This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Dao Kim Phuong - Department of Examination - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital
Currently, the indications for treatment with OTSC are mainly primary bleeding or bleeding during interventional procedures, gastrointestinal perforation clamping, gastrointestinal fistula. The advantage of this system is that it can be used as soon as the lesion is visible, simple, easy to use, very firm tissue closure, high success rate.
1. Clip OTSC in gastrointestinal tract disease
Fistula is an abnormal connection between two epithelial surfaces. Epithelial surfaces are present in hollow structures (such as blood vessels and organs) and include skin surfaces. Gastrointestinal fistulas are connections from the intestine to other nearby organs, other parts of the intestine, or external skin surfaces. Gastrointestinal fistulas often develop secondary to trauma, infection, surgical procedure, or some underlying inflammatory disease process. Gastrointestinal fistulas can cause pus and digestive juices to leak to the outside of the body or to connected organs through small sinuses. This can lead to infections and other complications. Gastrointestinal fistulas often require surgical treatment in conjunction with antibiotic therapy.
Weaknesses with a prognosis that the fistula can heal spontaneously: the fistula site in the esophagus, duodenal apex, biliary tract, jejunum, with good nutrition, small fistula, no complications surrounding abscess.. .will be a favorable factor for the path to heal naturally.
If active medical treatment, the fistula does not heal spontaneously, surgery is required. Depending on the type of probe, there is an appropriate surgical method.
With the basic principle of gastrointestinal tract treatment is to close the fistula, close the fistula, since flexible endoscopy, people have tried to use the endoclip to close the fistula. However, this method has a low success rate, especially in the case of difficult-to-reach fistula, large-diameter fistula...
Today, with the advancement of flexible gastrointestinal endoscopy, has successfully contributed to the treatment of gastrointestinal fistula. One of the techniques used to treat gastroenteritis is the Over-the-scope clip (OTSC).
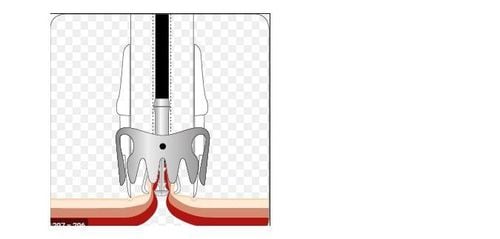
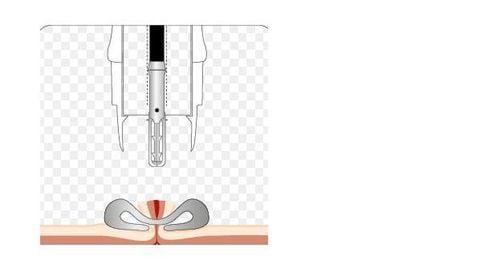
Over-the-scope clip (OTSC) is a new type of clip that is very useful not only in suturing perforations and fistulas but also in endoscopic hemostasis. The advantage of the over-the-scope clip (OTSC) is that the operation is simple and quick, like ligation of the esophageal varices, and the clip adheres very tightly to the wall of the gastrointestinal tract... This instrument includes 1 stick. sickle for tissue pulling, 1 ligation kit (similar to esophageal sphincter set), 'crocodile teeth'-like attachments for tissue closure, 2 types of clamps with different diameters for use in upper and lower gastrointestinal tract or with fistulas of different sizes
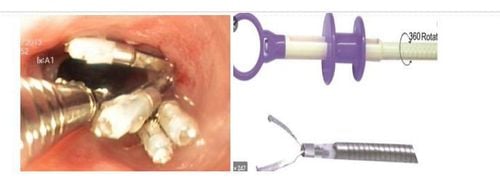
2. How to use OTSC
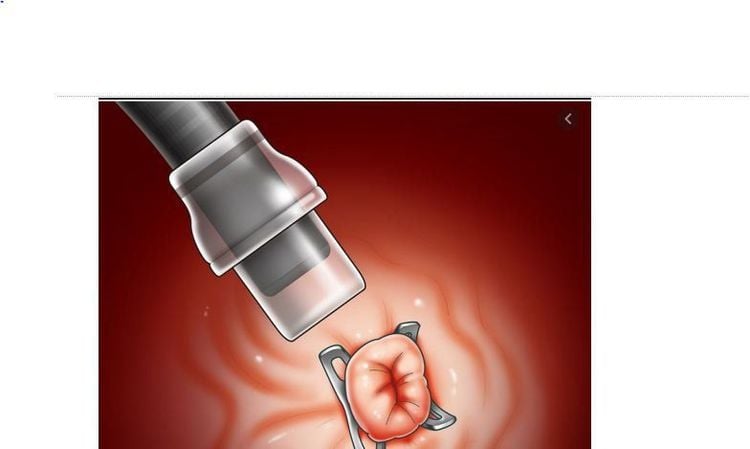
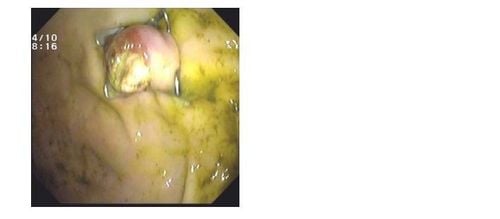
After determining the condition of the fistula, tissue is pulled inside the “cap” (a cylindrical instrument attached to the end of the bronchoscope to make the procedure more convenient) using a specialized clamp. After making sure that all the fistula tissue has been removed into the hood, shoot the OTSC clip. Check the clip firing position, can use up to 2 or 3 OTSC clips in 1 procedure to close the probe hole.

