This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Specialist II, Senior Doctor Doan Du Dat - Head of Medical Examination Unit - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital
1. Women need hepatitis B vaccination before getting pregnant
Hepatitis B is a globally prevalent disease caused by the HBV virus. The disease is transmitted mainly through 3 ways, including:
Through blood Through sex From mother to child If the mother is infected with HBV and has HBeAg (+), the chance of transmitting it to her baby is more than 80%; About 90% of babies are born with chronic HBV and 100% of liver cancers in children are caused by hepatitis B.
Therefore, women should actively vaccinate against hepatitis B to protect mother and child. The best time to vaccinate is before pregnancy so that the vaccine has enough time to create antibodies.
Viêm gan virus B là một bệnh phổ biến toàn cầu do virus HBV gây ra
2. So can pregnant women get hepatitis B vaccine?
According to recommendations, the hepatitis B vaccine is recommended to be given to women before pregnancy to have a certain time to create antibodies.
The hepatitis B vaccination schedule for adults includes:
1st dose: 1st time coming for injection. 2nd dose: 1 month after 1st dose: 3rd dose: 6 months after 1st dose. 1 booster dose 5-10 years after the previous injection. there. However, for some reason, if you do not get vaccinated against hepatitis B before you become pregnant, you can still get the hepatitis B vaccine during pregnancy, because this is an inactivated, safe vaccine. should not affect the fetus as well as the health of the pregnant mother.
Therefore, if you did not get vaccinated before becoming pregnant, you should still get vaccinated when you are pregnant.
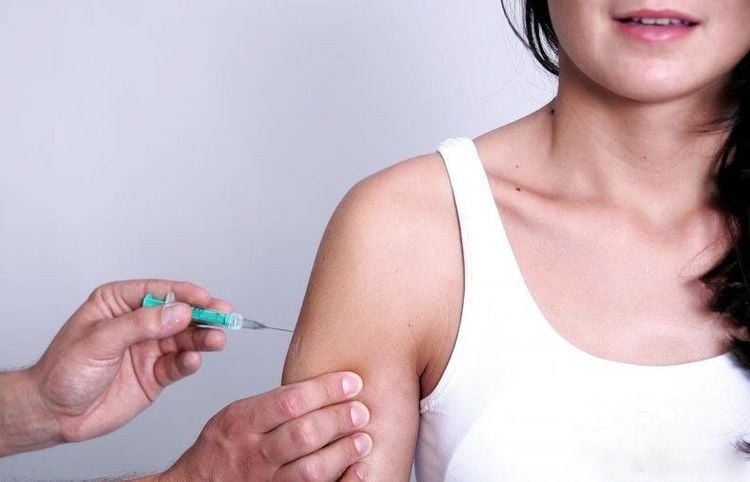
Vắc-xin phòng viêm gan B được khuyến cáo nên tiêm cho phụ nữ trước khi mang thai
3. Prevention of mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B
Pregnant women test positive for HBsAg (+):
Administer hepatitis B vaccine after giving birth to children according to the expanded immunization program, and combine it with injection of anti-HBV antibodies for children. Fully vaccinated children with hepatitis B vaccine according to the provisions of the expanded immunization program. Pregnant women who test positive for HBsAg (+) but have not received antiretroviral therapy should:
For pregnant women who are eligible: Treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. For pregnant women who do not meet the criteria: Monitoring and prevention of hepatitis B virus transmission from mother to child. Babies born to HBsAg-positive mothers should receive hepatitis B antisera and hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth. Then inject the child with all doses of hepatitis B virus vaccine as prescribed. For women on treatment for chronic hepatitis B who want to become pregnant, if on treatment with a drug other than TDF, switch to TDF at least 2 months before becoming pregnant. For women found to be pregnant while on antiretroviral therapy for hepatitis B, continue TDF, if the drug is not TDF, switch to TDF.
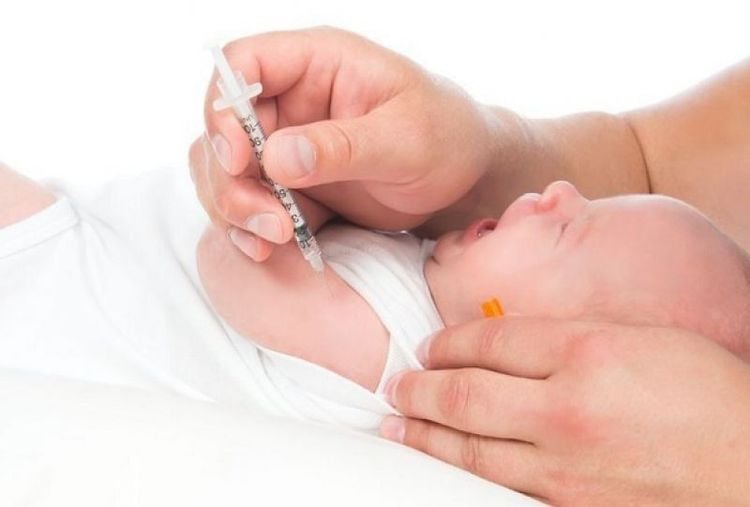
Tiêm vắc-xin viêm gan B liều sau sinh cho trẻ theo chương trình tiêm chủng mở rộng
In case of pregnant women with HBV DNA load > 200,000 IU/mL or quantitative HBsAg > 104 IU/mL need:
Monitor the mother's status and HBV DNA load within 24 weeks postpartum. Use TDF from 24 - 28 weeks of pregnancy, later should start at least 4 weeks before delivery, then continue treatment 4 - 12 weeks postpartum. Testing for HBsAg and anti-HBs for children > 12 months old to assess the status of hepatitis B virus infection. At Vinmec International General Hospital, a package maternity service is available as a solution to help pregnant mothers feel secure because had the companionship of the medical team throughout the pregnancy. When choosing Maternity Package, pregnant women can:
The pregnancy process is monitored by a team of qualified doctors Regular check-up, early detection of abnormalities Maternity package helps to facilitate the process. birthing process Newborns get comprehensive care
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
MORE
Diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis B according to the guidelines of the Ministry of Health Transmission of hepatitis B virus from mother to child A handbook from A to Z on hepatitis B