This is an automatically translated article.
This article was written by Specialist Doctor II Khong Tien Dat, Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital. The doctor has a lot of experience with more than 14 years working in the field of diagnostic imaging.Esophageal x-ray is an imaging method that helps doctors have a more specific view of the digestive tract components behind the oropharynx and mainly focuses on the esophagus. The esophagus is a section of the digestive tract that originates from the back of the tongue in the pharynx and extends to the stomach.
1. What is an esophageal x-ray?
The esophagus is a muscular tube in the digestive system that carries food from the oropharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is divided into three segments corresponding to its anatomical position inside the body, including the cervical esophagus, the thoracic esophagus, and the abdominal esophagus. The average length of the esophagus is about 25cm. On the path of the esophagus, there are 3 narrowest places: the junction of the pharynx and the esophagus corresponding to the cricoid cartilage, the crossing of the aortic arch, and the passage that descends into the diaphragm equivalent to the lower esophageal sphincter.Your doctor will order an x-ray of the esophagus to diagnose conditions that cause symptoms such as difficulty swallowing or other abnormalities of the upper digestive tract including the esophagus, stomach, and the first part of the small intestine. duodenum. To perform an esophageal x-ray, the patient will be asked to swallow a contrast agent that has been mixed with water. The most commonly used contrast agent in clinical practice is barium, which captures bright contrast on radiographs. This feature helps to highlight the esophagus, the inner lining as well as the conformational changes in the swallowing movement of the esophagus. Abnormalities detected on x-ray of the esophagus will be suggestive for the diagnosis of diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract.

2. Esophageal x-ray film helps diagnose what diseases?
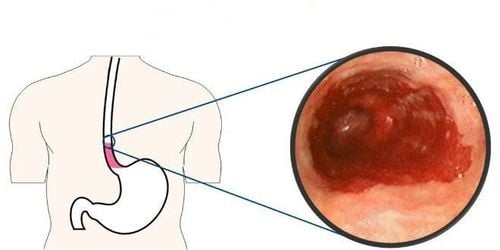
Esophageal radiographs are often indicated for the diagnosis of pathologies associated with structural and functional abnormalities of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Some of the disorders that X-ray of the esophagus can be helpful in diagnosis include:Diaphragmatic hernia Esophageal diverticulum Cardiac spasm Esophagitis Esophageal lumen obstruction Esophageal muscle dysfunction manifested by dysphagia or abdominal cramps Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Esophageal ulcer Tumors in the lumen of the esophagus, including both benign and malignant tumors Tumors from The surrounding structures compress and deform the esophageal lumen Recurrent vomiting The endoscope cannot be inserted into the esophagus during gastrointestinal endoscopy Evaluation of esophageal fistulas Sometimes esophageal radiographs are part of radiographs of the entire upper gastrointestinal tract, involving both the stomach and duodenum. Another imaging modality commonly performed with an esophageal x-ray is gastroesophageal endoscopy or gastro-oesophageal duodenoscopy.
3. Contraindications to perform esophageal X-ray
Barium contrast agents should be replaced with water-soluble contrast agents in the following cases to ensure patient safety:Suspected esophageal perforation Evaluate gastrointestinal fistulae after surgical repair When using water-soluble contrast agents in patients, the risk of aspiration of liquid into the respiratory tract should be kept in mind. Accidental inhalation of water-soluble contrast agents can lead to large-scale and life-threatening pulmonary edema. Low osmolarity agents such as Omnipaque should be used instead in these cases.
4. Procedure for performing esophageal X-ray

Prepare the patient: the patient should be consulted about the procedure and the risks and risks. variables and possible risks before, during and after the radiograph. Note that the patient needs to fast before the procedure for at least 12 hours and do not bring jewelry and metal into the imaging room. Immediately before the scan, administrative information such as name and medical history, history of drug allergies should be checked to avoid errors. Prepare necessary equipment such as X-ray film machine, contrast agent, syringe, cotton swab, ... Selecting position for the patient: can guide the patient to stand upright or lie down depending on the purpose of the survey. in each case. When suspecting abnormalities in esophageal motility such as achalasia, dysphagia, or wanting to detect foreign bodies in the esophageal lumen or narrow passages on the esophageal wall, a standing position should be selected for the patient. . During the scan, the patient needs to take a sip of the contrast medium and swallow or stop swallowing according to the technician's instructions. Patients need to hold their breath a few times during the scan to ensure the quality of the film is free from image noise. Esophageal X-rays take an average of 30 minutes per scan. Some of the abnormalities that can be obtained on x-ray of the esophagus include
Esophageal motility disorder with abnormal images of secondary waves. Dilated, tortuous oesophagus. Bird beak-shaped esophagus in spasmodic pathology Esophageal lumen deformity due to compression from tumors in surrounding organs Picture of esophagitis Esophageal cancer .
5. Side effects of contrast agents

Patient's stool after X-ray is usually lighter in color because the body does not absorb barium. Stool color will return to normal after the contrast is eliminated.
Patients need to see a doctor immediately if the following problems occur:
There is an abnormality related to bowel movements and loss of bowel movements Abdominal pain or swelling in the abdomen Passing stools that are smaller than usual In addition to In addition, esophageal radiography is also a procedure that increases exposure to X-rays. The risk of adverse events related to X-ray exposure increases over time and is related to the number of times. X-ray films throughout life. Radiation exposure during pregnancy can also cause birth defects. Therefore, pregnant women should not have an esophageal X-ray.
Esophageal X-ray with contrast is an imaging method to evaluate the anatomical structure of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, patients should choose reputable medical facilities that have enough modern medical equipment systems to perform this technique.
In order to improve the medical examination and treatment process, Vinmec International General Hospital has now applied esophageal X-ray technique in examination and diagnosis of many diseases. X-ray technique at Vinmec is carried out methodically and according to standard procedures by a team of highly qualified medical professionals, modern machinery system, thus giving accurate results, making a significant contribution to diagnosis and staging of the disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE MORERelationship between X-ray and Pregnancy In what case is X-ray of the uterus and fallopian tubes (HSG scan) done? Mammomat Inspiration X-ray machine - an effective "assistant" in the diagnosis and treatment of breast tumors