This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Resident Doctor, Specialist I Trinh Le Hong Minh - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
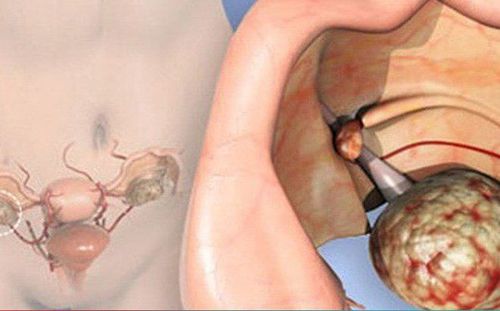
Ovarian cancer begins in the ovaries, one of a woman's reproductive organs. It usually doesn't have obvious symptoms until it's advanced. To accurately diagnose and understand the progression of the disease, patients often have to use a combination of different types of diagnosis such as ultrasound, endoscopy, CT scan, MRI, PET/CT, etc.
1. Things to know about ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer starts in the ovaries, one of the pairs of female reproductive organs located in the pelvis on either side of the uterus. The ovaries are where egg cells or egg cells form.
To assess your condition, your doctor may do a pelvic exam and perform blood tests. If the patient has symptoms of ovarian cancer, a pelvic ultrasound, CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis, exploratory laparotomy, laparoscopy will be performed to remove the cancer. To determine the extent and size of the tumor, procedures such as body CT scan, body MRI, PET/CT or GI are also performed on the patient.
The biggest contributors to ovarian cancer are age and personal family history of ovarian cancer. Women who have never been pregnant, women with mutations in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes are also at increased risk of ovarian cancer.
In the early stages, ovarian cancer often has no obvious symptoms until it has progressed to a late stage. As cancer grows, possible signs include:
Pressure or pain in the abdomen or pelvis Abdominal swelling or bloating Nausea, indigestion, bloating, constipation or diarrhea Persistent fatigue Urgent urination or urinating a lot Unusual vaginal bleeding, such as heavy periods or bleeding after menopause

Treatment depends on how much the cancer is confined to the ovary or has spread to other parts of the body. Possible treatments include:
Ovarian ablation: Your doctor may recommend removing one or both ovaries. Women who have one ovary removed can still get pregnant, but if both ovaries are removed, they can no longer become pregnant. Lymph nodes and other abdominal tissues are also evaluated during surgery and the patient is also biopsied to make sure that the tumor is confined to the ovary. A hysterectomy is surgery to remove the uterus, cervix, and other tumor that may have spread outside the ovaries. Once the uterus is removed, a woman can no longer become pregnant. Chemotherapy or drugs that kill cancer cells are the options most often used in more advanced ovarian cancer after surgery. In patients with unresectable ovarian cancer, chemotherapy is used as the initial treatment. Chemotherapy is usually given over time and alternates with periods of no treatment. Radiation therapy is rarely used in ovarian cancer, it is mainly to treat limited areas of the tumor involving the pelvis and/or lymph node areas that cause pain and other symptoms.
2. How is ovarian cancer diagnosed and evaluated?
To make a diagnosis, the doctor will start by learning about the patient's medical history and symptoms. In addition, the patient also has a physical and gynecological examination, along with a blood test (called CA-125). If there are any symptoms of ovarian cancer, the doctor will recommend one or more of the following tests:
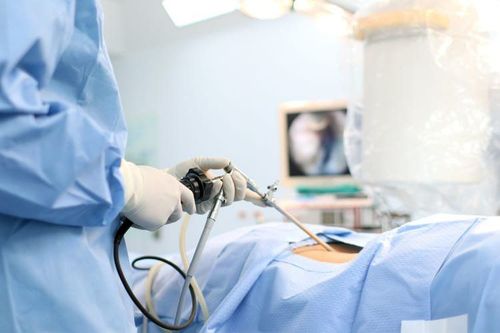
Pelvic ultrasound : This uses sound waves to create pictures of the structures structures and organs in the pelvis to identify ovarian or uterine cancer. If the ultrasound is transvaginal, a probe is inserted into the vagina to get a better view of the uterus and ovaries. Abdominal and pelvic CT scan: This takes pictures of the entire abdominal cavity to diagnose the cause of abdominal or pelvic pain and to detect ovarian cancer. During a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis, the patient will receive an injection of contrast or oral contrast material to enhance the visibility of the lymph nodes and other tissues during the exam. Exploratory laparotomy: To do this, the surgeon makes an incision in the abdominal wall to examine the abdominal organs and pelvis for signs of cancer. If cancer is found, this surgery usually involves removing the ovaries, uterus, and as much tumor tissue as possible from the abdomen. Laparoscopy: To perform this test, your doctor will use a thin, lighted tube through a small incision in your abdomen to look for signs of cancer. If in the case of examination results show that the patient has cancer, then imaging is essential to determine the extent of tumor growth in the abdomen. The following imaging tests will be performed to stage the disease:
Body CT scan: This will be done if the patient has not been done before. A body CT scan is a series of detailed pictures of a patient's pelvis, abdomen, or chest. Sometimes, your doctor will prescribe an injection of contrast or oral contrast material to enhance the visibility of your lymph nodes and other tissues during the scan. A CT scan can detect cancer in the lymph nodes, lungs, or elsewhere.
