This is an automatically translated article.
Most hemangiomas are easily seen at birth, but can be many months or years later. Hemangiomas can be found anywhere on the body, but are most common on the face, skin, head, chest, or back. Small hemangiomas with a diameter of <10cm are most commonly seen on the skin and in pediatric patients, congenital in children.
1. Hemangiomas progress through what stages?
Hemangioma progresses through 3 stages including:
Proliferative stage: Takes place from 3 to 6 months in case of superficial hemangioma and about 8 to 10 months for deep hemangioma. This is the stage when the hemangioma increases in size quite quickly, can double or triple. This stage needs to be closely monitored because it can cause a number of complications, even life-threatening and affect the patient's life. affect children's aesthetics. Stable phase: It can be from 18 to 20 months, the size of the hemangioma becomes more stable during this stage. Stage of hemangioma regress: The hemangioma becomes paler and collapses under the skin. This stage is usually recognized when the patient is about 6 years old.
Tăng sinh mạch máu
2. How to treat small hemangiomas in children?
Infantile hemangiomas usually do not require treatment, most will resolve on their own. However, in some cases, hemangiomas will have indications for treatment, including cases where hemangiomas interfere with body functions (obscuring vision, making it difficult to breathe), ulcers, bleeding. or infection. In addition, in cases where hemangiomas are likely to affect aesthetics, cause dilation or leave scars, surgery is required.
3. Surgery for small hemangiomas in children
For the treatment of hemangiomas, the surgical method for non-invasive hemangiomas is still the most effective method. Surgery aims to remove the hemangioma while minimizing damage to the adjacent anatomical areas. In addition, there are a number of other methods such as laser, sclerotherapy.
Surgery for hemangiomas in children under 1 year of age is a problem that is still poorly researched and published. This surgery can be judged as dangerous due to the existence of natural blood vessels at the site of injury. However, surgery in older children causes more problems because of the greater connection between connective tissues and blood vessels. Because it is difficult to distinguish between hemangiomas and normal cells, during surgery, more cells will have to be removed. Scarring is a common problem after hemangioma surgery. Early surgery when the hemangioma is small will leave a smaller scar. Delays in surgery for hemangiomas increase the risk of larger scars and more blood loss during surgery.
During the surgery, the patient will be anesthetized and the surgeon will perform surgical procedures to remove the tumor.
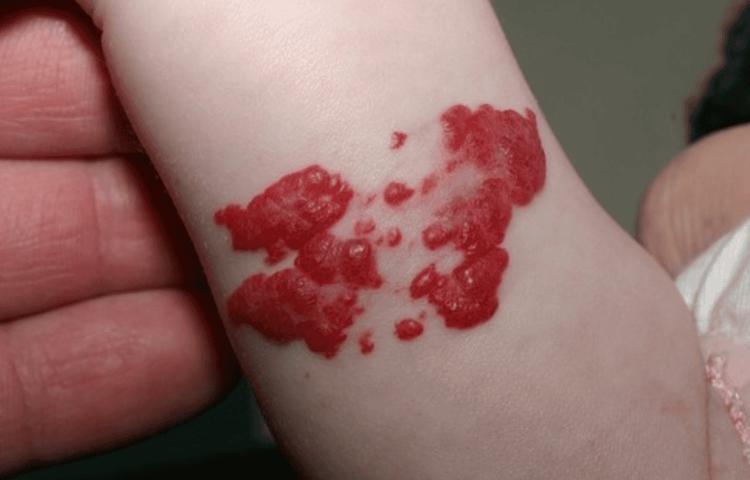
U máu nhỏ ở trẻ
4. Care after surgery
After surgery for hemangioma, the patient should be monitored for the index of red blood cells and hematocrit, to prevent postoperative bleeding complications. Antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent venous infections. Based on laboratory parameters, blood or blood substitutes may be used. After surgery, the patient should be mobilized early on the first day after surgery.
Surgery is one of the methods to completely solve for small diameter hemangiomas. For children whose family members or relatives have had a hemangioma, this is an option that should be considered. In addition, the doctor should advise the patient's family about the possibility of failure or possible complications after surgery. Currently, with the ease of finding information through internet access, it is necessary to directly exchange ideas with doctors about how to treat hemangiomas in children so that the patient's family can make appropriate choices about the treatment. The treatments.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
Recommended video:
Fetal screening - A healthy baby is born
MORE:
Benign and malignant liver tumors: What you need to know Treatment of hemangiomas in children Is there any effect on treating head hemangiomas for babies born prematurely at 5 months old?