This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Huy Nhat - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.
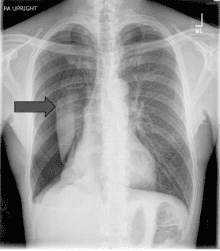
Pneumothorax or pleural effusion are considered common diseases related to respiratory function today. One of the methods of treating this disease is opening the pleura and placing a pleural drain. Minimal pleural drainage is a measure to release the compressed pleural space, which requires clear indications and follows specific procedures.
1. What is pleural drainage?
Besides the treatment methods of pneumothorax, pleural effusion such as conservative treatment, monitoring, aspiration of air and fluid in the pleural space with a needle, pleural drainage tube placement is an interventional treatment to release the pleural space from the compression of the fluid or air in it.Since minimal pleural drainage is a method of placing a pleural tube through the patient's chest wall, it is invasive, so it needs to be performed by qualified, technical, and experienced doctors and at the same time. must ensure the principles of drainage to treat pneumothorax and pleural effusion effectively.
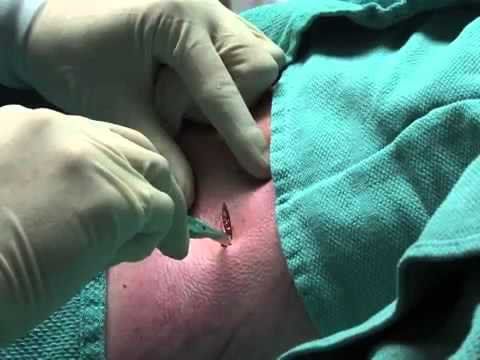
2. Indication for pleural drainage tube placement
In the following cases, doctors will prescribe minimal pleural drainage:Patients with effusion, pneumothorax leading to lung compression and ultimately affecting respiratory function or make it difficult to breathe. In patients with pneumothorax, pleural effusion recurred many times. Patients with empyema have indicated drainage to wash the pleural space. After trauma or complications after surgery leading to hemothorax. Malignant diseases leading to effusion, hemothorax need to be placed with a pleural drain tube to cause pleural adhesions. Patients with trauma leading to pneumothorax require artificial ventilation. In case of chronic pneumothorax, open pneumothorax, with valve... Patients with pneumothorax but treated with methods such as aspiration and catheterization failed.
3. Contraindications to thoracocentesis
Placing a thoracocentesis tube usually has no absolute contraindications, but when performing it, it is also necessary to pay attention to the following cases:Patients with problems with coagulation - hemostasis, specifically: when laboratory tests show prothrombin ratio <50%, and/or platelet count <50 g/L. Patients with hemodynamic problems Patients with a history of thoracic surgery or who have had pleural adhesions at the intended site of pleurectomy, causing skin lesions.
4. Preparing to place a pleural tube
4.1 Patient preparation The person performing the thoracentesis procedure has the duty to clearly explain the thoracentesis procedure to the patient and the patient's family. Have the patient's family member and the patient sign the agreement to perform the procedure. Prepare psychologically and encourage the patient to feel secure and worry-free before and during the procedure. Let the patient go to the bathroom before performing the thoracentesis. Test the Xylocaine response on the patient. Administer intramuscularly to the patient with Atropin 0.25 mg, administered approximately 15 to 30 minutes prior to the procedure. Inject pain medication to the patient 15 minutes before the pleural tube is inserted. 4.2 Prepare equipment 1 sterile tray. Aseptic chancre consists of 1 closed and 1 perforated chancre. Surgical gown, mask, sterile gloves. Betadine 10% antiseptic solution and 70° alcohol. Xylocaine 2% local anesthetic. Atropin solution 1/4mg x 2 ampoules. First aid supplies and medications include adrenaline 1mg, methylprednisolone 40mg, intubation kit, Ambu balloon, sputum aspirator, and oxygen system. Syringe 20ml, N2 gauze, scalpel, 20g needle, 2 sets of suture needles. pleural drainage tube size 28-31G. The thoracentesis set includes 1 curved pince, 1 needle clamp, 2 hemostatic pinces, 1 surgical dissection with nodule and 1 dissection without a node, 1 suture scissors, and 1 sphincter forceps. Three-pot pleural drainage system.
5. Steps to perform pleural drainage tube placement
To conduct thoracocentesis, it is necessary to go through the following steps of examination and technical implementation:Check that the patient's medical record has all the necessary laboratory results for surgery. surgery, such as chest X-ray, computed tomography scan, total peripheral blood cell analysis, blood coagulation function test, blood chemistry... Recheck the patient's status, condition hemodynamic, respiratory, cardiovascular, coordination ability when placing pleural drainage tube. Place the patient in a semi-recumbent position, with the head elevated at an angle of 30°, and administer pre-anesthetic injections to the patient if necessary. Wear a hat, mask, surgical gown, and sterile gloves. Locate the thoracocentesis at 4-5 anterior axillary intercostals for pneumothorax and 4-5 or 5-6 midaxillary intercostals for pleural effusions. Disinfect the area where the pleural drainage tube is placed. Inject local anesthetic to the patient right at the pleural opening area, anesthetic layer by layer, from the skin to the parietal leaf of the pleura, taking care not to let the anesthetic come into contact with the vascular lumen. Simultaneously, an anesthetic needle is used to probe the pleural space. Using a scalpel, make an incision in the upper border of rib No. 6 about 0.5-1cm, then use a pince without a node to remove the subcutaneous tissue pointing the pince towards the upper border of rib No. 5, firmly pressing the palm of your hand through the muscles. In the case of pneumothorax, the intercostal space and wall of the pleura can be heard when the pince's nose touches the pleural space. Separate the two pince ends just enough to open the hole for the drainage tube to be inserted into the pleura, bring the tube forward and up to the midclavicular line in case of pneumothorax, and if it is effusion pleural cavity, the tube is moved posteriorly and downward. Place the pleural tube about 2-3cm deep for preterm patients, 3-4cm for full term babies and check for air or discharge. Stitch to fix the drain. Position the patient in a comfortable drainage position and notice any problems that arise during movement. Attach the other end of the tube to the continuous pleural drainage aspirator. In case of pneumothorax, it is possible to sew a U-shaped suture around the tube to close the hole in the chest wall when the drain is removed. Record the time, date, time, and name of the person who placed the drain. An X-ray examines the position of the drain tip and the pleural space. After thoracocentesis, the patient should be monitored for the following, including vital signs and drainage system (aspiration pressure, volume, and color of pleural fluid). Placing a pleural drainage tube is an interventional procedure that can leave some important complications such as bleeding, organ damage, infection, etc., so in the process of performing pleural drainage, it is necessary to ensure minimal care. protected according to basic principles such as aseptic, one-way, hermetic, continuous with controlled pressure.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals with a team of quality doctors and nurses, who are leading experts of the departments, highly qualified, experienced and famous in the industry. Comprehensive professional cooperation with major domestic and foreign hospitals (USA, Japan, Singapore) gives patients the best treatment conditions.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.