This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Tung Hoanh - Interventional Cardiologist - Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Ventilator patients need comprehensive care, combined with monitoring of clinical signs, subclinical and parameters on ventilators. Ventilator patients are often critically ill, so care and nutrition of ventilated patients need to be done properly.
1.Goal when taking care of ventilator patients
Taking care and protecting the lungs in mechanically ventilated patients is one of the important things that greatly affects the quality and effectiveness of treatment for patients. In mechanically ventilated patients, the endotracheal tube often causes damage to the upper respiratory tract.The air the patient breathes in through the ventilator is often not warm and humid enough and not filtered. Meanwhile, the cough reflex is limited by the endotracheal tube or partly by the use of sedative analgesics. Since then, patients often have a lot of stagnant secretions in the respiratory tract leading to severe lung diseases such as pneumonia, bronchitis, atelectasis ...
Measures to monitor patients on ventilators to protect lungs All are aimed at preventing and limiting harmful effects on the respiratory tract for patients.
2.Measures for taking care of ventilator patients
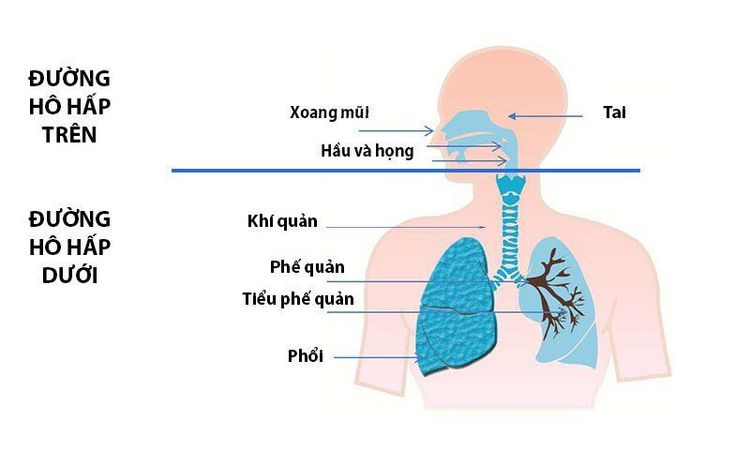
Đường hô hấp trên có tác dụng làm ấm và làm ẩm không khí thở vào trước khi đến phổi
Warm and humidify the inhaled air. Tracheal sputum suction. Physical therapy practice. Warm and humidify inhaled air The human upper respiratory tract warms and humidifies inhaled air before reaching the lungs. The humidity of the inhaled air is highly dependent on the temperature and pressure inside the airway, the higher the airway temperature, the higher the humidity of the inhaled air, the higher the airway pressure, the lower the humidity of the breathing air. Therefore, warming the inhaled air and reducing airway pressure will increase the humidity of the air.
A system that warms and humidifies the inhaled air, also known as a prosthetic nose, includes:
HME: Heat and moisture exchanger HMEF: Heat and moisture exchange filters HCH: Hygroscopic condenser humidifier HCHF: Hygroscopic condenser humidifier filters All patients breathe All machines must be humidified with air inhaled through a prosthetic nose. Note, the HME system should only be used for the first 4 days of mechanical ventilation, not for prolonged use.
The temperature of inhaled air at the endotracheal tube is ≤ 37 degrees Celsius, if the temperature is too high, it can easily burn the patient's respiratory mucosa. The solution in the HME inhalation humidification system should only be distilled water, not saline solution.
However, the HME breathing air humidification system is a favorable environment for bacteria to grow, so the water tank must be changed and disinfected every day. Remove the system when aerosolizing the patient.
Hình ảnh hút đờm qua khí quản cho bệnh nhân
When conducting, need to prepare: ECG - Monitor, SpO2, suction system, oxygen, Ambu, sterile gloves, sterile suction line (diameter < 1/3 of endotracheal diameter), sterile 09% physiological saline solution
Give the patient 100% FiO2 ventilation for 2 minutes before aspiration sputum. The suction time lasts < 10 - 15 seconds, wash the trachea with 09% NaCl solution 1-2 ml/time, withdraw the suction cord slowly and rotate it slightly. After aspirating patients on ventilators 100% FiO2 for 1-2 minutes
Physiotherapy for mechanically ventilated patients Physiotherapy is performed to prevent and treat complications due to sputum sputum in the lungs , which facilitates gas distribution in different regions of the lung. Physiotherapy methods include:
Massaging and vibrating the patient's chest. Stimulating the patient to cough Postural drainage of the patient every 20 - 30 minutes, perform 3 - 4 times/day Breathing exercises Allow the patient to breathe with a large dead space Breathe with the Spirometrie device Special, conduct treatment Positioning is usually effective in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: the prone position for mechanical ventilation.
3.Nutrition of ventilator patients

bệnh nhân thở máy cần cung cấp đủ các chất thiết yếu
Glucose (1g of glucose provides 4 kcal) needs to account for 50-70% of the total energy provided in the nutritional regimen of ventilator patients. Lipids (1g provides 9 kcal) need to account for 30-50% of the total energy provided in the patient's diet. Protein (1g provides 4 kcal): ensure adequate supply of 1.25g/kg of patient's weight. In addition, ventilator patients need comprehensive care in terms of hygiene, anti-infection, anti-ulcer when lying for a long time...
4.Prevention of complications due to mechanical ventilation
Reflux of gastric juice, oropharyngeal fluid into the lungs It is necessary to check the patient's cuff pressure daily. Place the head at 30 degrees (if the patient has no contraindications) Give gastric drip, do not give more than 300 ml/meal. When regurgitation of fluid into the lungs requires postural drainage or bronchoscopy with a flexible bronchoscope Pneumothorax Recognize by signs such as: cyanosis, rapid decrease in SpO2, slow pulse, chest on the side of tension pneumothorax. , resounding percussion, subcutaneous emphysema... must be conducted immediately, otherwise the thoracic pressure will increase very quickly, leading to respiratory failure, acute cardiac tamponade that can lead to death fast death.Emergency minimal pleural effusion with a large enough drainage tube, connected to a continuous suction machine with a pressure of 15-20cm of water. Check the drains daily for kinks or blockages. The suction system must be sealed, in good working order, the water in the drainage tank must be closely monitored and emptied daily, the water in the tank to detect gas out must always be clean. Attach the drain tube until the air is out, clamp it again after 24 hours, then take a chest X-ray to check, if the lung is fully expanded, remove the drain tube.
Bệnh nhân thở máy có thể dẫn đến viêm phổi
It is necessary to re-evaluate the processes of sputum suction, cleaning the wiring and ventilator to ensure sterility or not. Administer strong, broad-spectrum antibiotics and a protocol combination of antibiotics. Prophylaxis of peptic ulcers Drugs to reduce gastric secretions: proton pump inhibitors, gastric mucosal coatings..
Prophylaxis and care of pressure sores due to long-term pressure Change the patient's position every 3 hours/ times: lying flat, lying on the right side, on the left side (if there are no contraindications to the patient's position), avoiding long-term pressure in one place to prevent ulcers and prevent atelectasis. If the patient is lying down for a long time, the patient should be placed on a water mattress or an air mattress with automatic change of position. When there is a sign of redness at the pressure site: Sanyrene should be applied to the pressure area. When there is an ulcer, it is necessary to clean, cut and change the bandage at the ulcer site daily. Prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis when the patient is lying down for a long time. For the patient to change position, exercise passively to avoid circulatory stagnation. Check pulse systematically to detect thrombosis, venous occlusion or arterial occlusion Using anticoagulants such as low molecular weight Heparin, Lovenox, Fraxiparine...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.