Individuals who have been successfully treated for gonorrhea are at risk of reinfection if they do not adhere to the treatment regimen, use medication incorrectly or inadequately, engage in unprotected sexual intercourse with people who are currently infected, etc,…
1. Overview of Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. This type of bacteria can grow in the cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, urethra, mouth, throat, eyes, and anus of the infected individual. The symptoms of gonorrhea differ significantly between men and women. They are as follows:
- Symptoms of gonorrhea in women: 86% of women infected with gonorrhea do not exhibit any unusual symptoms. Others may experience some characteristic symptoms such as: The cervix discharges thick pus that is yellow or green in color, urethral inflammation, a burning sensation and redness at the urethral opening during urination, swelling and discomfort of the labia minora, etc,... Due to the subtle symptoms, most women with gonorrhea tend to seek medical attention late, typically 8 to 10 weeks after infection. If treated late, the gonococcus causing chronic gonorrhea can invade the endometrium, ascending from the cervical canal to the fallopian tubes, causing salpingitis with symptoms such as irregular menstruation, pain, heavy bleeding, lower abdominal pain, fever, etc... Patients may experience complications such as: inability to restore certain ovarian functions, prolonged menstruation, abnormal uterine bleeding, occasional menorrhagia, and blocked fallopian tubes, which can lead to ectopic pregnancy or infertility. Pregnant women with chronic gonorrhea may transmit the infection to their child during labor. Newborns can suffer from blindness, joint infections, or severe blood infections.
- Symptoms of gonorrhea in men: 55% of men do not exhibit clear symptoms after being infected with gonorrhea. Others may develop urethritis with symptoms such as purulent discharge from the urethra, thick discharge, cloudy or slightly greenish discharge, dysuria, etc… Urethritis may improve or self-resolve after two weeks even without treatment, but the gonococcus bacteria may still persist, invading the posterior urethra, and the prostate gland. The gonococcus can also invade the vas deferens and then the testicles, causing inflammation of one or both testicles, which can lead to scarring of the epididymis, obstructing the spermatic duct, and resulting in infertility.
If left untreated, chronic gonorrhea can lead to serious complications such as blindness, infertility, or even death.
Treatment of gonorrhea should consider these follows:
- When symptoms of the disease are detected, it is essential to visit specialized medical facilities for examination, diagnosis, and timely treatment.
- Check the source of infection and provide simultaneous treatment for both wives/husbands or partners.
- Administer the correct medication, at the appropriate dosage, and adhere to the treatment regimen prescribed by the specialists.
- During the treatment process, patients should not engage in sexual relations with others until the gonorrhea is completely treated to prevent the spread of the infection and avoid the risk of reinfection (of) gonorrhea.
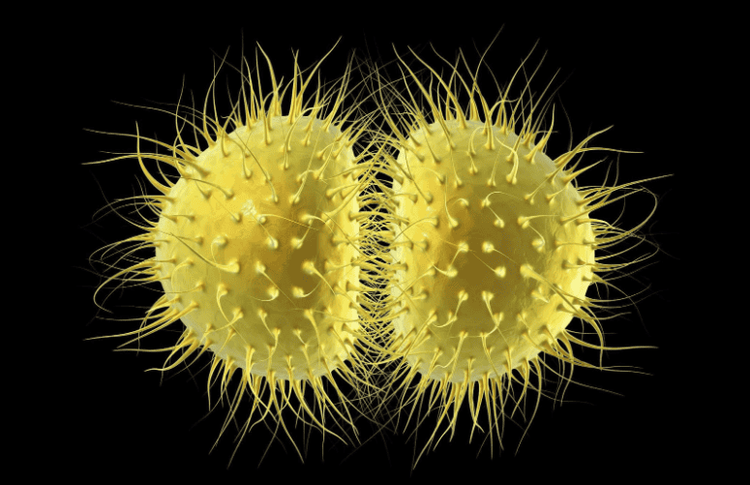
2. Causes of recurrent gonorrhea
Does gonorrhea recur? The answer is yes. Gonorrhea can recur due to the following reasons:
- Lack of persistence in treatment: Some patients with chronic gonorrhea often feel hesitant and do not want to undergo prolonged treatment. When they notice an improvement in their condition, they may stop treatment on their own or engage in sexual activity during the treatment process, leading to reinfection.
- Incorrect medication use: One reason for the unsuccessful treatment of chronic gonorrhea is that patients may use the wrong medication due to self-purchasing or receiving incorrect prescriptions from doctors. Additionally, gonorrhea is a condition with a high rate of antibiotic resistance, so antibiotics previously used to treat gonorrhea may not bring positive outcomes for patients, resulting in prolonged recovery and an increased risk of recurrence;
- Failure to treat associated complications: Gonorrhea often accompanies conditions such as urethritis, prostatitis, cervicitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, etc… To achieve complete treatment, it is important to identify the underlying causes and simultaneously treat any complications. Otherwise, it will be challenging to treat the root cause, leading to continuous recurrence of gonorrhea.
- Insufficient dosage of medication: Many patients discontinue gonorrhea treatment prematurely, causing interruptions in their medication regimen or failing to meet the requirements for complete treatment. As a result, patients are at risk of developing chronic, long-term gonorrhea, which is more likely to recur and difficult to treat effectively;
- Unsafe sexual intercourses: Many individuals experience recurrent gonorrhea infections because they continue to engage in unsafe sexual intercourses with infected partners. Doctors often advise patients with gonorrhea to have their wives/husbands or partners tested and treated simultaneously because treating only one side will never achieve complete treatment resulting in reinfection.
3. Measures to reduce the risk of gonorrhea reinfection
To reduce the risk of gonorrhea recurrence after treatment, patients should follow the guidelines below:
- Get tested and treated for gonorrhea simultaneously with your wives/husbands or partners if they are also infected.
- Maintain monogamous relationships.
- Avoid sharing underwear or towels with others.
- Adhere strictly to the doctor's treatment regimen regarding the duration and dosage of medication.
- Not engaging in sexual intercourses until fully recovered.
- Attend regular follow-up appointments after treatment to ensure that the gonorrhea bacteria have been completely eradicated.
- Once treatment is completed and sexual activity resumes, use condoms during every sexual intercourses.
Gonorrhea can be treated but it has a high recurrence rate if patients do not follow the treatment regimen prescribed by their doctors. The treatment duration for gonorrhea varies for each individual depending on their condition and severity of the disease. Therefore, when symptoms of gonorrhea appear, patients should seek medical attention promptly to receive early treatment, shorten the duration of the illness, return to normal life as soon as possible, and minimize the risk of unpredictable complications.
Vinmec International General Hospital offers a Screening Package for sexually transmitted infections that enables customers to detect diseases early and receive effective treatment, preventing serious complications. The screening package for sexually transmitted infections at Vinmec is available for all age groups, including both men and women.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.