This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by CKI Doctor Nguyen Thi My Linh - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. Uncle has 12 years of experience in the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric diseases, especially neonatal resuscitation and neonatal treatment. In addition, the doctor has strengths in the field of breastfeeding counseling as well as examination, counseling and nutritional intervention in children.Young children's resistance is still weak, so they are susceptible to upper respiratory infections caused by external influences such as changes in weather, polluted living environment, etc. When sick, children often have mild fever and cough. , runny nose, fussiness and aborting. Parents need to monitor to detect and take their children to medical facilities for timely examination and treatment to prevent complications.
1. What is an upper respiratory infection?
The upper respiratory tract is the outermost organ exposed to the air. Therefore, this is the part that is easily affected by all adverse conditions from the outside environment such as dust, cold, heat, toxic vapors, viruses, bacteria, mold...Upper respiratory tract Measured from nose to larynx including nose, pharynx and larynx. When pathogens enter, the symptoms of a cold will appear, if not treated promptly, it can lead to rhinitis, pharyngitis, VA, tonsillitis, laryngitis, sinusitis, and laryngitis. otitis media ... These diseases are collectively known as upper respiratory tract infections.
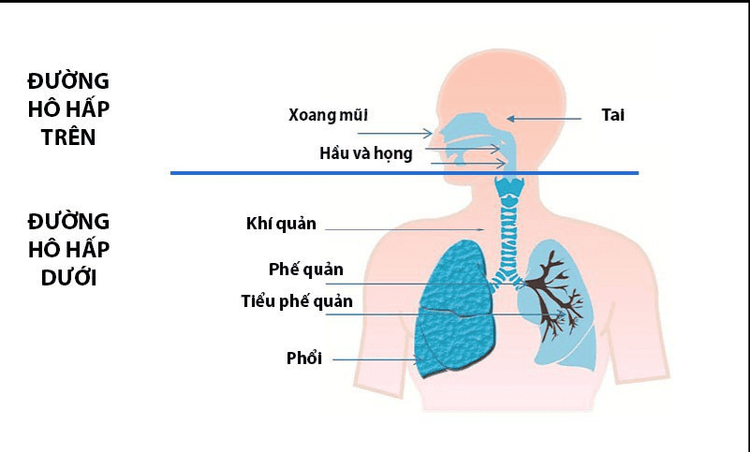
Đường hô hấp trên được tính từ mũi đến thanh quản bao gồm mũi, họng và thanh quản
>> See more: Upper respiratory tract infection in children and how to avoid illness in the cold season - Article written by Doctor Le Tuyet Nga - Specialist I - Pediatric Center - Vinmec International General Hospital Times City
2. Signs of an upper respiratory infection
Upper respiratory tract infections in infants and young children are common, easy to treat, but often recur with the following symptoms:For infants: The main symptom is mild fever (about 38.50C). , cough, runny or no runny nose, wheezing, fussy, crying... For older children: Common symptoms are runny or stuffy nose, runny nose, cough, sore throat, hoarseness, low-grade fever , fatigue, loss of appetite... Symptoms if not treated promptly can lead to pneumonia. Symptoms of pneumonia in infants are also very sketchy, some children have fever but some children do not have fever, even the body temperature drops, so many parents are subjective, when they come to the doctor, their child has pneumonia. When seeing signs of anorexia, weak suckling, fussiness, blue skin, irregular breathing, rising and falling nostrils, intercostal recess, the disease has turned severe.
Depending on the severity of the disease, the methods of care and treatment are different:
Mild: With symptoms of cough, low fever, runny nose (yes or no), it means only mild inflammation of the respiratory tract. On steaming, just let your baby sip a little honey (every 6 hours, half a teaspoon each) or sip kumquat juice with diameter (squeeze out the water from the kumquats, steam them with the inner diameter of the kumquat). 20 minutes, strain the water, occasionally let the baby sip). Moderate: With symptoms of cough, fever, rapid breathing (> 50 times / minute), it means that the baby has bronchitis or mild pneumonia. In this case, it is necessary for the baby to go to the medical station for medical examination and medication according to the doctor's instructions.
