This is an automatically translated article.
Potato is a food source with many vitamins and minerals, which can bring many health benefits such as anti-inflammatory, pain relief, immune system booster,... In addition, potatoes are also a food. has beauty benefits.
1. Nutritional composition of potatoes
Potato is a healthy food, but the benefits that potatoes bring in the diet depend on: how it is prepared, how it is combined with other foods or how it is stored.. .. Whole potatoes are a relatively low-calorie food. Besides, it also provides important nutrients, such as vitamin C, vitamin B6 and minerals.
A serving containing 100 grams of potatoes will have a nutritional profile including: 94 calories; 0.15 grams of fat; 0 grams of cholesterol; 21.08 grams of carbohydrates; 2.1 grams of fiber; 2.10 grams of protein; 10 milligrams of calcium; 0.64 mg iron; 27 mg of magnesium; 75mg phosphorus; 544 mg of potassium; 12.6 mg vitamin C; 0.211 mg vitamin B6; 38 micrograms of folate... In addition, potatoes provide niacin, choline and zinc.
Unprocessed potatoes contain very little sodium, only 10mg per 100g. However, this is in contrast to products made from potatoes, such as french fries, which are quite high in sodium.
Potatoes also contain a compound alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), which helps the body convert glucose into energy. Some evidence suggests that alpha-lipoic acid may help control blood sugar, improve vasodilation, protect against diabetic retinopathy, and preserve brain and nerve tissue.
Quercetin is a type of flavonoid found in potato skins, and at the same time it has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, protecting the body's cells from damage caused by free radicals. Potatoes contain vitamin C, which acts as an antioxidant. The role of antioxidants may help prevent cell damage and cancer, and promote healthy digestive system and cardiovascular function. The fiber in potatoes plays a role in maintaining a healthy digestive and circulatory system.

Khoai tây chứa lượng lớn vitamin C và các chất chống oxy hóa
2. What are the benefits of eating potatoes?
In fact, when you include potatoes in your diet, it can contribute to a healthy lifestyle, including preventing osteoporosis, maintaining heart health as well as reducing the risk of infections. Here are some health benefits of potatoes:
2.1. Bone Health Minerals including: Iron, phosphorus, calcium, magnesium and zinc in potatoes all help the body build and maintain bone structure and strength. Furthermore, Iron and zinc play important roles in collagen production and maturation.
Phosphorus and calcium are both important in bone structure, but it's important to balance these two minerals for proper bone mineralization. Too much phosphorus and too little calcium lead to bone loss and contribute to osteoporosis.
2.2. Blood pressure Low sodium levels are essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure, but increasing potassium intake is equally important. Potassium is a substance that aids in vasodilation or widening of blood vessels.
According to the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), less than 2% of American adults meet the 4,700-milligram daily recommendation.
In addition, minerals such as potassium, calcium and magnesium are present in potatoes. These minerals have all been shown to naturally lower blood pressure.
2.3. Heart Health Potatoes are packed with fiber, potassium, vitamin C and vitamin B6 along with a lack of cholesterol, all of which support heart health. Potatoes are foods that contain a significant amount of fiber. Fiber plays a role in helping to lower total blood cholesterol, thereby reducing the risk of heart disease. Research based on NHANES has found an association of high potassium and sodium consumption with a reduced risk of death from heart disease.

Khoai tây có ảnh hưởng tích cực đến sức khỏe tim mạch
Maintains the structure of cell membranes Transmits nerve impulses Fat absorption Early brain development The choline content in one large potato contains 57 mg. The daily requirement for adult men is 550 mg, and women are 425 mg.
2.5. Cancer Potatoes also contain folate. Because, folate is involved in DNA synthesis and repair. Therefore, it will prevent many types of cancer cells from forming due to mutations in DNA.
Fiber intake from vegetables, including potatoes, has also been linked to a reduced risk of colorectal cancer.
2.6. Digestion The fiber content in potatoes helps prevent constipation while promoting regularity for a healthy digestive tract.
2.7. Weight management and satiety Fiber is generally recognized as an important factor in weight management and weight loss. They act as bulging factors inside the digestive system. With this activity, they will increase satiety and reduce cravings. So, when using potatoes, you will feel full for longer and are less likely to consume more calories.
Khoai tây có vai trò quan trọng trong việc quản lý cân nặng
2.8. Metabolism Potatoes are an excellent source of vitamin B6. This vitamin plays an important role in energy metabolism, by breaking down carbohydrates and proteins into glucose and amino acids. These are simple compounds that can easily be used for energy by the body.
2.9. Skin Collagen is the support system of the skin. And in potatoes, the vitamin C content is quite high. This will help protect the skin because vitamin C acts as an antioxidant to help prevent damage from the sun, pollution and smoke. Furthermore, vitamin C also helps collagen smooth wrinkles and improve overall skin texture.
2.10. Immunity Several studies have found that vitamin C may help reduce the severity and duration of colds. Potatoes are a rich source of vitamin C.
3. Some risks when using potatoes
Potato plants, along with tomatoes and eggplants, belong to the ornamental family. Some of these plants often contain a number of toxins that affect health. Potatoes were previously thought to be inedible. Because, potato shoots and leaves have toxins such as:Solanin: Potatoes that have sprouted or are discolored may contain solanin. The compound was found to cause circulatory and respiratory problems, as well as headaches, muscle cramps, and diarrhea. If a potato has definitely sprouted or has formed "eyes," it is enough to remove all the sprouts. However, if the potato is shriveled or has a green color in the skin, it should not be eaten.
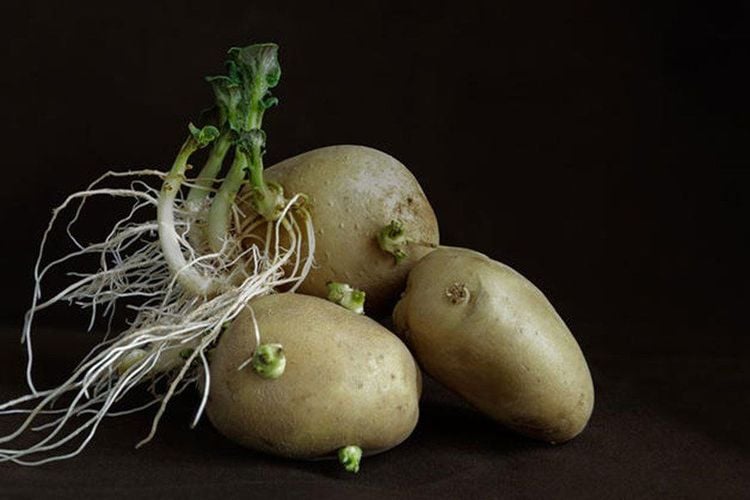

Khoai tây mọc mầm chứa Solanin gây ảnh hưởng đến sức khỏe người dùng
Acrylamide: Studies have shown that potatoes when cooked above 120 degrees Celsius produce a chemical known as acrylamide. This compound is found in plastics, glues, dyes and cigarette smoke. Acrylamide has been implicated in the development of some cancers. Furthermore, it also has neurotoxic properties and it can have negative effects on genes and reproductive health. If you have any questions about nutrition, you can leave a question in the ASK DOCTOR VINMEC section on the website. The question will be consulted by the doctor and sent to you as soon as possible.
The article is referenced at the source: Nutrition.org.uk