The development of information technology helps everyone easily access a vast source of information. However, many people still lack a true understanding of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), leading to situations where they contract illnesses without knowing why.
1. Images and information about sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
1.1. Genital warts (HPV)
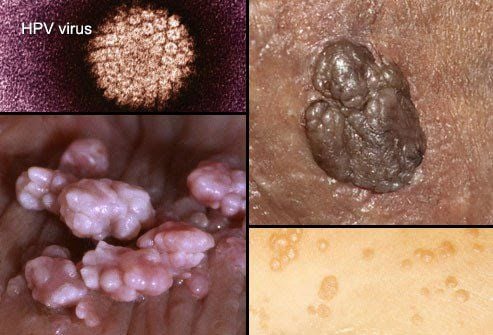
Genital warts are caused by the HPV virus, which spreads through unsafe sexual activity. HPV can even spread through skin-to-skin contact. Some types of the virus that cause warts are often harmless, but others can lead to cervical or anal cancer. Currently, vaccines are available to protect us from some of the most dangerous HPV strains.
The signs include:
- Warts are pink or flesh-colored raised, flat-surfaced, or cauliflower-shaped.
- Apart from the warts, patients usually have no symptoms.
1.2. Pubic lice

Pubic lice infestation is also considered a sexually transmitted disease (STD). These lice can crawl from one person to another during close contact. They can be eliminated with certain medications.
- Symptoms of pubic lice infestation include:
- Severe itching in the pubic hair region.
- Small eggs attached to pubic hair.
- Visible lice crawling.
1.3. Scabies
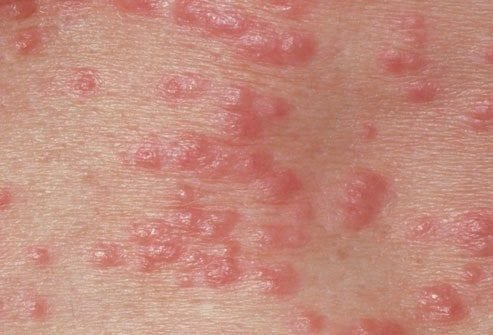
Scabies is caused by small mites burrowing into the skin to lay eggs. It does not always spread through sexual contact and can spread through any form of skin-to-skin contact. Among younger individuals, scabies is often transmitted through unsafe sexual activity. It can be treated with topical creams.
- Symptoms of scabies include:
- Intense itching, especially at night.
- A rash resembling pimples.
- Symptoms may appear 2–6 weeks after exposure to an infected person.
1.4. Gonorrhea
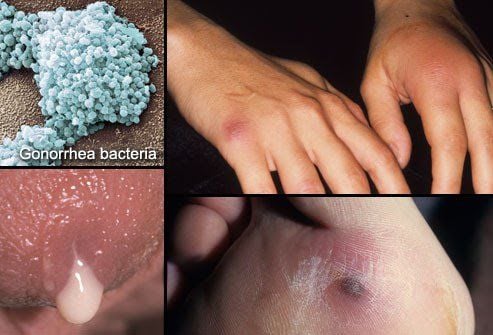
Gonorrhea is caused by the bacterium Gonorrhea bacteria, which spreads easily through unsafe sexual activity. If untreated, it can lead to infertility in both men and women. Antibiotics can help stop this infection.
Symptoms of gonorrhea include:
- Burning sensation during urination and ejaculation in men.
- The infection may later cause a skin rash or spread to joints and lead to blood infections.
- In men: Discharge from the penis and swollen testicles.
- In women: Vaginal discharge, pelvic pain. Symptoms may be mild and often confused with urinary tract infections.
1.5. Syphilis
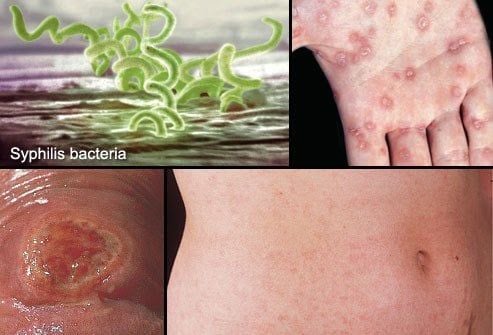
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease caused by unsafe sexual activity. Most people do not notice early symptoms. If untreated, it can lead to severe complications, including paralysis, blindness, and death. Syphilis can be cured with antibiotics.
Symptoms of syphilis include:
- The first sign is usually firm, round, painless sores on the genitals or anus.
