This is an automatically translated article.
The acid-fast stain is a simple and inexpensive method widely used in medicine. This test technique will help support the diagnosis of infections caused by bacteria with acid-fast properties.1. What is the “acid rapid” staining test?
Acid-fast stain is a laboratory technique that is performed on a specimen such as blood, sputum, urine, bone marrow, skin tissue, etc. to detect and stool distinguish "acid-fast" bacteria from other bacteria. Your doctor may order this test to find out if you have tuberculosis (TB) or another type of bacterial infection.
This technique is used to detect bacteria that cannot be stained by conventional Gram staining, especially Mycobacterium, which are resistant to alcohol, acid and can only be detected by this method. rapid acid staining. The use of this staining method for the detection of acid-resistant bacilli was first introduced by Paul Ehrlich and modified by two German scientists, Franz Ziehl and Friedrich Neelsen. A staining method using Ziehl-Neelsen reagent but eliminating the heating step developed by Joseph Kinyoun was later named Kinyoun staining.
2. What is the principle of the rapid acid staining method?
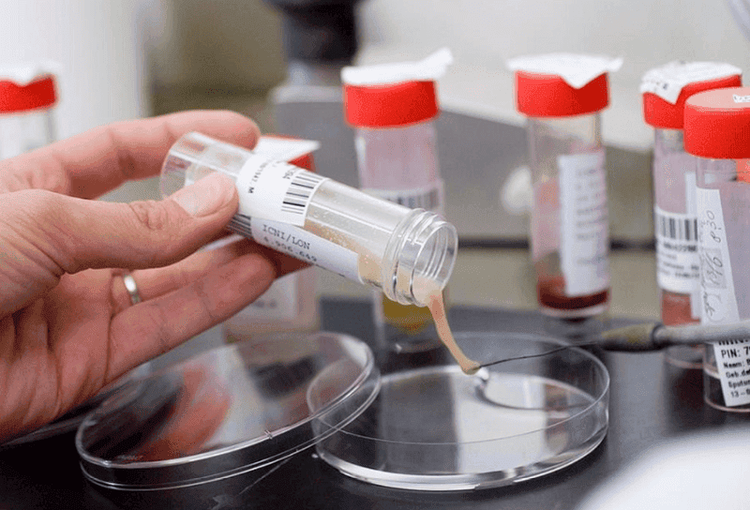
This method uses 2 dye chemicals, fuchsin red and methylene blue, combined with bleach (a mixture of HCL acid and 96 degrees alcohol) to detect bacteria belonging to the Mycobacteriacae family, which are resistant to bacteria. alcohol, antacid. These bacteria can survive in an acidic environment, certain alcohol concentration and do not lose color when bleached with alcohol and acid. First, the addition of fuchsin dye will complex with mycolic acid in the cell wall of acid-resistant microorganisms. As a result, they are resistant to being washed by acid-alcohol (decoloring agents) and retain the original dye color. Then, a contrast dye, methylene blue, is added and helps to visualize the stained organism.
Xét nghiệm nhanh với axit sử dụng xanh methylen giúp phát hiện vi khuẩn
3. What is the rapid acid stain test used for?
This test helps to detect bacteria with antacid properties in patient samples. Sputum is often used to test for tuberculosis bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) to find out if a patient has TB. The result is positive when observing the rod-shaped, slightly curved, fuchsin-red bacilli that can stand alone, in pairs or in clusters on a blue background.
In other acid-resistant bacteria such as Nocardia, only certain parts of the bacterial cell retain the dye color, such as the cell wall. A positive test result identifies an infection caused by Nocardia. Nocardia bacteria is quite uncommon, but the disease is dangerous. Nocardia infection begins in the lungs, and it can spread to the brain, bones, or skin of people with weakened immune systems.
4. How are test results interpreted?
If your test results are normal and antacids are not found, this means that you may not have an antacid infection or that the bacteria count is insufficient to detect. If the test results are abnormal, it means you may have an infection by strains of acid-fast bacteria. Based on the test results, the doctor will advise and recommend an appropriate treatment course.
5. How to collect patient samples?
To perform this test your doctor will need to take one or more samples from your body. How to collect some specimens is as follows:
5.1 Collecting a blood sample The medical staff will draw blood from your vein through the following steps:
First, the blood collection area will be cleaned with a substance. disinfectant like alcohol. Then an elastic band is wrapped around your arm. This makes your veins more prominent to facilitate blood collection. The medical staff will gently insert a syringe into the vein and draw out the blood. After a sufficient amount of blood is drawn, the needle will be withdrawn. The elastic band is then removed and the wound is covered with sterile gauze to stop the bleeding. This procedure poses almost no risk to the patient. In rare cases, taking a blood sample can have side effects such as excessive bleeding, the patient fainting or feeling light-headed, hematoma under the skin, infection. However, these side effects are very rare.
