This is an automatically translated article.
Although the cause of upper respiratory tract infection is mainly a virus, in some cases doctors still prescribe the patient to use antibiotics for upper respiratory infections. So, in what cases do you need antibiotics to treat upper respiratory infections?
1. Common cold
The common cold is an inflammatory disease of the upper respiratory tract with mild severity, a self-limited illness with symptoms of runny nose, sore throat, cough, sneezing and stuffy nose. Between 1991 and 1999, overall antibiotic use for upper respiratory tract infections (Upper respiratory tract infections and URTs for short) declined in the United States. However, the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics increased. One study reviewed randomized controlled clinical studies from 1966 to 2009 that compared antibiotic treatment with placebo in people with acute URI symptoms lasting less than seven days for a period of less than 10 days. . The authors did not find sufficient evidence to recommend antibiotics for the treatment of purulent or non-purulent rhinitis in children or adults.
2. Flu
Influenza is an acute URI caused by influenza A or B viruses, which occurs in all ages, but children have the highest incidence. Adults over 65 years of age and children under two years of age have the highest rates of death from influenza. Accordingly, the flu vaccine is the most effective way to prevent influenza. Supportive care is the cornerstone of treatment, but antiviral therapies such as the neuraminidase inhibitors oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza) can reduce the duration of illness if started within 48 hours of treatment. from the onset of the first symptoms. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (U.S. CDC) does not recommend the use of amantadine in the treatment of influenza.
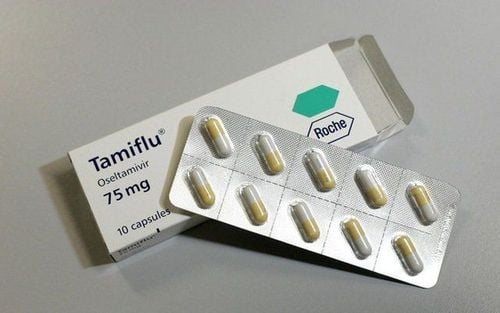
Thuốc ức chế neuraminidase oseltamivir (Tamiflu)
For severe cases, people over 65 years of age or younger than two years, pregnant women and people with chronic illnesses should be treated with antiviral drugs. Empiric antibiotic therapy should not be continued after influenza diagnosis, unless secondary upper respiratory tract infection is present. Gram stain and culture of body fluids can be used to determine whether antibiotics should be added to the regimen along with antivirals.
>> See more: Upper respiratory tract infection in children and how to avoid illness in the cold season - Article written by Doctor Le Tuyet Nga - Specialist I - Pediatric Center - Vinmec International General Hospital Times City
3. Acute sinusitis
Acute sinusitis is a common condition and is treated as an outpatient with an annual incidence of about 13% in adults. In this pathology, inflammation takes place in the lining of the nose and sinuses with symptoms including nasal congestion, anterior or posterior rhinorrhea, facial pain, decreased sense of smell, and cough. Acute sinusitis is classified as acute when the above symptoms appear for less than 4 weeks, subacute from 4 to 12 weeks, and chronic for more than 12 weeks.
Mild cases of acute bacterial sinusitis may not require immediate medication and only observation. If symptoms worsen within seven days, the doctor will begin to prescribe antibiotics for these patients. Antibiotic therapy is acceptable in patients with severe or complicated acute bacterial sinusitis.
4. Acute otitis media
Diagnosis of acute otitis media is only diagnosed when the patient has acute symptoms and middle ear effusion. The most common causes of otitis media are H. influenzae, S. pneumoniae and M. catarrhalis. In addition, the virus has also been found in respiratory secretions of patients with acute otitis media and may be the cause of antibiotic failures. Group B Streptococcus, gram-negative enterococci, and Chlamydia trachomatis are the major causes of middle ear disease in infants younger than eight weeks of age.
Thuốc kháng sinh Amoxicillin
Regarding the treatment regimen, antibiotics should be started immediately in children under two years of age with acute bilateral otitis media and children with acute otitis media with fluid leakage through the ear canal. Amoxicillin (80 to 90 mg per kg/day in two divided doses) is recommended as first-line treatment for acute otitis media.
If there is no response to initial antibiotic therapy within 48 to 72 hours, the patient should be reviewed to confirm the diagnosis and amoxicillin/clavulanate (Augmentin) should be started.
Children with acute otitis media should be followed up in three months for evaluation. Prolonged antibiotic therapy has been shown to reduce the number of recurrent otitis media, but is not recommended due to the risk of antibiotic resistance.
5. Pharyngitis and tonsillitis
About 90% of adults and 70% of children with sore throats have a viral infection. In people with bacterial pharyngitis, the leading cause is group A hemolytic streptococcus. Appropriate antibiotic treatment in these cases has been shown to reduce the risk of rheumatic fever. , relieves symptoms of the disease, but antibiotic treatment does not prevent nephritis.
Currently, there are many treatment methods for upper respiratory tract infections, but the disease is mainly caused by viruses, so all methods are symptomatic treatments without treating the specific cause. .

Trước khi sử dụng thuốc, người bệnh nên tham khảo Dược sĩ về cách dùng thuốc an toàn hiệu quả
Some commonly used upper respiratory tract infections are: analgesics, antipyretics, anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent high fever and convulsions caused by high fever. However, the use of antibiotics for upper respiratory infections requires advice from qualified doctors, patients should not arbitrarily buy drugs for use and treatment at home.
Periodic health check-ups help detect diseases early, thereby planning treatment for optimal results. Currently, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital has general health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy, including:
Health checkup package diamond general health checkup package Vip general health checkup special health checkup package Comprehensive general health checkup package standard general health checkup The patient's examination results will be returned to your home. After receiving the results of the general health examination, if you detect diseases that require intensive examination and treatment, you can use services from other specialties right at the Hospital with quality treatment and services. outstanding customer service.
To register for medical examination and treatment at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital, you can contact Hotline: 0898 563 189 or register online HERE.
References: emedicine.medscape.com, aafp.org, drugs.com