- The disease spreads through direct contact with these sores.
- Patients may later experience rashes on their palms and other parts of the body.
- Patients may experience fever, hair loss, or fatigue.
- In late stages, symptoms appear due to damage to organs like the heart, liver, brain, nerves, and eyes.
1.6. Chlamydia
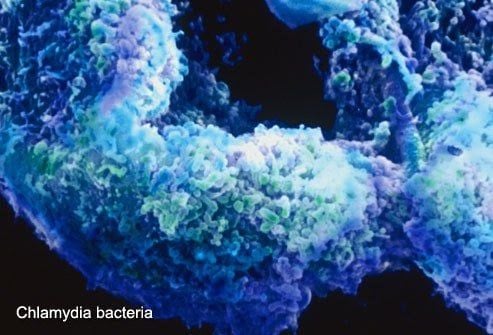
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted disease caused by the Chlamydia bacterium. If untreated, it can lead to infertility. It can be treated quickly with antibiotics. However, the disease often goes undetected due to vague or absent symptoms. Chlamydia can also cause throat and rectal infections from oral or anal sexual activity.
Symptoms of chlamydia include:
- In men: Itching at the tip of the penis, discharge, pain during urination.
- In women: Vaginal itching, discharge that may have an odor, pain during urination and intercourse.
1.7. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 (HSV-1)
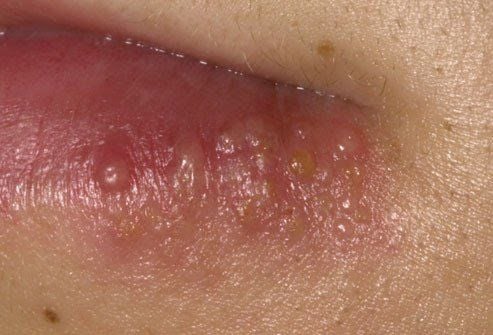
Herpes simplex virus 1 causes herpes on the lips and is not typically a sexually transmitted disease. It spreads easily among family members through kissing. However, it can also cause genital infections through unsafe oral sex.
Symptoms of the disease include: sores or blisters on the lips. Small blisters or ulcers may also appear on the genitals.
1.8. Herpes Simplex Virus 2 (HSV-2)
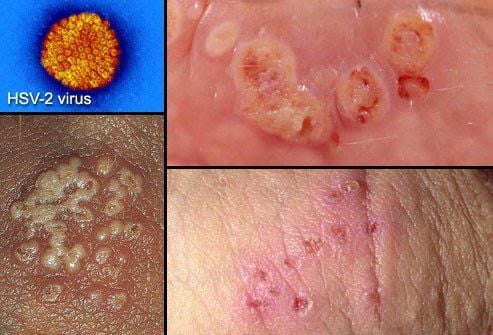
Most cases of genital herpes are caused by Herpes Simplex Virus type 2 (HSV-2). It spreads easily through intercourse or direct contact with sores. Similar to HSV-1, there is currently no cure for the disease. Antiviral medications only help reduce the frequency of outbreaks and relieve symptoms more quickly.
Symptoms of genital herpes include:
- Fluid-filled blisters that form painful sores and scabs on the genitals, anus, thighs, or buttocks.
- Blisters may also appear on the lips through oral sex.
1.9. Hepatitis B
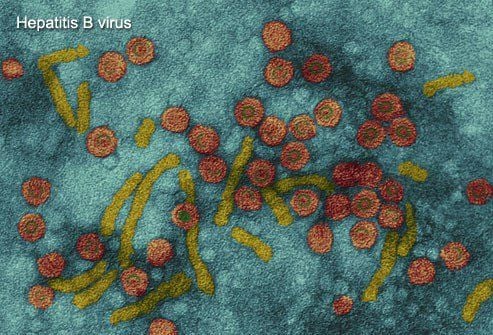
The hepatitis B virus is a "silent" virus that can cause severe liver damage. It is called "silent" because many people carry the virus without showing symptoms, unknowingly transmitting it to others. It spreads through direct contact with the blood and bodily fluids of infected individuals.
People can become infected through sexual activity, sharing needles, sharing razors or toothbrushes, or during childbirth from mother to child. There is currently no cure, but antiviral medications can control the hepatitis B virus. Vaccines are also available to prevent hepatitis B.
Symptoms of hepatitis B:
- Many people have no symptoms for years.