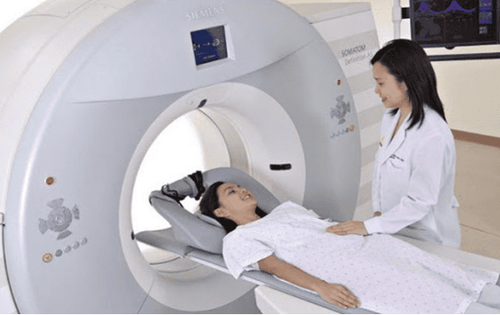
Body MRI: An MRI is less common than a CT scan, but it can be used to create detailed pictures of the uterus, lymph nodes, and other tissues in the abdomen and pelvis. Your doctor may also prescribe contrast injections to enhance the visibility of your lymph nodes and other tissues during the exam. PET/CT : This is a nuclear medicine imaging test that uses a small amount of radioactive material to determine the extent of or provide treatment for many diseases, including cancer. PET scans can be combined with CT or MRI to create optimal viewing angles for more accurate conclusions. PET/CT can also be used to evaluate the response of ovarian cancer to therapy, such as chemotherapy. Lower gastrointestinal (GI) X-ray: This is an X-ray test of the large intestine (colon) using a flexible tube inserted into the rectum to get a better look at how cancer has spread in the digestive tract. chemical. To diagnose ovarian cancer, patients will often be applied more than one test to determine the disease. Many scientific and practical studies have demonstrated that the use of radiographic procedures can provide accurate information in disease diagnosis and in assessing the impact of treatment. Especially, PET imaging technique with the ability to record images at the molecular level should be able to diagnose the disease at an early stage, evaluate the return of the disease in people who have had cancer, and consider the effectiveness of the treatment. results of treatment. The combination of CT and PET scans will provide comprehensive information on anatomical images and metabolic functions in the patient's body.
When detecting early ovarian cancer symptoms from the beginning, you can completely treat them effectively under the direction of a specialist. However, in many cases, women do not have the above symptoms until the disease is in the late stages to show signs of end-stage ovarian cancer.
Women should pay attention to monitor their health, should not be subjective with any small signs because it can warn of dangerous diseases such as ovarian cancer. When detecting suspicious signs, women should go to the hospital for examination as soon as possible.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the leading prestigious facilities in the country in the field of screening and early detection of gynecological cancers, including ovarian cancer. Vinmec currently has a package of screening and early detection of gynecological cancer with the following advantages:
A team of highly qualified and experienced doctors. Comprehensive professional cooperation with domestic and international hospitals: Singapore, Japan, USA, etc. Comprehensive treatment and care for patients, multi-specialty coordination towards individualizing each patient. Having a full range of specialized facilities to diagnose the disease and stage it before treatment: Endoscopy, CT scan, PET-CT scan, MRI, histopathological diagnosis, gene-cell testing, .. There are full range of main cancer treatment methods: surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, stem cell transplant... If there is a need for further consultation and examination at the Hospitals of the Health system Vinmec nationwide, please book an appointment on the website to be served.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: radiologyinfo.org