This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Doctor Nguyen Ngoc Phuong Nam - Emergency Medicine Doctor, Emergency Department - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalAcute pulmonary edema is an urgent emergency, causing acute respiratory failure because the alveolar lumen (lungs) is filled with fluid, resulting in the inability to exchange air (receiving 02 and exhaling C02). If detected, diagnosed early, treated promptly, the disease is likely to recover quickly. If not treated promptly, it will lead to severe acute respiratory failure, high risk of death.
1. What is acute pulmonary edema?
Causes of acute pulmonary edema :
Cardiovascular disease Heart valve disease , especially mitral and aortic valve disease . Hypertensive crisis (especially due to adrenal myeloma). Heart attack . Myocarditis . Severe heart failure. Noncardiac disease Renal disease, most commonly glomerulonephritis Acute glomerulonephritis in children (due to increased blood volume). Chronic glomerulonephritis in adults: end-stage renal failure or hypertension.
Có nhiều nguyên nhân gây ra tình trạng phù phổi cấp
2. When should acute pulmonary edema be mechanically ventilated?
Based on the clinical assessment of the degree of respiratory failure caused by pulmonary edema and the progression of respiratory failure, the doctor will decide whether to give the patient a non-invasive ventilator or an invasive ventilator based on:
Based on respiratory failure: Moderate to severe or in a life-threatening emergency. Responding to initial drug therapy? If the patient responds well to initial drug therapy, there is no need for noninvasive mechanical ventilation. But if the patient's progress is worsening, breathing is faster, respiratory failure is worse, the doctor will decide to give non-invasive or invasive mechanical ventilation to treat the patient: Moderate to severe dyspnea, yes use accessory muscles of respiration and have paradoxical abdominal mobility. Moderate to severe respiratory acidosis (pH < 7.3). Hypoxemia Pa02 < 60 mmHg. Breathe > 25-30 times/min.
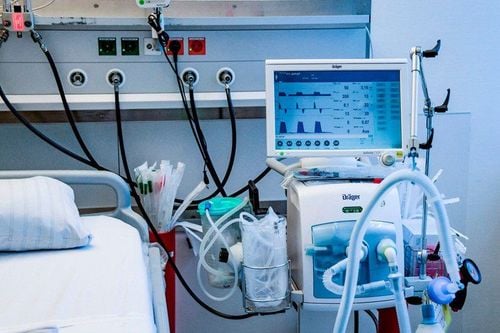
3. What is non-invasive mechanical ventilation and invasive mechanical ventilation?
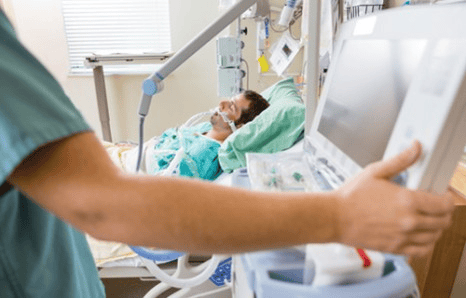
3.1 Non-invasive mechanical ventilation The patient will be attached to a ventilator through a mask (breathing mask) placed on the patient's nose and mouth, and the ventilator will support breathing for the patient through a breathing mask.
In the case of non-invasive mechanical ventilation, usually the patient has respiratory failure but is awake, and is supported by a ventilator for breathing.
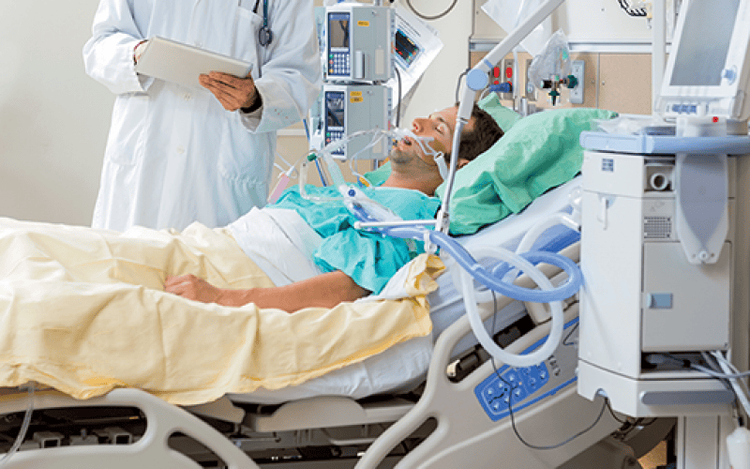
Bệnh nhân được gắn với máy thở thông qua mặt nạ đặt trên vùng mũi miệng
Benefits
Studies show that the benefits of noninvasive mechanical ventilation improve:
Reduce the risk of intubation, invasive ventilation Reduce mortality Improve signs of upper respiratory failure clinical Improvement of paraclinical indicators of respiratory failure 3.1 Invasive ventilation During non-invasive mechanical ventilation, physicians will monitor for signs of respiratory failure, if respiratory failure is due to pulmonary edema If the problem is not resolved or worsens, endotracheal intubation and invasive mechanical ventilation will be warranted. Or this respiratory failure is critical right from the moment of receipt such as: lethargy, apnea, cardiac arrest, then invasive mechanical ventilation will be indicated from the beginning. The patient will be intubated (a breathing tube) that enters the airway through the mouth, and then connected to a ventilator for life-threatening breathing protection, the patient will usually be sedated. to perform mechanical ventilation and monitoring.
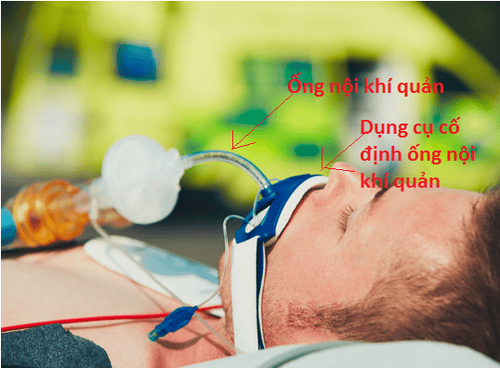
Thở máy xâm lấn sử dụng nội khí quản đi vào đường thở qua đường miệng
4. When will the patient be able to wean off the ventilator?
The decision to stop mechanical ventilation or practice to stop breathing so that the patient can breathe spontaneously will depend on:
Progression of the disease: Clinical signs of respiratory failure and laboratory tests returning to normal often. The doctor will assess the respiratory status and related pathological factors to decide to temporarily stop, practice weaning or completely stop the ventilator so that the patient can breathe naturally and return to normal activities. The medical problems that cause respiratory failure are improved such as: Treating heart failure leads to better heart function, or treating kidney diseases better.
5. Conclusion
Artificial ventilation (non-invasive ventilation and invasive mechanical ventilation) is a life-saving treatment for severe cases of pulmonary edema. If not treated promptly, the patient can die very quickly from respiratory failure.
This is also a complex technique that requires experience and proficiency in practical skills, so it is often prescribed and performed in well-equipped medical facilities.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.