This is an automatically translated article.
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a chronic, progressive autoimmune disease. The mechanism of disease is when the immune system attacks healthy tissues in the body, causing damage to the skin, kidneys, heart, lungs, nerves or blood cells.
The diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus will require tests that detect and quantify autologous antibodies circulating in the blood.
1. An overview of antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus
Antibodies form in the body as a response to infection. When something foreign enters the body, called an antigen, white blood cells called B lymphocytes respond by making special proteins called antibodies. Antibodies are the immune system's way of remembering an antigen; If they enter the body again, the antibodies will recognize, combine, and quickly neutralize, helping to prevent the body from getting an infection. However, with autoimmune diseases like lupus, the immune system can make antibodies on its own, which attack normal cells in the body as antigens, causing damage. injury and even irreversible destruction.
Accordingly, an antibody test is a set of blood tests that check for the presence and quantification of specific circulating levels of antibodies, thereby helping to clarify the diagnosis of lupus.
Autoantibodies in this disease include:
Antinuclear antibody (ANA) Anti-dsDNA Anti Smith (Sm) Anti-U1RNP Anti-SS-A (also known as Ro) Anti-SS-B (also known as Ro) is La). These antibody tests are usually positive when the patient has lupus. As such, these are tools that can aid in the diagnosis if the clinical criteria are not clear or if the ANA test is negative but still cannot rule out lupus.
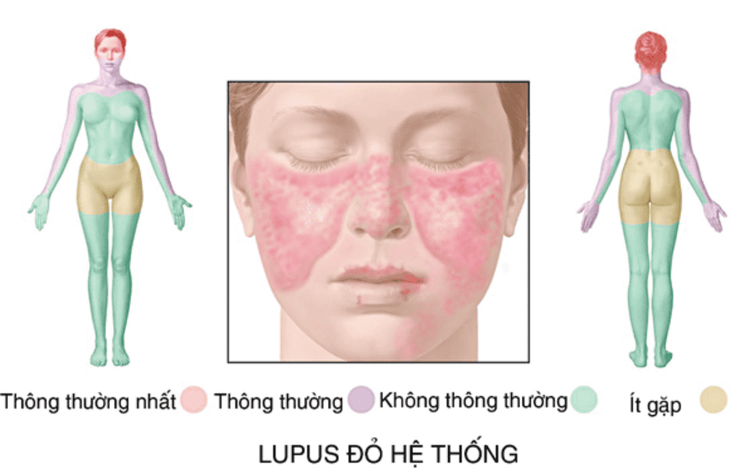
Bệnh Lupus ban đỏ hệ thống cần được phát hiện và điều trị sớm trước khi bệnh gây biến chứng
2. Antinuclear antibody (ANA) test
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) are autoantibodies to the nuclei of cells in the body.A series of pathogenesis statistics show that up to 98% of people with systemic lupus have a positive ANA test for antinuclear antibodies. Therefore, ANA becomes the most sensitive diagnostic test for lupus erythematosus to detect this pathology.
The mechanism by which the test for antinuclear antibodies is performed is an immunofluorescence assay. In this lupus erythematosus test, a blood sample is drawn from a vein and sent to a laboratory. Serum extracted from the patient is then added to the “primer” cells (usually liver or kidney cell lines or from living human tissues) and examined under a microscope. If the patient has antinuclear antibodies, the serum will show complexes that bind to the added cells. In the next step, a second antibody labeled with a fluorescent dye is added to bind to the antibodies in the serum once they have bound. Finally, the blood slide will be viewed with a fluorescence microscope, and based on the staining intensity and binding complex recorded at different dilutions, the concentration of antinuclear antibodies will be quantified.
Usually, the ANA test is only done for the first time when a diagnosis is needed. Thereafter, re-quantification of both ANAs is not necessary, as they may increase and decrease over the course of the disease, these fluctuations not necessarily correlating with the level of disease activity.
In addition, it is important to note that although 98% of people with lupus will be ANA positive, ANA is also present in 5 to 10% of perfectly healthy individuals as well as those with have other connective tissue diseases, such as scleroderma and rheumatoid arthritis. Furthermore, about 20% of healthy women will have a weakly positive ANA, or low concentration, and the majority of these women will never show any signs of lupus. Therefore, a positive ANA test is not sufficient to diagnose lupus but depends on clinical criteria as well as the presence of other autoantibodies.
