This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Interventional Cardiologists, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Coronary stenting is a technique to help revascularize coronary arteries to improve symptoms of chest pain and reduce the risk of myocardial infarction, but besides the benefits that the technique brings, when performing this technique also certain risks may arise.
1. When to place coronary stents
Coronary stents are drug-coated or non-medicated metal or polymer mesh tubes that are used as supports in the lumen of an artery, helping to widen a narrowed or weakened artery in the body.
Coronary stenting is a method of percutaneous coronary intervention, helping to recirculate the coronary artery lumen by ballooning and leaving a fixed stent at the blocked coronary artery to improve coronary circulation. stabilize atherosclerotic plaque and reduce symptoms of angina caused by myocardial ischemia, reduce the risk of myocardial infarction.
The heart is nourished by the coronary artery system, because of a cause such as advanced age, lipid metabolism disorders, hypertension, diabetes ... causing atherosclerosis, this atherosclerotic condition can cause atherosclerosis. can cause rupture of the artery wall, attracting platelets to attach to it, forming thrombus inside the coronary artery wall, causing the coronary artery to narrow, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to patients suffering from heart failure. angina pectoris, worse than myocardial infarction.
Indications for coronary stenting include:
When the coronary artery is completely blocked (myocardial infarction), it is necessary to immediately restore flow to the artery. Coronary artery stenosis from 70 % on coronary angiography. Stable angina that is not controlled despite optimal medical therapy. Stable angina with evidence of myocardial ischemia and damage to a coronary artery that supplies a large area of myocardium Unstable angina, non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction . which is high risk stratified Angina pectoris occurs after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. There are symptoms of restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention.
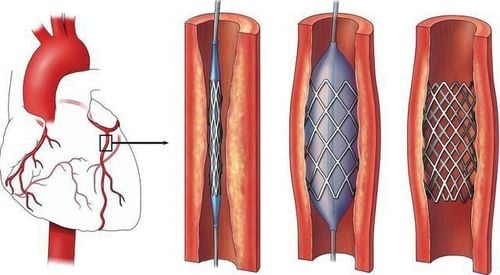
Hình ảnh đặt Stent mạch vành
2. Risks of coronary stents
Coronary stent placement helps to significantly reduce symptoms caused by coronary atherosclerosis, prevent myocardial infarction. However, there are also complications of coronary stenting such as:
Infection, pain or discomfort at the catheter insertion site. Reactions to anesthetic or contrast agents during placement. There can also be complications such as stroke, kidney failure. When threading can cause damage to the artery wall, causing stenosis in another location or the stent may not fully expand or may be displaced. Re-stenosis of the coronary artery after surgery due to scar tissue, thrombus development in the lumen of the stent can reduce the time the stent takes effect. Thrombosis is often caused by patients not complying with the use of anticoagulants according to the doctor's instructions. Hemorrhage due to anticoagulation Drugs that appear sooner or later are complications after stenting and directly affect the outcome of treatment, increasing the risk of re-occlusion.
3. How to reduce the risk of barovascular restenosis after stenting

Để giúp tuổi thọ của stent kéo dài hơn, người bệnh cần sử dụng thuốc theo chỉ định của bác sĩ
To help prolong the life of the stent, the patient needs to take the following measures:
Use the drug as prescribed by the doctor, do not change or stop the drug on your own. Compliance with regular drug use and periodic examination at 1 month, 3 months, 6 months and 1 year after stenting. At 1 year, it is necessary to have a follow-up examination and do a stress test to check the perfusion capacity of the myocardium. Change in diet: Quit smoking, alcohol, lose weight if you are overweight or obese. Reduce eating animal fat, fried foods, limit the amount of salt put into the body, should eat more fruits and vegetables. Exercise regularly every day: Patients should not drive or go far, should not have sex for 2 weeks after the procedure. Should not participate in vigorous physical activities, should walk gently 30-60 minutes a day. When there are signs of chest pain, excessive shortness of breath, immediately stop exercising and rest and notify the doctor about the condition. When you have to use drugs that are not prescribed, you need to notify the treating doctor for specific advice. Coronary stenting technique has been implemented at Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital with a success rate of up to 98%. The technique is performed by a team of interventional cardiologists from Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital and Vinmec Times City (Hanoi). With modern cathlab system, sterile medical equipment, quiet space, helping patients quickly recover and minimize risk after stenting.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.