This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Hung - Endocrinologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital. The doctor has 36 years of working experience.If kidney stone disease is not detected and treated early, it can lead to many serious complications such as infection, urinary retention, pyelonephritis, even loss of kidney function or atrophic pyelonephritis. So how to accurately detect kidney stones?
Kidney stone disease often has clinical manifestations to recognize such as back pain, pain in the lower ribs, pain when urinating, patients may have urinary incontinence, urinary incontinence, even blood in urine,... However These symptoms can also be seen in other diseases. Therefore, it is not possible to rely only on clinical symptoms to diagnose kidney stone disease, but it is necessary to conduct examination and do paraclinical tests for kidney stones to detect kidney stones.
The following are the laboratory methods used when examining kidney stones to check for stones:
1. X-ray method
1.1 Unprepared nephrography:
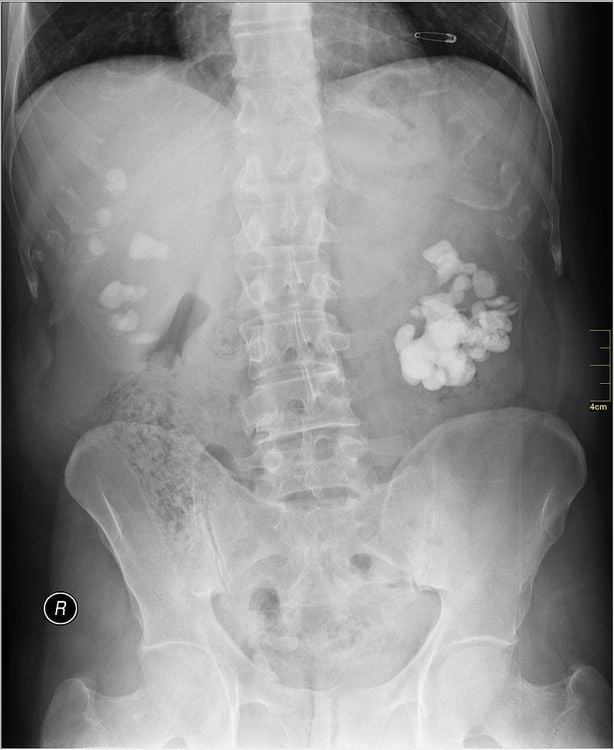
An unprepared nephrogram, also known as a nephrogram, is an X-ray of the kidney without the use of contrast. This laboratory method will be indicated by the doctor when suspected that the patient has kidney stones.On the acquired image, we can see that the contrast-enhanced kidney stone is a contrast-enhanced image located in the renal fossa. Doctors can definitely diagnose kidney stones when they see special contrast images like corals, parrot beaks.
However, this method cannot detect non-contrast stones.
1.2 Method of intravenous drug nephrography UIV
This is an X-ray of the kidneys using intravenous contrast. With this method, the doctor can locate the contrast stone, detect even the non-contrast stones. At the same time, the method also helps to evaluate the excretory function of the kidneys, the changes in the shape of the renal pelvis and the state of the urinary tract. Specifically, this method allows to clarify the following contents:1.2.1 Identify kidney stones With contrast stones:
Because the stone is submerged in the contrast agent, it is difficult to see, so it is necessary to taken early when the amount of drug is still thin or late, when the contrast has been pushed down the bladder with standing position. If the image is taken in the Abreu position, it is also possible to determine which kidney stone is located in which calyx, anterior or posterior calyx. With small stones located in small calyces, it is easy to be confused with contrast-enhanced urine, sometimes indistinguishable. In addition to locating stones, this imaging method allows determining the number, shape and size of stones. Because with stones with a surrounding border without contrast, the kidney radiograph often cannot determine the exact size of the stone. This method can even show the movement of stones in the dilated renal calyces. With non-contrast stones: In the acquired image, a void is seen with a round or oval shape or a polygonal shape, smooth border lying on the contrast background of the renal pelvis. The stone may be slightly mobile while in the renal pelvis. However, the image of that defect may not be a kidney stone but an image of air in the abdomen, computed tomography will help differentiate in this case.
1.2.2 Evaluation of the influence of kidney stones on renal parenchyma and excretory tract Kidney stones affect renal parenchyma and excretory tract. These effects may not be proportional to the size of the stone, but depend on the degree of obstruction caused by the stone. On film, the obstruction is shown by the dilated urinary tract above the stone. With simple urinary tract infections, there are often no typical manifestations on UIV nephrographs. In severe infections, the renal pelvis mucosa will be thickened or granular. Obstruction and infection will lead to consequences that are urinary retention, pus-filled kidneys, or retrograde nephritis. This long-term condition will cause deterioration of the renal parenchyma and eventually the kidney will lose its function completely. 1.2.3 Find the cause of stones on the urinary tract Kidney stones, urinary tract stones can form primary, it can also be secondary due to other damage to the kidney, urinary tract. On nephrography, intravenous drug UIV can detect the following causes:
The first cause of stone formation in the urinary tract is obstruction. UIV nephrography can detect various obstructions in the urinary tract such as narrowing of the pyelonephritis - ureteral junction,... Bacterial infection is the second cause of kidney stone formation. Renal tuberculosis combined with kidney stones is not a rare phenomenon, so it is necessary to pay attention to check for TB lesions. Renal papillary necrosis will create necrotic plaques, which is the basis for minerals in the urine to be deposited and attached to form kidney stones with a special image of a ring-shaped, bright lumen.
2. Computerized tomography (CT) method to diagnose kidney stones
3. Ultrasound method
On the ultrasound image, the doctor can identify:Image and size of echogenic stones in the kidney, ureter, if any. Determine kidney size. Determine the dilatation of the renal calyces. Determine the thickness of the renal parenchyma. Above are the paraclinical methods to help detect kidney stones. Doctors may choose one or more methods for each patient when kidney stones are suspected.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.