Xét nghiệm kháng thể kháng nhân (ANA) giúp chẩn đoán bệnh Lupus ban đỏ hệ thống
3. Anti-DNA antibodies (anti-dsDNA)
Anti-DNA (Anti-dsDNA) antibody is an antibody found in about 30% of people with systemic lupus. Since less than 1% of healthy people have this antibody, it is also a useful test in confirming a diagnosis of lupus. However, the absence of anti-dsDNA does not rule out a diagnosis of lupus.
The principle of qualitative testing and measurement of anti-DNA antibodies in laboratories is enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), immunofluorescence assay and radioimmunoassay .
In clinical practice, the presence of anti-DNA antibodies often suggests that lupus is in an advanced stage, with complications such as lupus nephritis. The mechanism is that when lupus is in the active stage, especially with damage to the kidneys, there is usually a high level of anti-DNA antibodies. Even so, the anti-dsDNA test cannot be used to monitor lupus activity because the antibody can still be present in the blood without any signs of active lupus.
4. Anti-Smith (anti-Sm) antibodies
Anti-Sm antibodies are ribonucleoprotein-binding antibodies found in the nucleus of cells. This is a fairly sensitive test that is also found almost exclusively in people with lupus. Although the rate of positive tests is only 20% among people with the disease and fluctuates between different ethnic groups, anti-Sm is rarely found in people with other autoimmune conditions. At the same time, the detection rate of anti-Sm in healthy individuals is less than 1%.
It is for these reasons that the detection and quantification of anti-Sm is useful in confirming the diagnosis of systemic lupus. In addition, unlike anti-dsDNA, anti-Sm does not correlate with the presence of the kidney-damaging form of lupus. Studies have been performed to test the hypothesis whether anti-Sm correlates with exacerbations of active lupus and the evidence that has been collected does not suggest such an association.
Hình ảnh Kháng thể anti-Smith
5. Anti-U1RNP (anti-U1RNP) antibodies
Anti-U1RNP antibodies are often found in association with anti-Sm antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. The prevalence of anti-U1RNP antibodies in these individuals is about 25%, while less than 1% of healthy individuals test positive for this antibody.
However, unlike anti-dsDNA and anti-Sm, anti-U1RNP showed somewhat more limited specificity for lupus. They can still be found in other rheumatic diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, Sjogren's syndrome, and polymyositis.
6. Anti-Ro/SSA and La/SSB antibodies (anti-Ro/SSA and anti-La/SSB)
Antibodies to Ro/SSA and La/SSB are antibodies found mainly in people with systemic lupus at an incidence of 30 to 40%. What's more, they are also commonly found in people with lupus despite having tested negative for ANA before.
However, Anti-Ro and anti-La can also be found in other autoimmune diseases, such as scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis and polymyositis; It is also present in low concentrations in about 15% of healthy individuals. Although these antibodies are not highly specific for lupus, they still have a certain diagnostic value when the patient has signs such as sensitivity to the sun, erythema on the skin, lesions. renal failure, anemia of unknown cause.
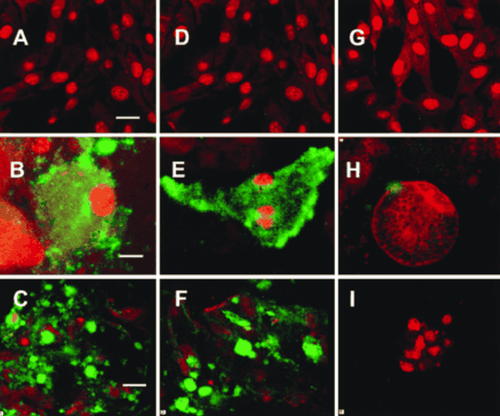
Hình ảnh nhuộm soi cấu trúc liên kết tế bào của SSA / Ro và SSB / La trong tế bào cơ tim
As soon as you have symptoms that suggest systemic lupus erythematosus, you need to see a doctor and get tested for antibodies in this disease. The information above will help you understand your results. Since then, even though it can't be completely cured, the adherence to treatment between doctors and patients also becomes better, helping to control symptoms and prevent acute attacks more effectively.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: hopkinslupus.org, cigna.com