This is an automatically translated article.
Late-stage bladder cancer often presents very complex symptoms. At this point, the cancer cells are no longer confined to the bladder, but have metastasized to the lymph nodes, affecting nearby organs such as the cervix, vagina, prostate, pelvic wall,... and metastasis to distant organs such as lungs, bones, liver.1. What is bladder cancer?
The bladder is a hollow organ located in the lower abdomen, whose main function is to store urine from the kidneys.Bladder cancer usually starts from the cells lining the inside of the bladder, the size of the tumor will be large or small depending on the stage of bladder cancer.
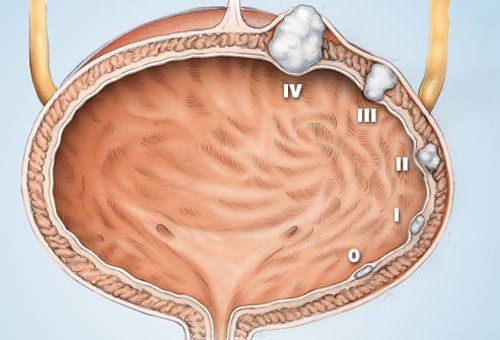
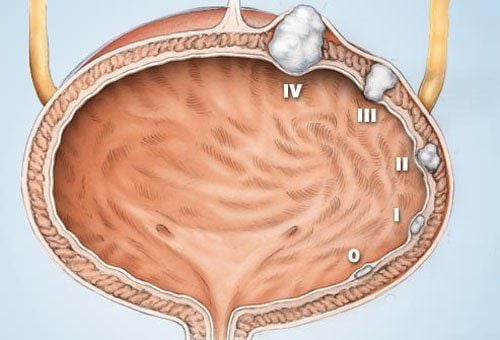
Bladder cancer includes stages:
Stage 0: Cancer cells occur only on the surface of the bladder wall with a very small size; Stage I: Cancer at this stage occurs in the inner lining of the bladder, but has not invaded the muscular layer of the bladder wall; Stage II: Cancer has invaded the bladder wall, but is still limited to the bladder; Stage III: Cancer cells have spread through the bladder wall to invade surrounding tissue. They can spread to the prostate gland in men or the uterus or vagina in women; Stage IV: Also called late-stage bladder cancer, at this stage, cancer cells have spread to the lymph nodes, or metastasized to other organs, such as the lungs, bones, or liver. Most bladder cancers are diagnosed at an early stage when it is still treatable. For patients with advanced bladder cancer, survival is only about 15%.
Ung thư bàng quang
2. Manifestations of late-stage bladder cancer
Symptoms of late-stage bladder cancer include:Blood in the urine: In the early stages, only a little blood appears in the urine, causing the urine to be pink or dark yellow. no abnormal color, only detect blood when doing the test. But in the final stage, the urine is bright red blood. There are cases where there are no symptoms until blood in the urine, when going to the doctor, the disease is found to be in a severe stage; Frequent urination several times a day; Difficulty urinating, painful urination, there are cases of patients with urinary retention: In the final stage, bladder cancer patients often experience extremely uncomfortable problems in urination. Bladder strain, urge to urinate but cannot go, causing discomfort and pain. In addition, the patient has no control over his bladder (urinary disorder); Abdominal pain and bloating, unusual skin rash: These are signs of a tumor that has spread to the liver. When the tumors in the liver are large, pressing on other parts, causing pain, abdominal distension and stiffness, skin rash, jaundice, yellow eyes; Chest tightness, pain spreading deep in the ribs, difficulty breathing: When cancer metastasizes to the lungs, patients often have chest tightness and difficulty breathing. To control the feeling of shortness of breath, the patient should keep a calm mind, regulate breathing; relatives need to talk and reassure the patient; Bone metastases: Pain in bones and joints, spine pain, weak bones, easy to break; Back pain and pain in the pelvis; Other manifestations such as fatigue, loss of appetite, rapid weight loss, blue skin, cold limbs, panic, loss of consciousness
3. Treatment of late-stage bladder cancer
Treatment of late-stage bladder cancer is difficult and complex. The main goal of treatment for cancer patients at this stage is to treat the symptoms of the disease, control to prevent the cancer from spreading further, and to increase the survival prognosis for the patient.Systemic chemotherapy, symptomatic treatment (anti-pain, anti-urinary tract obstruction) is common for cancer patients at this stage.
