This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Quoc Vinh - Emergency Doctor - Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. Doctor Tran Quoc Vinh has more than 6 years of experience (starting in 2011) in the field of Emergency Medicine.Smoking is the main cause of death and disease in our country. Smoking harms nearly every organ in the body, including the heart, blood vessels, lungs, eyes, mouth, reproductive organs, bones, bladder, and digestive organs.
1. How does smoking affect the heart?
You probably know that smoking causes breathing problems and lung cancer. But did you know it also makes you more susceptible to heart disease? According to statistics, about 1 in 5 deaths from heart disease are directly related to smoking.Tobacco smoke is a toxic mixture of more than 7,000 chemicals and when inhaled can interfere with vital processes in the body. One of these processes is the delivery of oxygen-rich blood to the heart and the rest of the body.
When you breathe, the lungs take oxygen and deliver it to the heart, which pumps this oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body through the blood vessels. But when you breathe in cigarette smoke, the blood that is delivered to the rest of your body becomes contaminated with smoke chemicals. These chemicals can damage your heart and blood vessels, causing cardiovascular disease.

Cigarette smoke contains CO. Inhaling CO will reduce the amount of oxygen in the blood because Hemoglobin (Hb) plays a role in transporting Oxygen from the lungs to the tissues, Hemoglobin has a higher affinity for CO, so instead of combining with Oxygen, Hemoglobin more combined with CO gas. Your heart has to work harder than usual to compensate for the reduced oxygen levels, leaving many dangerous complications over time. The nicotine in cigarette smoke is the main cause of many people becoming addicted to cigarettes. When entering the body, nicotine stimulates the production of adrenaline, causing manifestations such as heart palpitations, tachycardia, and elevated blood pressure. Therefore, smoking can cause hypertension in smokers.
Other rare but serious cardiovascular conditions that can be caused by smoking include:
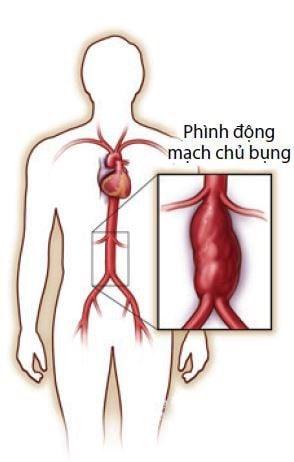
Peripheral artery disease (and peripheral vascular disease): A condition in which blood vessels are narrowed resulting in insufficient blood flow to the arms, legs, hands and feet, which can lead to amputation.. Smoking is the leading preventable cause of this condition. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: A bulge formed in the aorta, the main artery that distributes blood through the body, located in the abdomen. When an abdominal aortic aneurysm ruptures, it can lead to sudden death. Nearly all deaths from this condition are caused by smoking.
Although smoking is a direct cause of cardiovascular disease and death, you are still not a smoker at risk. People who don't smoke but are regularly exposed to secondhand smoke have a 25 to 30 percent higher risk of cardiovascular disease than those who aren't exposed. Secondhand smoke is just as harmful as the chemicals inhaled by smokers. Cigarette smoke weakens cells in the heart, lowers good cholesterol, and raises blood pressure levels beyond a safe threshold. Women, adolescents and children are the most vulnerable to secondhand smoke.
2. What should be done to protect heart health
The best way to protect your heart from smoking-related disease and death is to never start using tobacco, but if you are a smoker, the sooner you can quit, the better. . Quitting smoking benefits your heart now and in the future:Twenty minutes after you quit, your heart rate drops Just 12 hours after quitting smoking, blood carbon monoxide levels drops to normal levels, allowing more oxygen to reach vital organs like your heart. Within four years of quitting, your stroke risk drops to that of a lifetime non-smoker.

3. How to help quit smoking
Quitting smoking is not easy. Statistics show that 70% of smokers want to quit, but only 5% of them succeed. Here are some tips to help you quit smoking:Make a plan to quit smoking, choose a special day to start smoking cessation. Write down your reasons for quitting smoking. Read through the list each day, before and after quitting. Record when you smoke, why you smoke, and what you are doing when you smoke. This will help you understand what triggers you to smoke. Make a list of things you can do instead of smoking. Be ready to do something else when you want to smoke. Ask your doctor about taking medication or using nicotine gum or patches. When you want to smoke, take a deep breath. Hold it for up to 10 seconds and exhale slowly. Repeat several times until the urge to smoke passes. Quitting smoking can be difficult at first, and you may have cravings for cigarettes, be irritable, feel hungry, cough frequently, have headaches, or have trouble concentrating. These symptoms are caused by your body getting used to nicotine, the active drug in tobacco. These symptoms will not last long. They appear most when you first quit, but usually go away within 10 to 14 days.

Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to sources: fda.gov, webmd.com, Vietnam Society of Cardiology