This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Huy Nhat - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang.To diagnose dysventilation, doctors will perform pulmonary function measurements for patients, this is the gold standard for definitive diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), differential diagnosis of bronchial asthma and bronchial asthma. COPD, screening people at risk for lung disease, risk assessment as well as prognosis before surgery, monitoring progress in the treatment of respiratory diseases and in addition, assessment of disability.
1. Pulmonary ventilation measurement
Pulmonary ventilation measurement is a fairly simple and painless exploratory technique for the patient, with almost no discomfort or complications, often used in diagnosis and monitoring to assess the severity of respiratory diseases. Breathing helps to record parameters related to lung function, thereby helping to evaluate the two syndromes of obstructive and restrictive ventilation disorders.Pulmonary ventilation measures airflow in the bronchi and lungs, and also assesses the degree of bronchial obstruction and the severity of alveolar dilatation. The accuracy of the results depends on the cooperation of the patient. Measurement results are expressed in specific numbers and as a percentage of the value of a normal person. The measured values of respiratory function are then plotted as a curve where one axis represents tidal flow measurements, and the other represents measurements of air volumes. present in the lungs, this curve is also known as the volume flow curve.
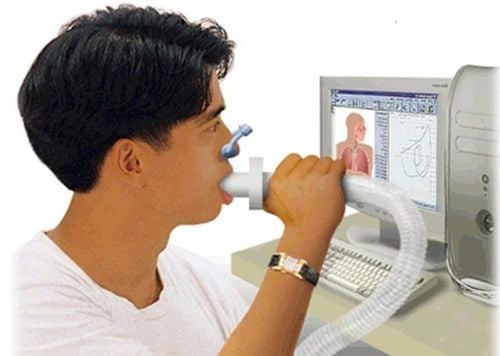
2. Meaning of respiratory dysfunction assessment
To diagnose dysventilation, doctors will perform pulmonary function measurements for patients, this is the gold standard for definitive diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), differential diagnosis of bronchial asthma and bronchial asthma. COPD , screening people at risk for lung disease, assessing risk as well as prognosis before surgery, monitoring progress in the treatment of respiratory-related diseases and in addition, assessing the degree of disability.There are 2 types of spirometry: volumetric spirometry and flow type spirometry to monitor and recognize the ventilation function of the lungs during inhalation and exhalation depending on the time of breathing. , is exertion or not and exertion is maximal on exhalation?
Usually the patient is asked to do 2 movements when measuring, the first is a normal inhalation and exhalation, then is asked to inhale as deeply as possible, then exhale as hard as possible, the second is to inhaling and exhaling normally, and then asked to inhale as hard as possible and blow out as quickly, as hard, as possible, and to continue exhaling for at least 6 seconds.
While performing any movement, you must do it continuously, do not stop because stopping suddenly or doing not exactly what the respiratory function technician requires will cause erroneous results. respiratory function leads to misinterpretation of results leading to inappropriate diagnosis and treatment. Just because a patient smokes and has a normal respiratory function test result does not mean that he or she is not at risk for COPD.
Subjects are assigned by doctors to measure ventilation function when there are clinical symptoms and other abnormal test results such as shortness of breath, wheezing, sitting breathing, difficulty exhaling, prolonged phlegm cough , persistent dry cough, chest deformity, hypoxia, hypercapnia, polycythemia, chest X-ray abnormality. Or measure ventilation for smokers, people working where there is smoke, exposure to toxic chemicals. Especially patients with chronic bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and restrictive lung disease need to be measured ventilation to control disease, assess disease progression
Should not perform pulmonary function measurement for cases of acute respiratory tract infection, unexplained hemoptysis, thoracic aortic aneurysm, abdominal aortic aneurysm, recent exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma less than 6 weeks, infarction myocardial infarction, ophthalmic, abdominal, chest surgery less than 3-6 months old, undiagnosed chest pain, 24 h unstable angina, and progressive pulmonary tuberculosis.
Doctor Nguyen Huy Nhat has many years of experience in the field of respiratory disease treatment at Hue Central Hospital, Hoan My General Hospital, .. before being a doctor of General Internal Medicine Department of General Hospital. Vinmec Danang International.
If you notice any unusual health problems, you should visit and consult with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.