This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Tran Hong Nhat - Interventional Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Coronary intervention by balloon angioplasty or stenting is a modern treatment technique for coronary artery stenosis. However, complications of restenosis after coronary stenting are a matter of concern for patients' health.
1. Re-stenosis rate after angioplasty and stenting
In the early stages with intervention by simple balloon angioplasty (insertion of a balloon into the narrow site and inflate to widen the coronary artery at that location), the rate of restenosis occurs relatively high (40 - 50%), due to vasoconstriction.Currently, coronary intervention is a combination of angioplasty and placement of a stent called a stent, which has helped doctors more successful in limiting restenosis after intervention. With single-metal holders (bare stents), the rate of restenosis in the stent is 20-30% over 12 months and this rate is lower with drug-impregnated stents. For the first generation of drugs, the rate of restenosis is about 15% at 5 years. With some new generation drug-eluting stents, this rate decreased to about 5 - 7% at 5 years after the intervention.
According to statistics, the most common time of restenosis is from 3 to 12 months after percutaneous coronary intervention.
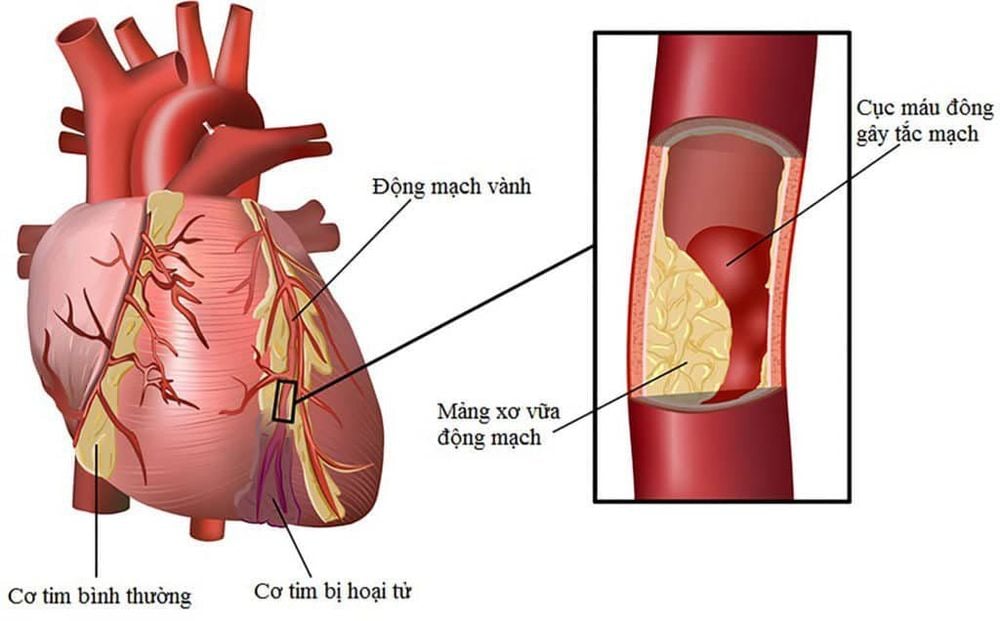
2. Causes of restenosis after angioplasty
2.1. Re-stenosis due to damage to the vessel wall
To perform vascular intervention, doctors will use an inflated balloon to widen the lumen of the artery. Then, a stent system is inserted into the narrowing position, whose job is to keep the enlarged artery from collapsing.Therefore, angioplasty and stenting, no matter how modern, are a form of trauma to the tissue and the vascular surface. The compression of plaque during dilation and stenting will almost create trauma to the vascular wall. This action triggers a cascade of inflammatory responses, granulation, cell repair, and endothelial cell proliferation.
Endothelial cells lining the coronary artery lumen will proliferate, multiply at the site of injury. If this increase is not controlled, the obstruction will lead to complications of restenosis in the stent.