- During acute infections, patients may experience nausea, abdominal pain, dark urine, fatigue, and yellowing of the skin or eyes.
- Chronic infections can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer.
1.10. HIV/AIDS
The HIV virus weakens the body's defense mechanisms, leaving the patient unable to fight common infections. HIV spreads through unsafe sexual contact, sharing needles, or from an infected mother to her child during birth. It may not cause symptoms for many years, so the best way to detect it is through a blood test.
Timely treatment is essential to prevent serious complications. If you have been exposed to HIV, starting medication immediately can help prevent infection. For those already infected, treatments can prevent HIV from progressing to AIDS.
Currently, there is no cure for HIV, but medications can suppress the virus's multiplication in the body. Additional treatments can help prevent or combat severe infections if the immune system has been weakened.
Symptoms of HIV/AIDS include:
- Many patients have no symptoms.
- Some may experience flu-like symptoms one to two months after infection: swollen lymph nodes, fever, headache, and fatigue.
- Mouth canker sores may also occur.
1.11. Trichomonas
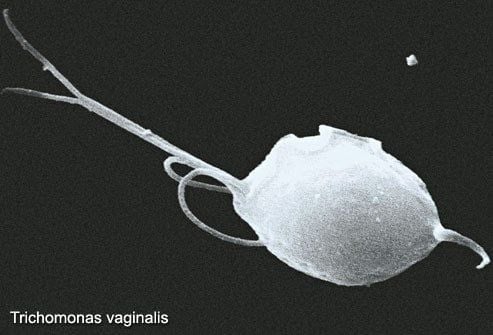
Trichomoniasis is caused by a parasite named Trichomonas vaginalis. The disease spreads through unsafe sexual activity. There is medication available to treat this condition.
Symptoms of trichomoniasis include:
- In men: Most men have no noticeable symptoms. Some may experience minor discharge or a slight burning sensation during urination.
- In women: Yellow-green discharge with a foul odor, vaginal itching, or pain during intercourse or urination. Symptoms usually appear 5–28 days after infection.
1.12. Chancroid
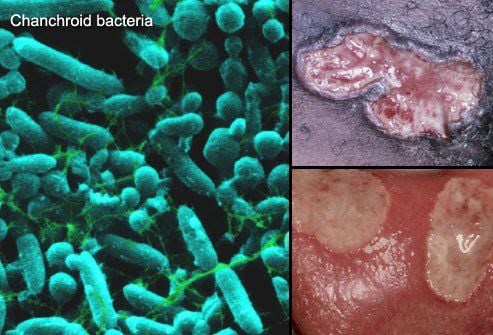
Chancroid is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the Chancroid bacterium. It is common in Africa and Asia but rare in the United States. The disease causes genital sores. Antibiotics can treat chancroid.
Symptoms of chancroid include:
- In men: Painful lumps on the penis that may develop into pus-filled sores, genital pain, and groin pain.
- In women: Painful sores in the genital area, swollen lymph nodes in the groin.
1.13. Lymphogranuloma Venereum (LGV)
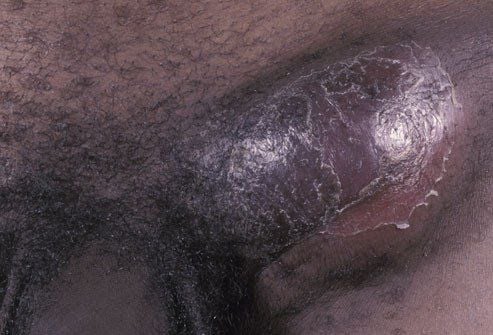
Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV), also known as genital lymphatic granuloma, is caused by a rare form of chlamydia in the United States. It is more common among men who have sex with men. Like other types of chlamydia, it can be cured with antibiotics.
Symptoms of LGV include:
- Open sores on the genitals or anus.
- Patients may experience headaches, fever, and fatigue.
- Swollen lymph nodes in the groin.
- If spread through anal sex, LGV may cause rectal bleeding or discharge.
1.14. Pelvic inflammatory disease
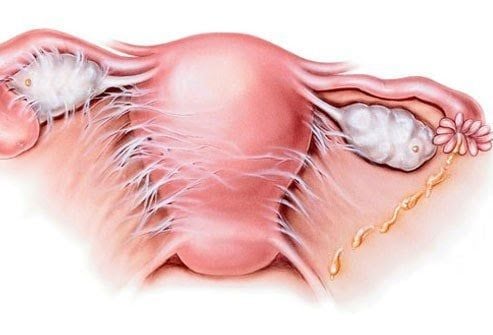
Pelvic inflammatory disease is not a sexually transmitted disease, but it is a severe complication of untreated sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), particularly chlamydia and gonorrhea.
