This is an automatically translated article.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that affects the health of the liver. The hepatitis B virus is transmitted through contact with blood or body fluids or through sex without a condom. In particular, pregnant women can transmit hepatitis B virus to their babies during vaginal delivery or cesarean section.
1. How does a pregnant woman with hepatitis B pass it on to her baby?
Hepatitis B can also be spread when blood, semen or other body fluids from an infected person enter the body of a healthy person. When a pregnant woman is infected with the hepatitis B virus, it can be passed on to the fetus. In the first 3 months of pregnancy, the rate of infection from mother to baby is 1%, if the mother is sick in the second 3 months of pregnancy, the rate of infection to the baby is 10% and will increase the rate of transmission. 60-70% if the mother is infected in the last 3 months of pregnancy. The virus is highly contagious and easily penetrates damaged skin or in soft tissues such as the nose, mouth, and eyes. It is even possible to become infected with the hepatitis B virus with a small amount of blood.

Sản phụ có thể truyền virus viêm gan B sang con trong quá sinh thường hoặc sinh mổ
2. Is it dangerous for pregnant women to have hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B virus infection is unlikely to cause any problems that put you or your unborn baby at risk during pregnancy. It is important for your doctor to know about your hepatitis B infection to monitor your health and protect your baby from hepatitis B virus infection after birth.
3. How can I protect my unborn baby from hepatitis B infection?
For pregnant women infected with hepatitis b, this shows that the hepatitis B virus is present in the blood and can be transmitted to the baby during pregnancy or labor.
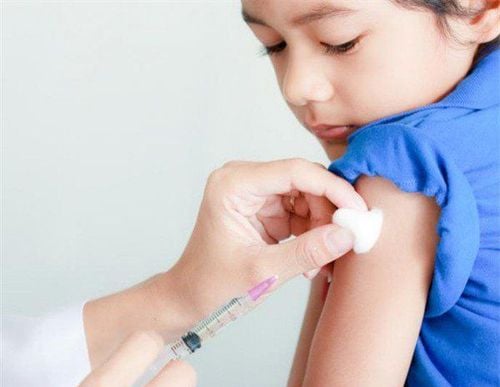
For these cases, the doctor will protect the baby by giving hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B specific immune globulin (Hepatitis B Immune Globulin, abbreviated HBIG) right after birth. These initial shots will give your baby protection from the hepatitis B virus. Both vaccines and immunoglobulins are safe and effective products so mothers with hepatitis B can safely breastfeed their babies, as long as the baby has received immunoglobulins and vaccines.
At follow-up shots, your baby will need to continue getting the hepatitis vaccine at 6 weeks, 3 months, and 5 months of age. This vaccine protects 95% of babies from hepatitis B infection.
At nine months of age, your baby will need a blood test to check for protection against hepatitis B or if your baby is already infected with the virus. If the child does not have protective antibodies, the doctor will prescribe two more doses of hepatitis B vaccine.
Bảo vệ trẻ bằng cách tiêm vắc-xin viêm gan B và Globulin miễn dịch đặc hiệu viêm gan B
Failure of hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG can occur in pregnant women who have a positive HBeAg test and have a very high viral load, so there is a high probability that hepatitis B can be passed on to the fetus. pediatric. Viral loads greater than 200,000 IU/mL or 1 million cp/ml indicate the extent to which the combination of hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG given at birth may have failed. Therefore, the mother will be first treated with an antiviral drug such as tenofovir, and then an antiviral drug including telbivudine or lamivudine will be given. Antiretroviral therapy begins at 28-32 weeks and continues for 3 months postpartum.
Vinmec International General Hospital uses a source of high quality vaccines, of clear origin, suitable for the age to be vaccinated, ensuring safety from registration, storage to use. Before vaccination, all customers are screened before vaccination with specialist doctors to ensure the best health when vaccinated. 100% of vaccinated customers are monitored and re-evaluated before leaving. In particular, the post-vaccination monitoring room is fully equipped with emergency facilities; the team of doctors - nurses are trained in anaphylaxis emergency management to ensure timely and correct treatment when an incident occurs.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Cdc.gov, Healthed.govt.nz