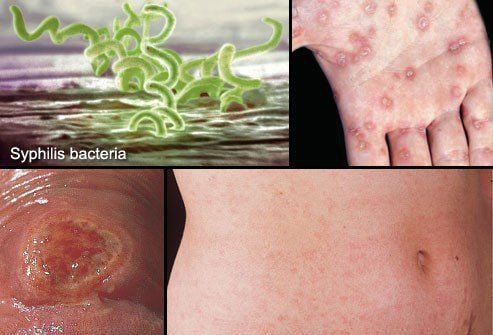
5. Syphilis
If not treated early, syphilis can lead to paralysis, blindness, chronic transmission from mother to child causing birth defects, and even death.
However, most people do not notice the early symptoms of syphilis. The first signs are usually hard, round, painless bumps on the vagina or anus. The disease is spread through direct contact with the sores of the disease. Then there may be a rash on the palms, soles of the feet, or other parts of the body. Along with that are other symptoms such as fever, hair loss, fatigue. In the final stages, symptoms arise from damage to organs such as the heart, brain, liver, nerves and eyes.
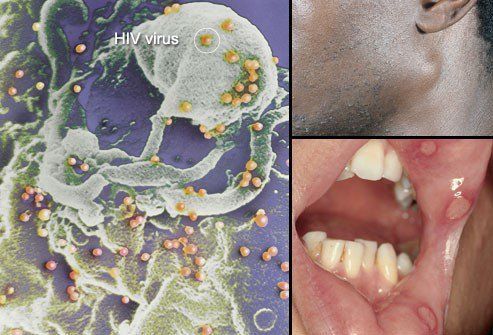
6. HIV
HIV is spread through unsafe sex, sharing needles or being born to an infected mother.
The vast majority of people with HIV do not have symptoms for many years. Some people have flu-like symptoms one to two months after infection: swollen glands, fever, headache and fatigue; mouth ulcers and pain may also occur. Therefore, a blood test is the only way to detect the disease.
7. Some other common sexually transmitted diseases
- Genital herpes: causes ulcers, pain, cracks in the genitals or anus, thighs, buttocks. There is currently no definitive treatment, only drugs to control outbreaks.
- Chlamydia: causes itching and burning, discharge in the genitals, pain when urinating; can be treated with antibiotics in the early stages.
- Herpes Group 1: painful ulcers on the lips, easily spread through kissing. There is currently no cure but outbreaks can be shortened or prevented with medication.
- Molluscum contagiosum: common in Asia and Africa, causing genital ulcers, can be treated with antibiotics
- Pelvic inflammatory disease: a serious complication of sexually transmitted diseases, if not treated promptly can cause infertility in women
8. How to effectively prevent sexually transmitted diseases
- Say no to unsafe sex
- Be monogamous
- Check your health before "making love" or when you suspect your partner has the disease
- Avoid sexual activity if your partner shows signs of disease
- Learn to identify symptoms and have regular health checkups
- Use a condom
However, it should be noted: Condoms are only effective in preventing the spread of certain diseases such as gonorrhea, chlamydia and HIV, and are less effective against herpes, syphilis and genital warts, especially scabies.
At Vinmec, the team of experienced and caring obstetricians and gynecologists are ready to listen to customers' concerns, remove their shyness and advise on the most appropriate treatment method for each patient depending on each disease.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.