It occurs when bacteria spread and infect the uterus and other female reproductive organs. Timely treatment is crucial to prevent infertility.
Symptoms of pelvic inflammatory disease include:
- Lower abdominal pain, and fever.
- Abnormal discharge.
- Pain during intercourse or urination.
- However, the disease often has no warning signs.
2. Who is at risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)?
Anyone who is sexually active is at risk of contracting STDs, regardless of gender, race, social class, or sexual orientation. Teenagers are more prone to STDs than older adults.
Statistics show that by age 25, half of all sexually active adults will have contracted an STD. Those with multiple sexual partners are at higher risk. Some STDs are on the rise among men who have sex with men, including syphilis and LGV.
3. Can virgins contract sexually transmitted diseases?
Virgins can still contract sexually transmitted diseases, as many STDs spread through any form of sexual activity, including skin-to-skin contact and oral sex. This is especially true for STDs that cause lesions or sores on the genitals.
4. How to prevent sexually transmitted diseases?
The best way to avoid contracting STDs is to avoid all unsafe sexual activity, practice monogamy, and ensure your partner is not infected. To reduce the risk of STDs, you can take the following actions:
- Ask your partner if they have any sexually transmitted diseases.
- Request your partner to get tested before engaging in sexual activity.
- Use condoms.
- Avoid sexual contact if your partner shows signs of STDs.
- Learn how to recognize the symptoms of STDs and get regular health check-ups.
5. Can condoms completely prevent sexually transmitted diseases?
As everyone knows, condoms are effective in preventing the spread of some STDs, but they are not absolute.
Condoms can effectively prevent STDs such as:
- Gonorrhea
- Chlamydia
- HIV
- Trichomoniasis
- Condoms are less effective in protecting against diseases like:
- Herpes
- Syphilis
- Genital warts
This is because these diseases can spread through contact with skin lesions not covered by the condom.
Condoms have little to no ability to protect against pubic lice or scabies.
6. Should you tell your partner?
If you think you have contracted a sexually transmitted disease, you need to inform your partner as soon as possible. You may still infect them even if you have started treatment or are using condoms. For some sexually transmitted diseases, doctors even recommend treating both you and your partner simultaneously. This may be a difficult conversation, but it is undoubtedly beneficial for both of you.
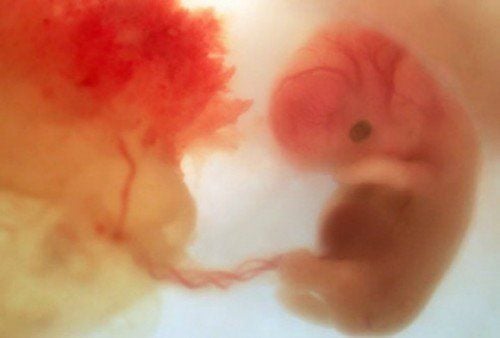
7. Sexually transmitted diseases and pregnancy
It is essential for pregnant women to get tested for sexually transmitted diseases. Many diseases can be transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or after the baby is born. The effects of STDs on the baby can include:
- Stillbirth
6. Should you tell your partner?
- Low birth weight
- Neurological problems
- Blindness
- Liver disease
- Severe infections
However, we now have treatments to minimize these risks. Treating STDs during pregnancy can cure certain diseases and reduce the risk of transmitting them to your baby.
8. Can sexually transmitted diseases recur?
Most treatments for sexually transmitted diseases do not protect you from the risk of contracting the disease again. A course of medication may cure gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia, or trichomoniasis, but if you are exposed to the causes of these diseases again, you can become reinfected.
If your partner is not treated, you may continue to infect each other repeatedly. Without proper prevention measures, you can quickly get reinfected or even contract another sexually transmitted disease.
There are many sexually transmitted diseases, and you can contract more than one at the same time if you do not know how to protect yourself. Although we have treatments for some diseases, there are still others for which we do not have cures, and they can lead to dangerous complications. Therefore, practicing safe sex is essential to prevent sexually transmitted diseases.
To make an appointment at the hospital, please dialHOTLINEor book directly HERE. Download and schedule an appointment automatically on MyVinmec application to manage, track schedules and book appointments anytime, anywhere right on the app.