This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Nguyen Van Duong - Interventional Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.Normally, blood clots are formed when the body is injured, they act as hemostatic plugs, helping to prevent blood from flowing out. However, in certain cases, these clots appear at the wrong time inside the blood vessel lumen. This can lead to serious health problems, such as a heart attack, or a stroke.
1. How are blood clots formed?
Normally, arteries carry blood from the heart to other organs in the body, and then veins send blood back to the heart. Sometimes, blood flow through these vessels is slowed or obstructed during circulation.When blood cells stick together, they form blood clots. This condition is called thrombosis. The extent to which these clots affect the body will depend on their location in the body.
2. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Deep veins are usually located deep inside your body and away from your skin. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition that mainly occurs in the veins of the legs or thighs (lower extremity thrombosis), sometimes they can appear in the brachial or subclavian veins (extremity thrombosis). above).Small blood clots can dissolve on their own, but for large clots, they often cannot move or disappear, thereby blocking blood flow in the vein. They will even become more dangerous if they break off and travel to the lungs.
3. Pulmonary embolism (PE)
This is a condition in which blood clots form somewhere else and travel through the body's bloodstream to the lungs. Usually, a blood clot will form in a vein in the leg or pelvis. When these blood clots form in the abnormal lungs, they can block blood flow in the lungs.In addition, it can also harm other organs in the body because the lungs cannot supply the required amount of oxygen. If the clot is very large, or there are too many blood clots in the body, a pulmonary embolism (PE) can lead to death if not treated promptly.
4. Deep vein thrombosis of lower extremities
This usually occurs when a blood clot forms in a vein in the thigh or lower leg area. It usually doesn't cause specific symptoms, but sometimes you may feel some swelling, redness, and pain in your legs.The formation of blood clots in the veins of the lower extremities stems from a variety of causes, including after surgery, lying or sitting for too long, taking oral contraceptives, or having had a deep vein thrombosis (DVT). before.
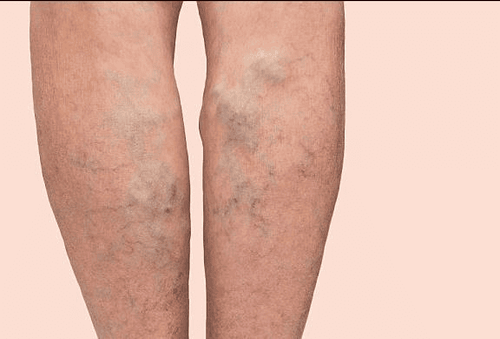
5. Paget-Schroetter Syndrome (PSS)
Paget-Schroetter syndrome is a rare type of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) that occurs mostly in healthy young adults who play sports that use their upper arms a lot, such as swimming. or baseball.With this syndrome, veins can be compressed by the muscles around them. From this pressure combined with repetitive hand movements can lead to a higher risk of blood clots forming on the body's shoulders. Some of the common symptoms of PSS syndrome include swelling, chest pain, and a sudden blue coloration. This is a medical emergency because it can be life-threatening if not treated immediately.
6. Heart attack (heart attack)
The arteries in the heart can be narrowed by plaque. When a blood clot forms on these plaques (caused by a ruptured or cracked plaque), it impedes blood flow to the heart. If this condition is not treated quickly, part of the heart muscle will die. Patients may notice a sudden heart attack, accompanied by chest pain when it occurs. For women, some other symptoms can occur without chest pain, such as fatigue or back pain.7. Superior vena cava thrombosis
The superior vena cava is one of the main veins, responsible for carrying blood from the upper parts of the body towards the heart. Blood clots can form when you place a central venous catheter (which delivers medicine into the body) in a vein near your heart. Your doctor may remove this catheter to treat or remove blood clots. In certain cases, patients may need to take blood thinners to prevent the formation of blood clots.8. jugular vein thrombosis
Normally, two veins in the neck carry blood from the head and neck back to the heart. Blood clots tend to form in these veins when a catheter is placed inside them.In addition, some other factors such as cancer, surgery or intravenous drug use can also cause jugular vein thrombosis. In extreme cases, these blood clots are at risk of breaking off, then traveling to the lungs and causing a pulmonary embolism (PE).
9. Thrombotic stroke

When you have a stroke, you need to get emergency care quickly because it can lead to long-term health problems, such as affecting the ability to talk or paralysis on one side of the body. The sooner a stroke is treated, the better the chance of brain recovery for the patient.
10. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
This is one of the rare types of stroke, occurs when a blood clot in the brain stops blood from flowing out and back to the heart. The backup blood can then leak into the brain tissues and lead to a stroke.Venous sinus thrombosis mainly occurs in infants, children and young people. If not treated in time, this type of stroke can lead to death.
11. Cavernous sinus thrombosis
Cavernous sinus thrombosis is a relatively uncommon condition that occurs when blood clots form in a vein that runs through the space behind the eye socket.The main cause of this condition is an infection that spreads from the nose, face, teeth, sometimes also from trauma. With cavernous sinus thrombosis, people often experience eye problems, such as pain, swelling, drooping eyelids, and find it difficult to control eye movements.
12. Retinal vein occlusion
It is one of the leading causes of vision loss in the elderly. This condition can occur when a blood clot blocks blood flow in the central vein of the retina (tissue lining the back of the eye). When blood leaks out, it can lead to serious vision problems, such as glaucoma or retinal detachment.
13. May-Thurner . Syndrome
The right iliac artery carries blood to the right leg of the body, while the left iliac vein carries blood from the left leg back to the heart. These two blood vessels usually intersect in the pelvis. With May-Thurner syndrome, an artery can press on a vein in the spine, causing blood clots to form in the left leg. This syndrome usually affects mainly young women with sudden swelling in the lower body.14. Portal vein thrombosis
Normally, the portal vein plays an important role in transporting blood from the digestive tract and spleen to the body's liver. People who have cirrhosis or are prone to blood clots are at increased risk of portal vein thrombosis.This condition usually does not cause specific symptoms and may not require intervention of treatments. However, in cases where pressure builds up in the vein behind the blood clot, it can cause the spleen to enlarge, swell the abdomen, and cause bleeding. When these symptoms appear, the patient needs to be treated early to prevent the clot from increasing in size.
15. Budd-Chiari . syndrome
Budd-Chiari syndrome occurs because a blood clot blocks or narrows the veins that carry blood from the liver to the body's heart. Although the nature of this syndrome is not the same as that of portal vein thrombosis, its symptoms are similar, including splenomegaly, abdominal swelling, and bleeding. In addition, Budd-Chiari syndrome often causes liver problems, impairing liver function, and patients may even need liver transplant surgery.16. Renal vein thrombosis
Nephrotic syndrome is one of the leading causes of blood clots in one of the two veins that carry blood out of the kidneys. People may not have any symptoms when they have slow-growing blood clots. However, blood clots that appear suddenly can cause pain in the lower back and blood in the urine.Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com