This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Dr. Le Thi Huong - General Doctor - Department of Examination - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
Cancer prevention is an action taken to reduce the risk of cancer. Some risk factors for cancer can be avoided, but many cannot. Therefore, the risk factors that a person can control are called modifiable risk factors.
1. What is cancer prevention?
Cancer prevention is an action taken to reduce the risk of cancer. In addition to the physical problems and emotional pain caused by cancer, the high cost of treatment is also one of the burdens for patients, families and society. Preventing cancer has reduced the number of new cancer cases.
Cancer is not a single disease but a group of related diseases. Many related factors including our genes, lifestyle and environment can increase or decrease our risk of cancer.
Trắc nghiệm: Thử hiểu biết của bạn về bệnh ung thư
Ung thư là nguyên nhân gây tử vong hàng thứ 2 trên thế giới. Thử sức cùng bài trắc nghiệm sau đây sẽ giúp bạn có thêm kiến thức về yếu tố nguy cơ cũng như cách phòng ngừa bệnh ung thư.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
2. Factors that cause cancer Carcinogens Carcinogenesis is a series of steps that take place when a normal cell becomes a cancerous cell. Cells are the smallest units and make up the tissues of the body. Each cell contains genes that control the body's growth, development, and self-repair. There are many genes that control whether a cell lives or dies, divides (multiply), or takes on special functions, such as becoming a nerve or muscle cell. Changes (mutations) in genes occur during carcinogenesis. Changes (mutations) in genes can cause normal control mechanisms in cells to disrupt. When this happens, cells don't die when they should and new cells are produced when the body doesn't need them. The accumulation of extra cells can cause a mass (tumor) to form.
Environmental Cancer Risk Factors Scientists study risk and protective factors to find ways to prevent new-onset cancers. Anything that increases the chance of developing cancer is called a cancer risk factor; Anything that reduces the chance of developing cancer is called a cancer-protective factor. Some risk factors can prevent cancer, but many cannot. For example, both smoking and inheriting certain mutated genes are risk factors for some types of cancer, but only smoking can be avoided. Risk factors that a person can control are called modifiable risk factors. Many other factors such as our environment, diet or lifestyle can cause cancer. . Therefore, you should follow a healthy lifestyle, eat scientifically and live and work in a clean environment are simple but effective ways to prevent cancer.
Infections Some viruses and bacteria can cause cancer. For example, the human papillomavirus (HPV) increases the risk of cancers of the cervix, penis, vagina, anus, and oropharynx. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses increase the risk of liver cancer. The Epstein-Barr virus may increase the risk of Burkitt lymphoma. Helicobacter pylori bacteria increase the risk of stomach cancer.
Two vaccines to prevent infection with cancer-causing agents are the hepatitis B vaccine and the HPV vaccine that prevents cervical cancer. Therefore, these two vaccines should be given to prevent cervical cancer and liver cancer.
Radiation Exposure to radiation is one of the causes of cancer. There are two main types of radiation that are associated with an increased risk of cancer. These are ultraviolet radiation from sunlight (the main cause of non-melanoma skin cancers) and ionizing radiation.
Studies show that ionizing radiation causes leukemia, thyroid cancer and breast cancer in women. Ionizing radiation can also be linked to myeloma and cancers of the lung, stomach, colon, esophagus, bladder, and ovaries. Exposure to radiation from diagnostic X-rays increases the risk of cancer in patients and radiologists. Diagnostic radiation in children and adolescents is associated with a higher risk of cancer at a young age.
The increased use of CT scans over the past 20 years has increased exposure to ionizing radiation. Cancer risk also increases with the number of CT scans a patient has and the dose of radiation used each time.
Immunosuppressive drugs after organ transplant increase cancer risk Immunosuppressive drugs are used after an organ has been transplanted from one person to another. These drugs prevent a transplanted organ from being rejected.
Immunosuppressants are associated with an increased risk of cancer because they decrease the body's ability to prevent cancer from forming. The risk of cancer, especially viral cancer, in the first 6 months after an organ transplant is higher, but the risk persists for many years.
Lifestyle Food and diet: being studied as a risk factor for cancer. It is difficult to study the effects of diet on cancer because a person's diet includes foods that may protect against cancer and foods that may increase risk. cancer muscle. Diets high in fat, protein, calories, and red meat increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
Alcohol consumption: Studies have shown that drinking alcohol is associated with an increased risk of the following types of cancer: Oral cancer. Stomach cancer. Breast cancer. Colorectal cancer (in men). Drinking alcohol can also increase the risk of liver cancer and colorectal cancer in women.
Less physical activity: Physically active people have a lower risk of certain cancers than physically inactive people. There is a strong link between physical activity and a reduced risk of colorectal cancer. Physical activity protects against postmenopausal breast cancer and endometrial cancer.
Obesity: Obesity is associated with a higher risk of the following types of cancer: Postmenopausal breast cancer. Colorectal cancer. Endometrial cancer. Stomach cancer. Kidney cancer. Pancreatic Cancer.
Diabetes: Diabetes can increase the risk of the following types of cancer: Bladder cancer, breast cancer in women, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, liver cancer, lung cancer, oral cancer, oropharyngeal cancer....
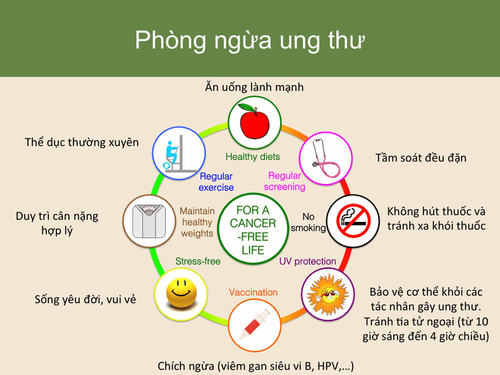
3. Interventions to reduce cancer risk
An intervention is a treatment or action taken to prevent or treat disease, or to improve health in other ways.
Chemotherapy is the use of substances to reduce the risk of cancer or prevent it from coming back. These substances can be natural or created in a laboratory. Several chemopreventive agents are tested in people at high risk for a certain type of cancer. Risk may be due to precancerous conditions, family history, or lifestyle factors.
Taking one of the following agents may reduce the risk of cancer:
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMS) such as tamoxifen or raloxifene have been shown to reduce the risk of breast cancer in women high risk. SERMS can cause side effects, such as hot flashes, so they are not commonly used for cancer prevention. Finasteride has been shown to reduce the risk of prostate cancer. COX-2 inhibitors may prevent colon and breast cancer. COX-2 inhibitors can cause heart problems. Because COX-2 inhibitors can cause heart problems, there hasn't been much research on their use to prevent cancer. In a nutshell, cancer prevention is an action taken to reduce the risk of cancer. In addition to the physical problems and emotional pain caused by cancer, the high cost of treatment is also one of the burdens for patients, families and society. Preventing cancer has reduced the number of new cancer cases.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.