This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Doctor of Radiology, Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Electrocardiogram ECG records the electrical signals in the heart. This is a common and painless diagnostic technique used to quickly detect heart problems and monitor heart health.
1. What is an electrocardiogram?
Electrocardiogram (English name electrocardiogram is and abbreviated as ECG or EKG), This is a non-invasive diagnostic technique used to evaluate the electrical system of the heart.
The technique uses flat metal electrodes placed on the chest to detect the electrical charges generated by the heart when the heart beats, then the electrocardiogram machine will plot the electrical activity of the heart.
The doctor can analyze the patterns of the chart to better understand the heart rate and rhythm of the heart, thereby identifying some types of structural diseases of the heart and evaluate the efficiency of the heart.
2. When is electrocardiogram done?
Painless, noninvasive electrocardiogram to help diagnose many common heart problems of all ages. Your doctor can use an electrocardiogram to identify or detect:
Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) If blocked or narrowed arteries in the heart (coronary artery disease) are causing chest pain or pain heart You have had a previous heart attack Assess whether certain heart conditions such as pacemakers are working well. You may need an ECG if you have any of the following signs and symptoms:
Chest pain Dizziness or confusion Palpitations Rapid pulse Shortness of breath Weakness, fatigue, or impaired ability to exercise. There are several different types of ECG such as:
Holter ECG (Holter monitor). A device called the Holter is a small, wearable device that records an ECG continuously for 24 to 48 hours. Event monitor. This handheld device is similar to the Holter, but it only records at certain times for a few minutes at a time. You can wear it longer than the Holter, usually 30 days. Some devices automatically record when an irregular rhythm is detected.
3. Some notes when performing an electrocardiogram (ECG)

Hãy cho bác sĩ biết nếu bạn đang dùng thuốc vì có thể nó sẽ ảnh hưởng đến kết quả kiểm tra của bạn
An electrocardiogram can be done in a clinic or hospital and is usually done by a nurse or technician.
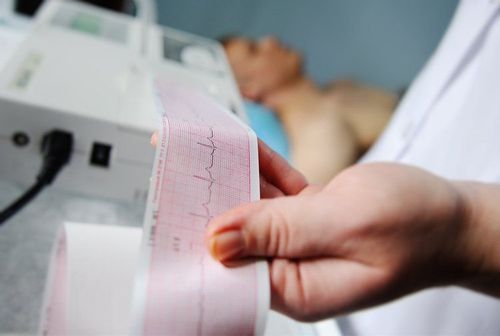
3.1 Before the test Tell your doctor about any medications and supplements you are taking as some drugs may affect your test results. You may be asked to change into a hospital gown. If you have a lot of hair where the electrodes are placed on your body, your nurse can instruct you to shave those areas so that the patches stick to your body. When you are ready, you will be asked to lie on an examination table or bed. 3.2 During the procedure During the ECG, up to 12 sensors (electrodes) will be attached to your chest and limbs. The electrodes are sticky patches with wires that connect to the screen. They record electrical signals in the heart, which are the electrical signals that make your heart beat. The ECG machine records the information and displays it as a wave on a screen or on paper. You should be able to breathe normally during the test, but you will need to lie still. Moving, talking, or shaking can falsify the test results. The measurement time for a standard ECG can take several minutes.
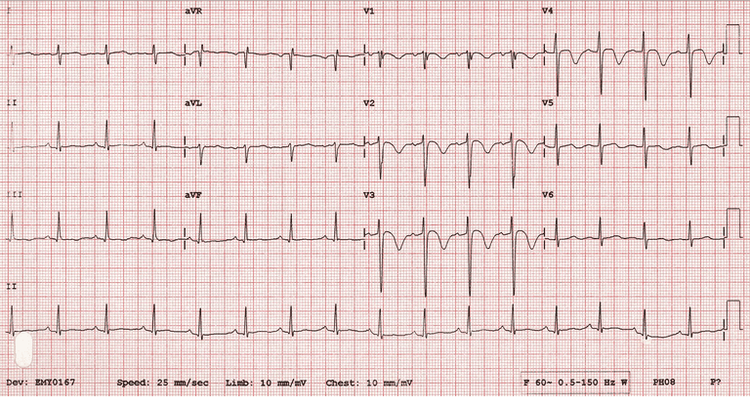
Điện tâm đồ ECG
3.3 After the measurement is complete You can resume normal activities after the ECG.
3.4 Notes on Reading ECG ECG Your doctor can discuss the results with you the same day after your EKG or at your next appointment.
If the ECG is normal, you may not need any other tests or imaging techniques. If the results show an abnormality, you may need another ECG or other diagnostic tests or techniques, such as an echocardiogram.
Your doctor will review the information recorded by the ECG machine and look for any problems with your heart, including:
Heart rate: Normally, your heart rate can be measured by checking your pulse. friend. An ECG can be helpful if your pulse is hard to catch or is too fast or too irregular for a medical staff to count correctly. An electrocardiogram can help your doctor identify an abnormally fast heart rate or an abnormally slow heart rate. Beat. An electrocardiogram may show an irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia). These conditions can occur when any part of the heart's electrical system malfunctions. In other cases, medications, such as beta-blockers, cocaine, amphetamines, and over-the-counter cold and allergy medications, can trigger this arrhythmia. Heart attack: An ECG may show evidence of a previous heart attack or a heart attack in progress. The ECG patterns can show which part of your heart was damaged, as well as the extent of the damage. Insufficient blood and oxygen supply to the heart: An electrocardiogram done when you have symptoms can help your doctor determine if chest pain is caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, such as chest pain in unstable angina. Structural Abnormalities: An ECG can provide clues about enlarged heart chambers or walls, congenital heart disease, and other heart problems. If any problems are found on your ECG, your doctor may order additional tests and imaging techniques to see if treatment is needed. suitable.
Electrocardiogram is a safe diagnostic technique for patients. There is no risk of electric shock to the patient during the procedure because the electrodes used do not generate electricity. The electrodes record only the electrical activity of the heart.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.