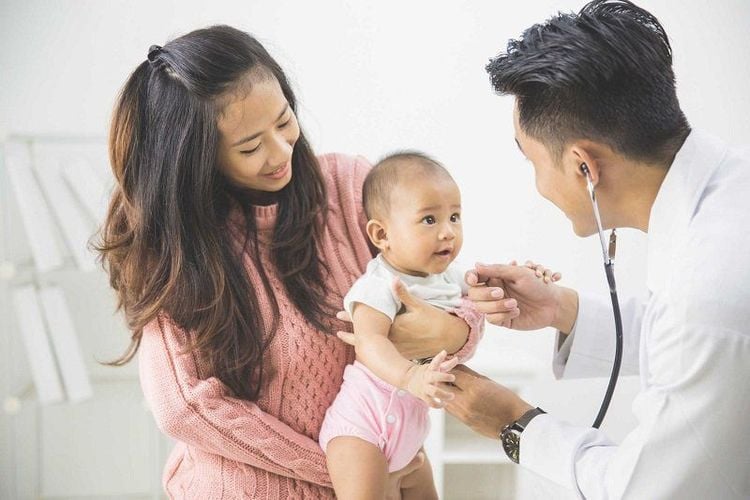

Bé bị viêm nhiễm đường hô hấp trên ở mức độ vừa mẹ cần cho bé đến trạm y tế khám bệnh và dùng thuốc theo chỉ dẫn của bác sĩ
3. What causes respiratory infections in young children?
Causes of respiratory infections are viruses and bacteria:Viruses: Rhino, Corona, Parainfluenza virus, Adeno, respiratory syncytial virus RSV... Bacteria: Group A hemolytic streptococcus, pneumococcal, Haemophilus Influenzae, .... Fungi: Rhizopus, Rhizomucor, Cunninghamella Factors that increase the risk of upper respiratory tract diseases, ie increase the opportunity for bacteria, viruses, fungi to enter Body conditions include:
Illnesses: Premature babies or caesarean sections, rickets, malnutrition, vitamin A deficiency, immunocompromised children due to HIV disease, prolonged corticosteroid therapy... Health The body's resistance: The younger the child, the more susceptible to disease, especially under 1 year old. Especially in the first 2 months postpartum. Habitat: Housing conditions are narrow, humid, exposed to smoke (stove, tobacco, charcoal honeycomb), poor hygiene. Babies lying in air-conditioned rooms with low temperatures are prone to dry nose and throat leading to inflammation. The disease often occurs during the cold weather season, especially during the winter-spring transition, so not wearing warm enough clothes, taking cold showers, not drying the body all increase the risk of getting sick.

Bệnh viêm đường hô hấp ở trẻ nhỏ thường gặp, dễ điều trị nhưng lại hay tái phát
4. How to prevent upper respiratory infections
Parents need to take the following supportive measures to help their child recover quickly and prevent the risk of recurrence:Room arrangement : The child's room needs to be cleaned and tidy. Note when using the air conditioner: Adjust the temperature to about 25 - 26 degrees Celsius and remember to turn off the air conditioner 30 minutes before the baby leaves the room so that the baby's body does not experience a sudden temperature difference. One way to check if the room temperature is right for your baby is to feel the back of his neck and back. If the baby is not sweating and sleeping well, the room temperature is appropriate. Nutrition: Mothers need to provide adequate nutrition for their children by feeding them enough meals during the day, supplementing with foods that help strengthen vitamins, DHA, and are easy to digest. If the baby has entered the weaning stage, the mother should balance the menu to ensure adequate nutrients. Care of the nose: Mother should clean the nose to help clear the baby's airway with products derived from deep sea water. Mothers should not use oral liquids such as garlic and onion juice to drop into the child's nose because it can cause burns to the nasal mucosa, making respiratory infections worse. To prevent diseases of the upper respiratory tract in children, parents should pay attention to a diet to improve the child's resistance. At the same time, add supporting foods containing lysine, essential micro-minerals and vitamins such as zinc, chromium, selenium, B vitamins,... snacks and less digestive problems.
Parents can learn more:
Why do you need to supplement Lysine for your baby?
The role of zinc - Guidelines for reasonable zinc supplementation
Please visit the website Vinmec.com regularly and update useful information to take care of your baby and family.