This is an automatically translated article.
The article was translated and synthesized by Dr. Nguyen Xuan Hung - Director of Vinmec Institute of Applied Research and Regenerative Medicine (VIASRM) and consulted with Dr. Tran Thi Phuong Thuy - Department of Internal Medicine. General - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital
2019 New Corona virus (referred to as 2019 nCoV) is a new respiratory virus strain, which has never appeared in humans and is currently causing an epidemic in Wuhan, China. Here is essential information about 2019-nCoV to help you proactively protect yourself and your family.
For complete information about the 2019 corona virus epidemic, you can refer to the sections of the document including:
[Q&A about the 2019 Corona virus] Part 2: How to protect yourself before the epidemic? [Q & A about the 2019 Corona virus epidemic] Part 3: When to get tested? Instructions for taking care of people suspected of being infected with 2019 nCoV at home [Q&A about the 2019 Corona virus epidemic] Part 4: How does 2019-nCoV spread? Is it possible to get it from animals or pets? Recommended video:
WHO: Complete and easy to understand information about the new Corona virus (2019-nCoV)
1. What is corona virus? Coronas are a large family of viruses, some of which are capable of causing disease when they infect humans, while others infect and survive only in animals including camels, cats and bats. Sometimes zoonotic coronaviruses evolve to infect humans and then spread from person to person, as is the case with Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) and severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Currently, the Wuhan coronavirus (2019-nCoV) is a new strain that has never appeared in humans and is capable of being transmitted from person to person.
2. What is 2019 corona virus? The 2019 new corona virus (referred to as 2019 nCoV) is a new respiratory virus strain that has never appeared in humans and is currently causing an epidemic in Wuhan, China.
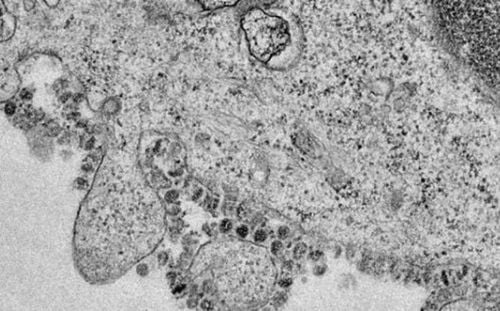
Hình ảnh 2019 - nCoV
3. What is the source of 2019-nCoV infection? The origin of the 2019-nCoV strain is currently unknown. Research on sequencing the genome of the virus shows that this virus strain has 96.3% similarity with the corona virus strain from bats, so there is a high possibility that this is a bat virus strain that mutated and then infected humans. Currently, the medical community has confirmed that 2019-nCoV has the ability to spread from person to person.
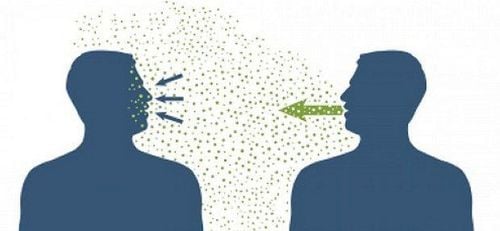
2019-nCoV lây từ người sang người chủ yếu qua đường giọt bắn
4. Is rubbing your eyes and nose contagious? How does it spread? Usually, person-to-person spread occurs through close contact (about 2 m) with an infected person. Person-to-person transmission is currently believed to be primarily via droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes, similar to the way influenza and other respiratory pathogens are spread. Droplets can land in the mouths or noses of people near or be inhaled into the lungs. It is not yet clear whether a person can contract 2019-nCoV by touching a surface or object that carries the virus and then touching their mouth, nose, or eyes. Usually, with most viruses, the virus is transmitted through the respiratory tract. , the most contagious person is the person who is in the most symptomatic condition (severe illness). However, with 2019-nCoV, there have been cases of transmission through close contact with patients infected with the virus without symptoms.
It should be noted that the ability of different viruses to spread from person to person is different. Some viruses are very contagious (like measles), while others are more difficult to spread. Because 2019-nCoV is a new virus that has never appeared in humans, its transmission, severity, and other characteristics are still under investigation. We will update this information as soon as it is available via Vinmec's website and fanpage.
5. Is 2019-nCoV the same as the virus that causes MERS and SARS? No. 2019-nCoV is a large family of viruses, only some are capable of causing disease in humans, the rest exist only in animals, such as camels, cats and bats. 2019-nCoV is not the strain that causes MERS (derived from camels) and SARS (derived from civets). However, genetic research suggests that 2019-nCoV may have evolved from a virus related to the virus that causes SARS. Studies are still underway to find the source of 2019-nCoV.

Một số biện pháp phòng ngừa dịch bệnh
6. Is the risk of contracting 2019-nCoV different in different people? Generally young children, the elderly, and people with medical conditions (such as high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, liver disease and respiratory disease) are at greater risk of developing more serious symptoms than others.
Source: CDC, WHO, ECDC
Recommended video:
Instructions for washing hands properly and properly to prevent new Corona virus (2019-nCoV)
MORE:
[Q&A about 2019 Corona virus] Section 2: How to protect yourself against the epidemic? [Q&A about the 2019 Corona virus epidemic] Part 3: Instructions for taking care of people suspected of being infected with 2019 nCoV at home [Q&A about the 2019 Corona virus epidemic] Part 4: How does 2019-nCoV spread? Is it possible to get it from animals or pets? Vinmec's advice and hotline to receive customer advice on the 2019 Corona virus epidemic







![[Q&A about the 2019 Corona virus epidemic] Part 4: How does 2019-nCoV spread? Is it possible to get it from animals or pets?](/static/uploads/small_20200204_141656_397082_theo_doi_than_nhiet_max_1800x1800_jpg_9276350bb5.jpg)