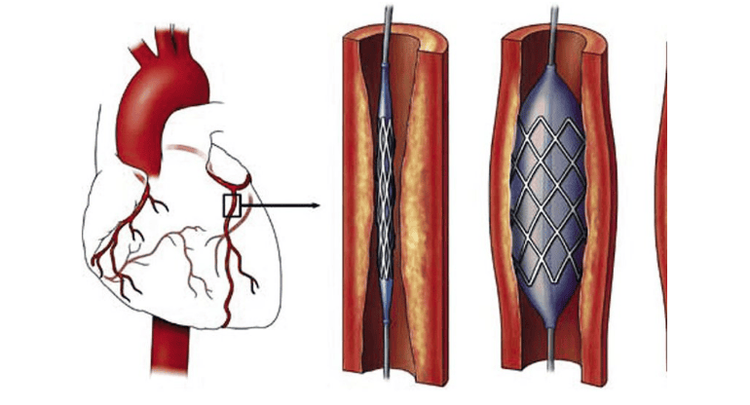
2.2. Re-stenosis due to atherosclerosis
Besides tissue injury, recurrent atherosclerosis is also implicated as a cause of restenosis after angioplasty and stenting. The most obvious difference is that the time to restenosis due to atherosclerosis is usually slower, appearing 1 year after coronary intervention.2.3. Re-stenosis after vascular stenting due to thrombosis
Thrombotic restenosis is an abrupt blockage of the stent, due to the formation of a blood clot. This is a relatively serious problem because a thrombus will completely block the coronary artery after stenting.The time of clot appearance ranges from days to months after coronary intervention, and the use of antiplatelet agents has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of restenosis after thromboembolic stenting. Research has demonstrated that patients need to take it for life after stenting to prevent thrombosis.
Quitting or taking the wrong drug can sometimes lead to late stent thrombosis - thrombosis occurs more than 1 year, but this issue is controversial and there is no research to confirm. exactly.
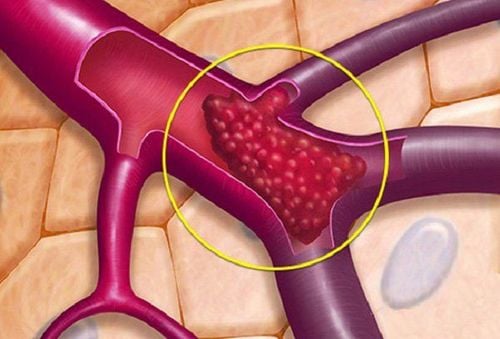
3. Types of stent restenosis according to AHA 1999
3.1. Re-stenosis in type I stents: in situ
Type Ia: Restoration at the joint or stent junction. Type Ib: Restoration at the edge of the stent. Type Ic: Re-stenosis within the stem of the stent. Type Id: Re-stenosis at multiple sites.3.2. Re-stenosis in type II, III, IV stents: diffuse
Type II: Re-stenosis in diffuse stent. Type III: Re-stenosis due to extensive tissue proliferation, not causing complete obstruction. Class IV: Re-stenosis causing complete occlusion of the coronary artery.4. Treatment of restenosis after angioplasty
Treatments for restenosis after coronary stenting include:Perform a revascularization intervention, place another stent at the site of the stent stenosis, or simply balloon angioplasty. Coronary artery bypass grafting is another option for patients with restenosis in stents, especially if restenosis after a second stent. Patients need to adhere to drug therapy after stenting, especially antiplatelet drugs to prevent thrombosis and control blood lipids against atherosclerosis with statins.
Besides, it is necessary to improve lifestyle, exercise, and eat healthy by limiting fat, alcohol, keeping a standard body weight, not smoking, and having regular check-ups for detection. early abnormalities.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a medical address for the treatment of cardiovascular and coronary diseases,... It has all the necessary medical equipment to perform simple treatments. to complicated procedures such as medical treatment, stenting intervention,... Accordingly, the procedures are handled by highly qualified medical staff who have undergone training and been granted technical certificates. quickly and effectively, especially in cases of urgent emergency. Therefore, patients with cardiovascular and coronary diseases can be assured of a strict, methodical and effective treatment process at Vinmec.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.