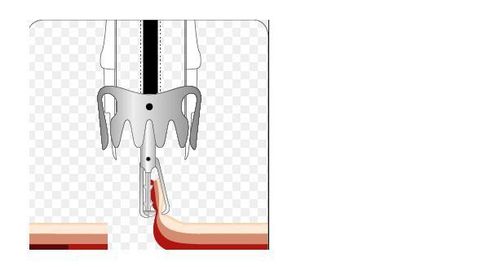
3. The role of OTSC in closing gastric fistula to the skin
Gastro-cutaneous fistula is an uncommon complication accounting for 0.5%-3.9% of gastric surgeries. Gastro-cutaneous fistulas after bariatric surgery account for 25-50% of gastrointestinal surgery. In addition, there is also a well-known complication: a gastro-dermal fistula caused by a physician after performing endoscopic percutaneous gastrostomy (PEG). Gastro-cutaneous fistulas rarely close spontaneously, they can cause sepsis, and fistula control is often difficult and ineffective with high mortality. In addition, the constant leakage of fluid from fistulas can severely irritate the adjacent skin and soft tissues of the abdominal wall leading to the development of cellulitis. The cause of gastric fistula formation is unknown. It may be related to direct or indirect trauma caused by the physician, or to an inflammatory reaction due to the formation of an abscess located close to the stomach. On the other hand, spontaneous fistula formation can also be caused by stress causing gastric ulcers to form fistulas. The optimal treatment for management of gastro-cutaneous fistula is still controversial. Conservative treatment: by placing drainage, controlling infection and sepsis, nasogastric tube placement, drugs to reduce gastric acid secretion, fasting, parenteral nutrition, this method is being used by many doctors. options before surgical intervention. Recently, several endoscopic methods have been described for management of gastro-cutaneous fistulas including plasma coagulation argon, fistula electrochemical cauterization, fibrin sealant, endoscopic clip or suture. , or simple stitching.

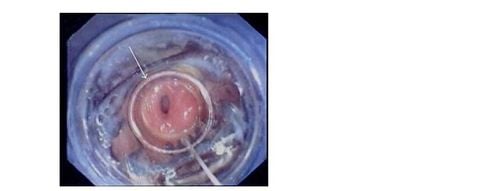
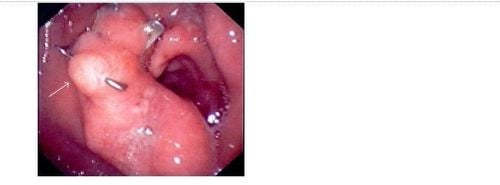
4. The role of OTSC in closing esophageal or colonic perforation
Perforation of the esophagus or colon is a surgical emergency because when it causes mediastinitis, peritonitis with a high mortality rate. The golden time for successful treatment of esophageal perforation is within 24 hours of esophageal perforation, while in the colon it is usually earlier. If detected and treated early in the first 24 hours, the mortality rate is 10% - 20%. If treatment is delayed after the first 24 hours, mortality increases by 50%. The most common cause of esophageal perforation in the community is swallowing bones while eating. Regarding treatment, depending on the infection status and the patient's general condition, we will choose the treatment strategy of stenting with a sheath and retractable or surgical suturing of the perforation. Currently, with the new endoscopic over-the-scope clip (OTSC) for suturing fistulas or gastrointestinal perforations, we are able to close perforations with a diameter of 2 - 3 cm as well as Safe and effective hemostasis of the gastrointestinal tract, without surgical intervention.
The two authors Baron and Sulz found that the success rate when using over-the-scope clip (OTSC) to close the anastomosis fistula is 65% - 83%. The author Sulz found that there are 2 reasons for failure when suturing the fistula, one is due to a narrowing of the gastrointestinal tract and the other is that the fistula has hard scar tissue so it is impossible to aspirate or pull the two edges of the fistula into the lumen. "cap" ("cap" is a transparent plastic cylindrical instrument attached to the end of the bronchoscope), thus the limitation of this clip is the low success rate when suturing chronic fistulas caused by radiation therapy or by trauma. injured by heat. Meanwhile, recent studies show a higher success rate when stopping bleeding in difficult cases that can reach 95%.
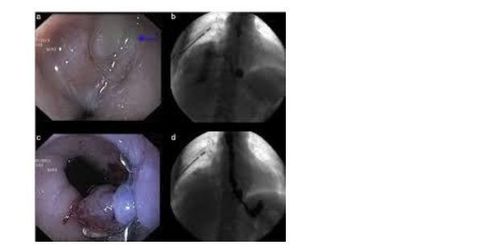
5. Conclusion
Currently, the indications for treatment with OTSC are mainly primary bleeding or bleeding during interventional procedures, gastrointestinal perforation clamping, gastrointestinal fistula. The advantage of this system is that it can be used as soon as the lesion is visible, simple, easy to use, very firm tissue closure, high success rate. Accuracy and certainty depend on precise tuning and traction technique into the cap ring. Clinical practices around the world increasingly show the role of OTSC clips in the closure of gastrointestinal fistulas and gastrointestinal bleeding, as well as its safety and efficacy. Not only that, this instrument is also applied in cutting in submucosal tumors of the gastrointestinal tract (EFTR gastrointestinal tract full wall resection technique), bringing a new direction to gastrointestinal endoscopy in the future.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.