This is an automatically translated article.
Hemangiomas are the most common benign tumors of the liver. 5-7% of healthy people may develop hemangiomas in the liver. The incidence of hemangiomas in the liver is 6 times more common in women than in men and is often larger in size than in men. The location of hemangiomas is usually in the right liver and in the subcapsular region. Hepatopancreatic hemangiomas are benign but can experience some dangerous complications, possibly death.
1. What is a hemangioma in the liver?
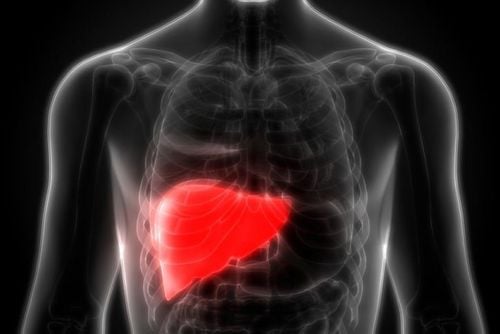
Hemangioma liver (English name hemangioma liver) is a noncancerous (benign) mass in the liver. A hepatic hemangioma is made up of a tangle of blood vessels. People with liver hemangiomas rarely experience signs and symptoms and usually do not need treatment. Most cases of liver hemangiomas are discovered incidentally through laboratory tests.
Hemangiomas can be single or multiple. Tumors are usually very small (no more than 5cm) and usually cause no symptoms. In some cases, the tumor can still grow larger. Large tumors will often cause symptoms such as abdominal pain or vomiting.
Intrahepatic hemangioma is a tangled network of blood vessels in or on the surface of the liver. This tumor is a benign tumor in the liver and there is no evidence that it will progress to cancer. An estimated 5-7% of healthy people may develop a hemangioma in the liver.
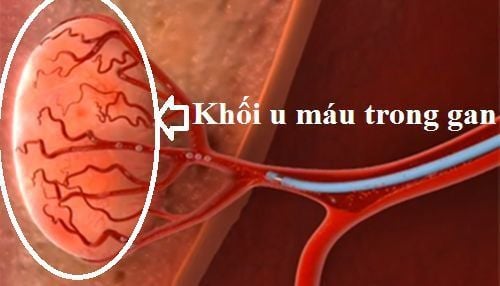
U máu trong gan là khối u lành tính hay gặp nhất của gan
2. Symptoms of hemangiomas in the liver
Hemangiomas in the liver have 2 types: capillary and cavernous. Most hemangiomas in the liver have no symptoms, but are discovered by accident in cases such as: physical examination, liver ultrasound or computed tomography. Hemangiomas can be single or multiple. The size of the tumor is sometimes less than 1cm, sometimes it can be more than 4cm, even giant. In rare cases, hemangiomas are large in size or located near the liver capsule causing compression or blood clots in the tumor causing the following symptoms: Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, feeling full after eating only a small amount of food or an enlarged liver. However, these symptoms are not specific and could be due to something else, even if you have a hemangioma.
Rarely, a hemangioma in the liver spontaneously ruptures, but often ruptures with a fall or trauma to the liver. However, if the hemangioma is large when it ruptures, it can also be life-threatening due to bleeding.
Trắc nghiệm: Làm thế nào để bảo vệ lá gan khỏe mạnh?
Làm test trắc nghiệm kiểm tra hiểu biết về gan có thể giúp bạn nhận thức rõ vai trò quan trọng của gan, từ đó có các biện pháp bảo vệ gan để phòng ngừa bệnh tật.3. Are liver hemangiomas dangerous?
Hemangiomas in the liver rarely cause complications. However, for pregnant women who are taking hormone therapy (including birth control pills) or have liver disease, there is a chance of developing the following complications:
Widespread hemangioma : The woman has been diagnosed Patients with liver hemangiomas face an increased risk of complications if they become pregnant. The female hormone estrogen, which increases during pregnancy, is thought to cause some liver hemangiomas to grow larger Liver damage Pain: A growing hemangioma can cause signs and symptoms that may require treatment, including pain in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, abdominal bloating or nausea

Khối u lớn thường sẽ gây ra các triệu chứng như đau ở góc phần tư phía trên bên phải của bụng
Having a liver hemangioma doesn't mean you can't get pregnant. However, discussing possible complications with your doctor can help you make a more informed choice.
Medications that affect hormone levels in your body, such as birth control pills, can cause complications if you are diagnosed with hemangiomas. These are controversial. If you are considering this medication, discuss the benefits and risks with your doctor.
Maintain healthy meals, quit smoking and limit alcohol use. Lifestyle changes can reduce your risk of other liver diseases.
4. Treatment
If a hemangioma in the liver is detected, the patient is often in a worried mood and seeks treatment. However, hemangiomas in the liver usually do not need treatment, this is a benign tumor, rarely causing malignancy.To date, there is no drug that works to lose or reduce the size of the tumor. Treatment only when the hemangioma grows rapidly or is very large, it can be treated to prevent hemangioma bursting causing life-threatening bleeding or large tumor causing pain due to compression, but this complication is very rare. Treatment methods can be surgical removal of a part of the liver with tumor or can embolize the artery feeding the mass such as burning, radiation therapy...

Thăm khám sớm nhất để được bác sĩ tư vấn về các phương pháp điều trị phù hợp
If your hemangioma is small and not causing any signs or symptoms, you will not need treatment. In most cases, a liver hemangioma will never develop and will never cause problems. Your doctor may schedule follow-up exams to check for liver hemangioma periodically for growth if the hemangioma is large.
Treatment for liver hemangioma depends on the location and size of the hemangioma, whether you have more than one hemangioma, your overall health, and your preferences.
Treatments may include:
Surgery to remove the liver tumor. If the hemangioma can easily separate from the liver, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the mass. Surgical removal of part of the liver, including hemangiomas. In some cases, the surgeon may need to remove part of your liver along with the hemangioma. Procedure to stop blood flow to the hemangioma. Without a blood supply, the hemangioma can stop growing or shrink. Two ways to stop blood flow are to tie up the main artery (hepatic artery ligation) or inject drugs into the artery to block it (arterial embolism). Healthy liver tissue is unharmed because it can draw blood from other nearby vessels. Liver transplant surgery. In the unlikely event that you have a large hemangioma or multiple hemangiomas that cannot be treated with other measures, your doctor may recommend surgically removing your liver and replacing it with a donor liver. Radiotherapy. Radiation therapy uses powerful beams of energy, such as X-rays, to damage the cells of the hemangioma. This treatment is rarely used because safer and more effective treatments are available.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: Mayoclinic.org