This is an automatically translated article.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common medical emergency. In recent years, the number of patients hospitalized and dying from acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in our country tends to increase. The cost of medical treatment is a financial burden for many households.
1. What is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease that impairs ventilation. Airflow obstruction progresses with abnormal inflammation of the lungs due to noxious gases and particles. The disease will gradually reduce the lung ventilation function.
The cause of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is chronic smoking, or close contact with many toxic substances, or environmental air pollution.
2. What is exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?
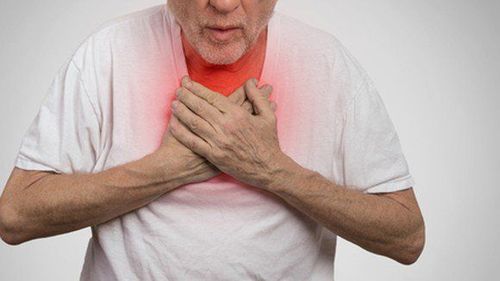
Acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease causes patients to have reduced respiratory function, poor physical condition, and difficulties in daily life. It is the main cause of death in people with COPD.

Viêm phổi tắc nghẽn mạn tính đợt cấp khiến người bệnh bị sụt giảm chức năng hô hấp
When the exacerbation occurs, the patient has inflammation in the respiratory tract and systemic inflammation occurs with a stronger degree with many changes than in the stable stage. Depending on whether the cause of the exacerbation is bacteria, viruses or non-infectious agents, the type of inflammation that occurs during an exacerbation is also different.
There are two main types of inflammation commonly seen in acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: eosinophilic inflammation and neutrophilic inflammation.
When the patient starts smoking, there will be inflammation, the level of inflammation gradually increases when the patient has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The more severe the disease, the greater the inflammation. They will increase higher during the level. When chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is acute, there will be increased inflammation of the airways leading to increased bronchial tone, edematous bronchial walls, and production of a lot of mucus. These processes that occur during an exacerbation can exacerbate ventilation-perfusion imbalances and limit expiratory ventilation.
At that time, the patient will find it harder to breathe than usual, cough a lot, increase sputum, mucus, and pus.
3. Treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)?
Currently, for the treatment of acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, depending on the condition, the general assessment of the disease, the doctor will choose the appropriate drug for treatment. Including:
Bronchodilators Systemic Corticosteroids Antibiotics Oxygen Therapy, Controlled Mechanical Ventilation Surgery
Có nhiều biện pháp điều trị COPD tùy thuộc vào tình trạng của bệnh nhân
In the methods of mechanical ventilation to treat acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, there are two types: noninvasive positive pressure mechanical ventilation and invasive mechanical ventilation.
Non-invasive positive pressure mechanical ventilation has advantages over invasive mechanical ventilation such as:
Improve ventilation Reduces blood CO2 helps to reduce respiratory acidosis Reduces the degree of dyspnea in the first 4 hours Reduces length of hospital stay Avoids the need for invasive mechanical ventilation Reduces mortality In addition, the doctor will combine in the treatment process for the patient:
Rehydration and electrolytes for the patient Ensure nutritional supply full due to the patient's difficulty in breathing, fatigue and inability to eat.
Bệnh nhân sẽ được bù nước và dinh dưỡng trong suốt quá trình điều trị
4. Caring for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)?
In addition to the treatment according to the doctor's schedule, the patient and his/her family must take the initiative to take care of their health with:
Must do exercises to restore lung function, they will help the patient to continue daily activities. Long-term oxygen therapy is essential to ensure the patient's survival. People with COPD should have a healthy diet such as: Eat thin, hot, soft foods for easy absorption. Daily diet must be full of nutrients, add more fiber such as: fruit juices, fruits, green vegetables. Elderly people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) often feel tired, so they lose their appetite, so to avoid malnutrition, they should divide up many small meals a day for the patient. Eat slowly, chew well, avoid using foods or drinks that cause bloating or have stimulants. Take the medicine exactly as directed by your doctor. Periodic examination according to the instructions of the doctor to control the disease as well as health. Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as if you want to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online. online HERE.