5.2 Collecting a sputum sample The medical staff will give you a special plastic cup to collect the sputum. The steps are as follows:
Rinse your mouth as soon as you wake up in the morning with filtered water. Do not use an antiseptic mouthwash. Breathe deeply and hold it for five seconds. Slowly exhale. Take another breath and cough vigorously until some phlegm enters your mouth. Sputum into a cup. Tighten the cup lid. Rinse and dry the outside of the cup and write the date of sampling on the outside of the cup. Give the sputum sample to the medical staff. The sample will be shipped to the laboratory as soon as possible. If necessary, samples can be refrigerated for 24 hours. Do not freeze or store at room temperature. In addition, in case the patient is unable to cough up sputum, the doctor can use bronchoscopy to collect a sample. The technique is quite simple and takes about 30 to 60 minutes. Patients usually remain awake for the procedure. First, your doctor will spray a numbing medicine into your nasopharynx to numb the area. The bronchoscope is inserted through the mouth or nose through the airways to the lungs. The patient is usually given an anesthetic that does not feel pain or discomfort, but in some cases an anesthetic may be prescribed. Rare risks of bronchoscopy include allergic reaction to the sedative, infection, bleeding, bronchospasm, and irregular heartbeat.
Thu thập mẫu đờm trong xét nghiệm nhanh cần thực hiện đúng quy trình
5.3 Collecting a urine sample The medical staff will give you a special cup to collect a urine sample from. It's best to collect a sample the first time you pee in the morning. At that time, the level of bacteria will be higher. The process of collecting a urine sample usually includes the following steps:
Wash your hands. Remove the cap of the sample vial. Men should clean inside and around the penis and foreskin. Women should use sterile tissue to wipe the folds of the vagina. Start urinating. After your urine has flowed for a few seconds, place the container in the stream and collect a sufficient amount of “midstream” urine. Then carefully close the lid of the box. Wash your cup and hands. If you are collecting your urine at home and cannot get to the lab within an hour, store the sample in the refrigerator. Urine samples can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 24 hours. 5.4 Collecting a bone marrow sample Bone marrow is the soft fatty tissue inside larger bones. In adults, bone marrow is usually obtained from the pelvis or sternum. In infants and children, bone marrow is usually obtained from the tibia or shinbone. A bone marrow biopsy is usually done as follows:
First, the site is cleaned with an antiseptic, such as iodine. Next, the doctor will inject a local anesthetic into the area to be biopsied. Once the sampling site has been numbed, your doctor will insert a needle through your skin and into your bone. The doctor will then use a special needle to pull out a sample of bone marrow. After the needle is withdrawn, a sterile bandage is placed over the site where the sample was taken. After the biopsy, you should lie still until your blood pressure and heart rate return to normal. You should cover and keep the sampling site dry for approximately 48 hours. There are some uncommon risks of a bone marrow biopsy including infection, persistent bleeding, or a reaction to the local anesthetic or sedative.
6. What preparation is required before performing the rapid acid staining test?
Depending on the specimen to be collected, there are separate ways of preparation. For blood, urine and stool samples, there is almost no preparation required prior to collection. For a bone marrow or skin biopsy, your doctor may instruct you not to eat or drink liquids before the procedure. Note that you must tell your doctor about any medications you are taking including vitamins, supplements, over-the-counter and prescription drugs. You should also let your doctor know about any allergies you have, any previous reactions to medications, or bleeding problems you've had. In particular, if you are pregnant, tell your doctor immediately.
In summary, "acid-fast" staining is a technique that is not too complicated and expensive. This technique will assist doctors in detecting and diagnosing infections caused by acid-resistant, alcohol-resistant bacteria. To ensure safety and effectiveness, you should choose reputable medical facilities to perform.
With the continuous development of scientific progress, Vinmec International General Hospital has now deployed many rapid test methods with acid to diagnose diseases. The diagnostic method is performed by a team of qualified medical professionals with a system of modern medical equipment, ensuring highly accurate results. After having an accurate diagnosis of the disease, the doctors will come up with a treatment plan and advise the patient to ensure the fastest recovery.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: healthline.com, sciencedirect.com, ucsfhealth.org