Treatments for late stage bladder cancer include:
3.1 Chemotherapy This is one of the treatments for the disease that involves chemotherapy. Doctors will prescribe this method first for patients if the cancer has spread to distant areas of the body.
The drugs used are usually prepared in the form of liquids, tablets, oral cystitis or intravenous drugs. When entering the bloodstream, the drug targets cancer cells, weakening and destroying them.
Hóa trị điều trị ung thư bàng quang giai đoạn cuối
Classical chemotherapy This is a traditional method of chemotherapy that uses drugs that are toxic to cancer cells to inhibit the growth and division of cancer cells. they.
Two common traditional chemotherapy regimens for bladder cancer include:
Gemcitabine (Gemzar) and cisplatin; Methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin (Adriamycin), and cisplatin. Classical chemotherapy can also kill healthy cells in hair follicles, cells in bone marrow, and cells lining the digestive tract. This leaves the patient facing a number of complications such as: hair loss, reduced blood cell production, immune system suppression, constipation, diarrhea, loss of appetite...
Targeted Therapy This medicine can help the immune system destroy proteins or enzymes made by cancer cells to stop growth or reduce the chance of spreading. Because the drug targets cancer cells, patients will experience fewer side effects than with classical chemotherapy.
3.2 Radiation Therapy Radiation therapy is the use of high-energy X-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells and stop them from growing.
Radiation will be focused on the cancerous area. It penetrates the body and destroys the DNA of tumor cells, preventing them from multiplying.
Chemotherapy is most useful when the cancer is in a small area. Therefore, radiation therapy is usually only used for people with advanced bladder cancer to shrink the tumor before they receive chemotherapy.
Side effects of radiation therapy include: dry skin, peeling, nausea, abdominal pain...
3.3 Surgery In most cases, surgical treatment for late-stage bladder cancer will not cure it. cure cancer or improve a patient's life expectancy. However, this method can help relieve symptoms and slow the spread of cancer. Lymph nodes that have been invaded by cancer cells can also be removed surgically.
When treating invasive bladder cancer with surgery, a patient may have to remove part or all of the bladder. This surgery is called a cystectomy.
In case the bladder must be completely removed, the doctor will make a small hole in the abdominal wall and attach the ureter with a plastic bag to excrete urine.
Depending on how advanced the cancer is, parts of nearby organs or tissues may also need to be removed. It is important that patients talk to their doctor about the benefits and risks of surgery.
Potential complications of surgery include:
Urinating more often due to a shrinking bladder; Infertility; Early menopause and sexual dysfunction in women; Decreased sexual ability in men.
4. Palliative care for people with advanced bladder cancer

Nên tập thể dục nhẹ nhàng hàng ngày
Ideally, palliative care should be started as soon as cancer is diagnosed and treated. Some of the following solutions can help patients control symptoms well and limit side effects of treatment:
Building a scientific diet Chemotherapy can cause weight loss and make patients tired and lose weight. feeling tasty. Eating several meals a day with less food can help maintain energy in the body.
People with stage 4 bladder cancer should eat cereals, fruits, vegetables, fish. Cut down on sugar and foods high in saturated fat such as sausages, chocolate, whole milk, butter, beef...
Gentle exercise Walk, swim, do yoga, do nourishing exercise. .. can help improve fitness, reduce fatigue, stress. These exercises are safe for most people with bladder cancer, but before doing so patients should consult a doctor for an appropriate exercise regimen.
Use of pain relievers Pain relief is an important part of the treatment and palliative care plan for someone with end-stage bladder cancer. Each patient will have a different level of pain. Please describe exactly to the doctor what the patient is going through so that he can prescribe the most effective pain reliever.
During treatment, people with late-stage bladder cancer need to follow the doctor's instructions and have regular check-ups according to the scheduled appointment. This will help patients have a better quality of life and increase life expectancy.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.