This is an automatically translated article.
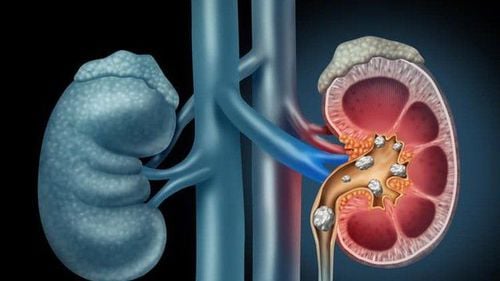
Shock wave therapy for kidney and urinary stones is a leading means of urolithiasis and is rapidly being replaced by open surgery in the treatment of ureteral stones.
1. Treatment of kidney stones with shock waves
Shock wave is similar to sound wave, is a type of mechanical wave that usually occurs in elastic medium such as liquid, gas. Shock wave treatment for urinary kidney stones is increasingly being used and is gradually replacing open surgery.
Principle of shock wave lithotripsy:
Shock wave generator Focus wave focusing device Stone locating system The medium of wave transmission Shock wave is a short wavelength negative pressure wave in nature 10 microseconds, with a maximum pressure of up to 100 megapascals
Stone locating system by ultrasound and fluoroscopy or a combination of both Shock wave generators include 3 types including: piezoelectric, hydroelectric force and electromagnetic fields. The successful prognosis of shock wave lithotripsy depends on the size of the stone, the location of the stone, and the chemical composition of the stone. In addition, for obese people with BMI >30, the distance from the skin surface to the stone will be greater. Therefore, the probability of failure of shock wave therapy will be high. Anatomical abnormalities in the urinary system have low stone clearance rates and are more likely to recur.
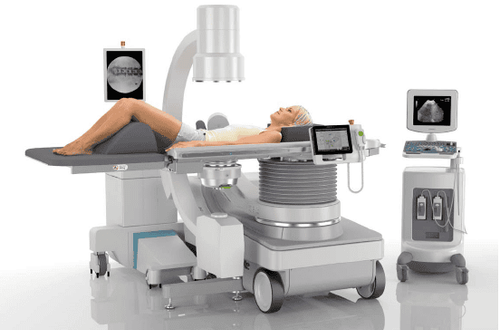
Tán sỏi bằng sóng xung kích là phương pháp hiện đại và hiệu quả
2. When is shock wave indicated for urolithiasis?
Treatment of kidney stones with shock waves is not only based on the treatment guidelines of the Urology Association but may also depend on the patient's choice of treatment method, the hospital's conditions and equipment, Treatment costs and experience of the surgical hospital
2.1 Indications for shock wave therapy Some cases can be treated with shock waves in urological diseases:
Kidney stones: For cases stones larger than 6-7 mm, should actively intervene with shock waves. However, the indication for intervention should be considered if the patient has symptoms. Shock wave is also indicated for the treatment of kidney stones, not uric acid stones, less than 20mm in size not located in the lower calyx and the kidney has an abnormal anatomical structure. Ureteral stones: Shock waves are indicated for upper ureteroscopy <10mm in size. For lower ureteral stones <10mm in size, shock wave therapy is not effective by endoscopic lithotripsy. Some other indications for treatment: Shock waves are indicated for the treatment of residual stones after percutaneous stone removal, stones stuck on the ureteral catheter for a long time. 2.2 Contraindications Absolute contraindications for cases such as: Pregnant women due to shock waves have the risk of harming the fetus. However, the shock wave did not affect the fertility of male and female patients.

Phụ nữ mang thai không tiến hành tán sỏi bằng sóng xung kích
Relative contraindications for cases such as:
Coagulation disorders: Shock wave lithotripsy but the patient is at risk of subcapsular hematoma or hematoma in the renal parenchyma. There is a risk of prolonged hematuria after lithotripsy even gross hematuria causing ureteral obstruction. Adjust coagulation function 12-48 hours before initiating shock wave therapy, and closely monitor bleeding for 24 hours after lithotripsy If the patient is taking antiplatelet drugs, it is imperative to take Use the drug 1 week before shock wave treatment. Patients with acute urinary tract infections should not be treated with shock waves to avoid spreading bacteria and toxins into the blood and body tissues. Aortic and renal artery aneurysms. Obstruction of the urinary tract below the stone site such as: renal pelvis stenosis, ureteral pyelonephritis, urethral stricture, ureteral stenosis, calyces diverticulum, prostatic hypertrophy,... natural movement of stone debris in the urine stream. Patients with musculoskeletal deformities, do not have a favorable lying position when lithotripsy Obese patients, the distance from the skin to the stone site exceeds the effective penetration of the shock wave

Bệnh nhân béo phì làm giảm độ hiệu quả của sóng xung kích
3. Complications of shock wave lithotripsy
Major complications of shock wave lithotripsy related to debris and urinary infection include:
Small pieces of gravel <5mm have the ability to pass out on their own with the flow of urine. high and there is a risk of prolonged urinary tract infection, renal colic, and the stone will grow larger again. During extracorporeal lithotripsy, bacteria and endotoxins in the urine can spread into the bloodstream, especially when there is tissue and vascular damage as a result of the shock wave. In conclusion, shock wave treatment for kidney stones is gradually being replaced by open surgical treatment. However, it can then cause some complications, so after lithotripsy the patient should be monitored, when there are any abnormal signs, it is necessary to notify the doctor immediately for timely intervention. time.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in neurological examination and treatment, patients can completely peace of mind for examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.